10 Respiratory System SB Powerpoint
... to move downwards and inwards during expiration at rest. Expiration at rest is a passive process. However, expiration during periods of exercise is an active process - it involves contraction of the internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles to produce ...
... to move downwards and inwards during expiration at rest. Expiration at rest is a passive process. However, expiration during periods of exercise is an active process - it involves contraction of the internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles to produce ...
Characteristics of Mammals
... • Endothermy enables mammals to be very active • Movement for long periods of time requires a lot of energy and a high metabolism – A mammal needs to eat 10x as much food as an ectotherm of similar sizes – Metabolizing food requires a lot of oxygen ...
... • Endothermy enables mammals to be very active • Movement for long periods of time requires a lot of energy and a high metabolism – A mammal needs to eat 10x as much food as an ectotherm of similar sizes – Metabolizing food requires a lot of oxygen ...
Respiratory System Reading HW
... The inhaled air travels through the windpipe, which is called the trachea. The human body contains two lungs. The lungs are pink, mushy, and like a sponge. The lungs are protected by the rib cage and keeps them protected and safe. The lung on the left side of the body is smaller than the right lung, ...
... The inhaled air travels through the windpipe, which is called the trachea. The human body contains two lungs. The lungs are pink, mushy, and like a sponge. The lungs are protected by the rib cage and keeps them protected and safe. The lung on the left side of the body is smaller than the right lung, ...
Science - Newpark Comprehensive School
... Describe the general properties of the alkali describe the reactions of the alkali metals with air and water (word equations for reaction with water) Write the following metals Cu, Mg, Ca and Zn in order of reactivity from most reactive to least reactive. Which group on the periodic table is called ...
... Describe the general properties of the alkali describe the reactions of the alkali metals with air and water (word equations for reaction with water) Write the following metals Cu, Mg, Ca and Zn in order of reactivity from most reactive to least reactive. Which group on the periodic table is called ...
Unit 5, Module 14 Animals
... environment and release carbon dioxide back to the environment 1. In some animals such as worms, oxygen is able to diffuse through moist skin and enter the bloodstream. Other invertebrate animals such as insects may have specialized structures in certain body segments to take in oxygen. Examples inc ...
... environment and release carbon dioxide back to the environment 1. In some animals such as worms, oxygen is able to diffuse through moist skin and enter the bloodstream. Other invertebrate animals such as insects may have specialized structures in certain body segments to take in oxygen. Examples inc ...
Respiratory system notes fill
... ________________ – process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells A. External Respiration Exchange of gases between ______ and __________ in the lungs Blood ______________ the lungs is oxygen-___________ and carbon dioxide-___________ __________________________________________ ...
... ________________ – process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells A. External Respiration Exchange of gases between ______ and __________ in the lungs Blood ______________ the lungs is oxygen-___________ and carbon dioxide-___________ __________________________________________ ...
Your Circulatory System
... Your Circulatory System The heart is the main organ of the circulatory system. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and rids itself of carbon dioxide. The left side of the heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. ...
... Your Circulatory System The heart is the main organ of the circulatory system. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and rids itself of carbon dioxide. The left side of the heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. ...
Nutrients WS
... All living things must have proteins to stay alive. Proteins and water form the basis of all living matter, protoplasm. Proteins repair damaged cells, build new tissues, and do many other vital jobs. All proteins are compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Most proteins also c ...
... All living things must have proteins to stay alive. Proteins and water form the basis of all living matter, protoplasm. Proteins repair damaged cells, build new tissues, and do many other vital jobs. All proteins are compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Most proteins also c ...
Animal Evolution – The Invertebrates
... • Gills evolved in water, then lungs for dry land • Paired fins were a starting point for other limbs ...
... • Gills evolved in water, then lungs for dry land • Paired fins were a starting point for other limbs ...
Early Metazoan Divergence Was About 830 Million Years Ago
... because mitochondrial genes they used are not evolving in a clocklike fashion in vertebrates (Nikoh et al. 1997). A number of factors can cause different time estimates from different molecular data (for detailed discussions, see Nikoh et al. 1997; Gu 1997). First, it is unclear how to determine the ...
... because mitochondrial genes they used are not evolving in a clocklike fashion in vertebrates (Nikoh et al. 1997). A number of factors can cause different time estimates from different molecular data (for detailed discussions, see Nikoh et al. 1997; Gu 1997). First, it is unclear how to determine the ...
Animal Structure and Function
... skin and gills, directly into the blood stream. Adult amphibians may also obtain oxygen by diffusion through their skin and the lining of their mouths. However, adult amphibians also have lungs which help with gas exchange in a terrestrial environment. The lungs may also have small sacs called alveo ...
