From lowest energy to highest energy, which of the following
... a) People do not emit any kind of light. b) People only emit light that is invisible to our eyes. c) People are too small to emit enough light for us to see. d) People do not contain enough radioactive material. ...
... a) People do not emit any kind of light. b) People only emit light that is invisible to our eyes. c) People are too small to emit enough light for us to see. d) People do not contain enough radioactive material. ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... a large, bright star near the top. More stars also are visible in the image’s upper region than in the dark, lower area. The infrared image reveals a softly glowing structure with gas and dust swirling around a rust-colored opaque region. The dark sky above the nebula is dotted with many stars. Two ...
... a large, bright star near the top. More stars also are visible in the image’s upper region than in the dark, lower area. The infrared image reveals a softly glowing structure with gas and dust swirling around a rust-colored opaque region. The dark sky above the nebula is dotted with many stars. Two ...
period ____ due date
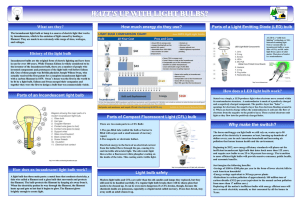
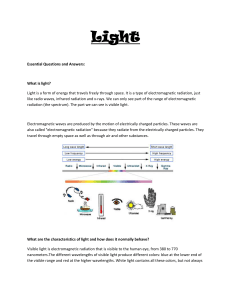
... A range (frequencies) of the electromagnetic spectrum which can be detected by the human eye. Phrase used to describe electromagnetic radiation of all wavelengths and frequencies. This includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays, etc. Waves which can mo ...
... A range (frequencies) of the electromagnetic spectrum which can be detected by the human eye. Phrase used to describe electromagnetic radiation of all wavelengths and frequencies. This includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays, etc. Waves which can mo ...
Unit C: Light and Optical Systems
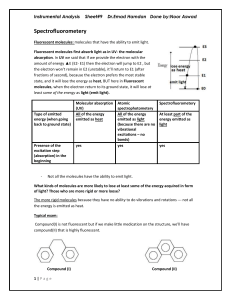
... Incandescent Sources An object can be heated to such a high temperature that it emits visible light, Incandescent source. The change happens as follows: Electrical EnergyThermal EnergyVisible Light Energy Incandescent lights give off about 95% of the energy as heat and the other 5% as light. Fluor ...
... Incandescent Sources An object can be heated to such a high temperature that it emits visible light, Incandescent source. The change happens as follows: Electrical EnergyThermal EnergyVisible Light Energy Incandescent lights give off about 95% of the energy as heat and the other 5% as light. Fluor ...
Light
... • If we see something as RED or BLUE – It reflected only the RED or only the BLUE wavelengths – The others were absorbed. ...
... • If we see something as RED or BLUE – It reflected only the RED or only the BLUE wavelengths – The others were absorbed. ...
Grade 10 Academic Science – Optics (Physics)
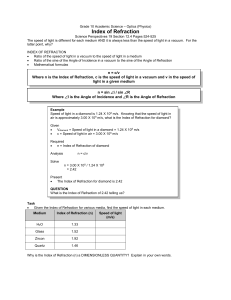
... Why is the Index of Refraction (n) a DIMENSIONLESS QUANTITY? Explain in your own words. ...
... Why is the Index of Refraction (n) a DIMENSIONLESS QUANTITY? Explain in your own words. ...
Physics 2C Summer Session II Quiz #4 statement or answers the question.
... the index of the liquid is found from p n1 sin c = n2 ! 1:76= 2 = nliq = 1:245 ! A If the index of the liquid is larger than this, then there is some refraction (no internal re‡ection). 7. An object at the bottom of a wading pool appears to be 52cm below the surface. How deep is the pool if the refr ...
... the index of the liquid is found from p n1 sin c = n2 ! 1:76= 2 = nliq = 1:245 ! A If the index of the liquid is larger than this, then there is some refraction (no internal re‡ection). 7. An object at the bottom of a wading pool appears to be 52cm below the surface. How deep is the pool if the refr ...
Jaume Bibiloni Isaksson
... • Both AAnBP and PRB are incapable of photoautotrophy (do not have enzyme RubisCO) and rely on heterotrophy of their cellular energetics ...
... • Both AAnBP and PRB are incapable of photoautotrophy (do not have enzyme RubisCO) and rely on heterotrophy of their cellular energetics ...
Polarization of Light Mica Sheet
... Polarized light occurs everywhere in nature, from reflected sunlight, to minerals, to even molecules used for cooking. It is a phenomenon that few realize that they experience every day, when it is apparent all around us. This lesson teaches what polarized light is, how it’s made and can be filtered ...
... Polarized light occurs everywhere in nature, from reflected sunlight, to minerals, to even molecules used for cooking. It is a phenomenon that few realize that they experience every day, when it is apparent all around us. This lesson teaches what polarized light is, how it’s made and can be filtered ...
Bioluminescence

Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria and terrestrial invertebrates such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is produced by symbiotic organisms such as Vibrio bacteria.The principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves the light-emitting pigment luciferin and the enzyme luciferase, assisted by other proteins such as aequorin in some species. The enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin. In some species, the type of luciferin requires cofactors such as calcium or magnesium ions, and sometimes also the energy-carrying molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In evolution, luciferins vary little: one in particular, coelenterazine, is found in nine different animal (phyla), though in some of these, the animals obtain it through their diet. Conversely, luciferases vary widely in different species. Bioluminescence has arisen over forty times in evolutionary history.Both Aristotle and Pliny the Elder mentioned that damp wood sometimes gives off a glow and many centuries later Robert Boyle showed that oxygen was involved in the process, both in wood and in glow-worms. It was not until the late nineteenth century that bioluminescence was properly investigated. The phenomenon is widely distributed among animal groups, especially in marine environments where dinoflagellates cause phosphorescence in the surface layers of water. On land it occurs in fungi, bacteria and some groups of invertebrates, including insects.The uses of bioluminescence by animals include counter-illumination camouflage, mimicry of other animals, for example to lure prey, and signalling to other individuals of the same species, such as to attract mates. In the laboratory, luciferase-based systems are used in genetic engineering and for biomedical research. Other researchers are investigating the possibility of using bioluminescent systems for street and decorative lighting, and a bioluminescent plant has been created.