* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Self Quiz Answers
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Holiday lighting technology wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
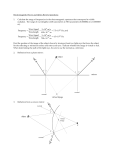
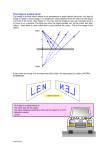
CHAPTER 11 Self-Quiz 1. (a); Choice (a) is correct. Light energy does not require a medium for transmission. It can travel through the vacuum of outer space. Radiation is a method of energy transfer that does not require a medium. Choice (b) is incorrect because inversion is not a method of energy transmission. Choice (c) is incorrect. Conduction is a method of energy transfer that requires a medium. Conduction involves transmission of energy through contact between particles of matter. Choice (d) is incorrect. Emission is not a method of energy transmission. 2. (d); Choice (d) is correct. A burning match produces light. A luminous object produces its own light. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are incorrect because these three objects are non-luminous. They can be seen because they reflect light produced by a luminous object. 3. (b); Choice (b) is correct. The light bulb is positioned at the centre of curvature, which produces an inverted, real image that is the same size as the original object. Choice (a) is incorrect. A virtual image is produced when the object is between the focus and the concave mirror, and the image is upright and larger than the original object. Choice (c) is incorrect. In order to produce an upright virtual image larger than the original object, the object must be placed between the focus and the mirror. Choice (d) is incorrect. All real images produced by a concave mirror are inverted. 4. (a); Choice (a) is correct because it shows the image flipped horizontally and in reverse order. Choice (b) is incorrect because it shows the image unchanged. Choice (c) is incorrect because it shows each letter written backwards but in the wrong order. Choice (d) is incorrect because it shows the image in reverse order only. 5. True. You can see a luminous object, such as a light bulb, because your eyes can detect light coming from the object. If the object is not luminous (that is, does not produce light), you can see it when reflected light travels from the object to your eyes. 6. False. Luminosity describes the amount of light produced by an object. Luminosity is not a characteristic of an image in a mirror because a mirror does not produce its own light. Location is the correct term. A true version of the statement would be: The four characteristics of an image in a mirror are size, attitude, location, and type. 7. convex or diverging; A convex mirror is a curved mirror in which the centre of the mirror bulges toward you. 8. virtual; When your eyes detect light reflected from a plane mirror, your brain projects the light rays backwards in a straight line, causing your eyes to “see” an image behind the mirror. Because the image is not actually behind the mirror, this type of image is called a virtual image instead of a real image. 9. (a)(iii) Most light bulbs in use today produce light from a hot, glowing filament, or incandescence; (b)(iv) Glow sticks, or light sticks, produce light as the result of a chemical reaction, or chemiluminescence; (c)(ii) Fireflies and certain other organisms can produce light as a result of a chemical reaction that takes place inside their bodies, or bioluminescence; (d)(v) In an energy-efficient fluorescent light bulb, a fluorescent material absorbs ultraviolet light and emits visible light, a phenomenon known as fluorescence; Lightning produces light by sending an electric discharge through the gases in Earth’s atmosphere. (e)(i) 10. Sample answer: Light travels at a very high speed. Light travels in a straight line. 11. Light travels in a straight line but can also change direction. A light ray changes direction when it strikes an object and is reflected. 12. Sample answers: a shiny spherical tree ornament; a shiny rounded button. 824 Unit E: Light and Geometric Optics 55308_02_ch11_p765-826 pp3.indd 824 NEL 11/20/09 6:56:37 PM 13. Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic wave; such waves do not need a medium for transmission. Based on this property, radio waves can travel through the atmosphere without using wires, and a cell phone operates by receiving and sending such waves during a phone call. 14. Sample answer: Three types of electromagnetic waves are radio waves, microwaves, and visible light. Radio waves carry the signals by which I can watch programs on my TV set. Microwaves cook my food when I use a microwave oven. Visible light allows me to see objects with my eyes. 15. Sample answer: I would tell them that LED lights are more energy efficient than incandescent lights, using less electricity and therefore costing less to operate. I would also tell them that LED lights produce very little heat and would be less of a fire hazard than incandescent lights. 16. (a) (b) 17. (a) (b) 18. (a) 19. A laser produces electromagnetic waves of exactly the same energy level (or frequency). As a result, visible light from a laser has only one colour. Electromagnetic waves emitted by a laser all have exactly the same energy, and they travel in unison in the same direction. As a result, the light energy from a laser is extremely concentrated and powerful, and a high-energy laser can be used to burn a hole through steel. Sample answer: It would be better to use a translucent material instead of a transparent one for a shower curtain or door, so that the occupant can receive sunlight and also have privacy. Sample answer: It would be better to use a transparent material instead of a translucent one for the lenses of eyeglasses, because you want to see through the material as clearly as possible. The hiker could use a mirror to reflect sunlight across a distance when signalling for help or guiding others to his or her location. (b) The dentist could use a mirror to examine teeth in parts of the mouth that are otherwise difficult to see. (c) The security guard could use a mirror to observe activity in various parts of the store, including the doorways. Light reflected from the hand would be diffuse reflection. The surface of a hand is irregular and dull, and it would therefore produce diffuse reflection. 20. (a) “Mirror image” describes an image that has its left and right sides reversed as if it were seen in a mirror. (b) Sample answer: When you look at your left hand in a mirror, the reflection in the mirror appears to be the right hand. 21. Sample answer: Real Mice Insist on Visiting their Uncles with Xylophones and Guitars (radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays) 22. Sample answer: I think it is false advertising for a laundry detergent to advertise that it can make clothes “whiter than white.” This type of ad makes people think that washing their clothes with this detergent will make their clothes cleaner than washing them with other detergents. This isn’t necessarily true. The detergent contains fluorescent dyes that make clothes glow slightly in visible light, giving the clothes the appearance that they are “whiter than white.” 23. Sample answer: I think my friend’s explanation is incorrect. A light ray striking a rough surface produces a reflected ray with an angle of reflection that is equal to the angle of incidence of the incident ray. The laws of reflection are true for rough as well as smooth surfaces. The reason the image appears fuzzy is that each incident ray strikes the surface at a different angle, so that the reflected rays have different angles of reflection and are not parallel to one another. 24. When one wall of a room is entirely covered with a plane mirror, the room appears twice as large as it really is. This happens because each object in the room produces an image in the mirror and each image appears to be as far behind the mirror as the corresponding object is in front of it. In other words, the size and contents of the room are apparently doubled. NEL 55308_02_ch11_p765-826 pp3.indd 825 Chapter 11 The Production and Reflection of Light 825 11/20/09 6:56:37 PM