... skin and gills, directly into the blood stream. Adult amphibians may also obtain oxygen by diffusion through their skin and the lining of their mouths. However, adult amphibians also have lungs which help with gas exchange in a terrestrial environment. The lungs may also have small sacs called alveo ...
Life Processes - My Dear Students
... The blood passes to aorta from the left ventricle. The aorta gives rise to many arteries that distribute the oxygenated blood to all the regions of the body. Since there are two circulations ie Pulmonary and Systemic, therefore, the blood passes twice through the heart to complete one circulation. H ...
... The blood passes to aorta from the left ventricle. The aorta gives rise to many arteries that distribute the oxygenated blood to all the regions of the body. Since there are two circulations ie Pulmonary and Systemic, therefore, the blood passes twice through the heart to complete one circulation. H ...
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of
... between 16 – 20 rings of cartilage that joins the nose and mouth to the lungs. It measures approximately 10-12” in length and runs from the lower part of the larynx to the lungs by dividing into the bronchi. The trachea contains an epithelial lining that secretes mucus, which traps any dust. It is t ...
... between 16 – 20 rings of cartilage that joins the nose and mouth to the lungs. It measures approximately 10-12” in length and runs from the lower part of the larynx to the lungs by dividing into the bronchi. The trachea contains an epithelial lining that secretes mucus, which traps any dust. It is t ...
Acute Response+Intro Prac
... 2 Ventilation increases as the demand for oxygen increases and the need to remove carbon dioxide. Ventilation is increased through an increase in the respiratory rate (the number of breaths per minute) and/or the tidal volume (the amount of oxygen breathed in or out in one breath). Diffusion increas ...
... 2 Ventilation increases as the demand for oxygen increases and the need to remove carbon dioxide. Ventilation is increased through an increase in the respiratory rate (the number of breaths per minute) and/or the tidal volume (the amount of oxygen breathed in or out in one breath). Diffusion increas ...
Chapter 22
... terrestrial animals (1) respiratory surfaces folded into body (2) Insects (a)tracheae (plural) – extensive branching networks (3) vertebrates (a)lungs – extensive branching with many internal sacs for gas exchange ...
... terrestrial animals (1) respiratory surfaces folded into body (2) Insects (a)tracheae (plural) – extensive branching networks (3) vertebrates (a)lungs – extensive branching with many internal sacs for gas exchange ...
The_Respiratory_System
... lungs (alveoli) into the blood and CO2 moves from the blood into the lungs (alveoli) ...
... lungs (alveoli) into the blood and CO2 moves from the blood into the lungs (alveoli) ...
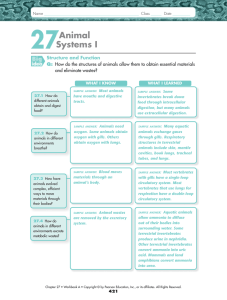
Animal Systems I
... Inhaling brings oxygen-rich air through the trachea into the lungs. The oxygen diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the capillaries into the air. Oxygen-poor air is then exhaled. ...
... Inhaling brings oxygen-rich air through the trachea into the lungs. The oxygen diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the capillaries into the air. Oxygen-poor air is then exhaled. ...
Biology B3
... Leaves are thin and flat giving them a large surface area for diffusion of gases (CO2 in and oxygen out). Guard cells around stomata can open and close to let CO2 in but stop too much water being lost! OK sometimes its placed in the ...
... Leaves are thin and flat giving them a large surface area for diffusion of gases (CO2 in and oxygen out). Guard cells around stomata can open and close to let CO2 in but stop too much water being lost! OK sometimes its placed in the ...
Respiratory System Outline
... cartilage in their walls to prevent collapse. The bronchioles, however, have no cartilage support in their walls and can collapse. As airways get smaller, the person has difficulty breathing and makes a wheezing sound while breathing. It can become a life-threatening situation when bronchioles const ...
... cartilage in their walls to prevent collapse. The bronchioles, however, have no cartilage support in their walls and can collapse. As airways get smaller, the person has difficulty breathing and makes a wheezing sound while breathing. It can become a life-threatening situation when bronchioles const ...
Animal Life Systems
... pulmonary circulation and then continues on through systemic circulation. Pulmonary and systemic are the two circuits in the two-circuit system of higher animals with closed circulatory systems. Mammals have a two-circuit circulatory systems: one circuit is for pulmonary circulation (circulation t ...
... pulmonary circulation and then continues on through systemic circulation. Pulmonary and systemic are the two circuits in the two-circuit system of higher animals with closed circulatory systems. Mammals have a two-circuit circulatory systems: one circuit is for pulmonary circulation (circulation t ...
Science 5th primary 1st term unite 2 lesson 2 Man requires the
... Science 5th primary 1st term unite 2 lesson 2 ...
... Science 5th primary 1st term unite 2 lesson 2 ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.