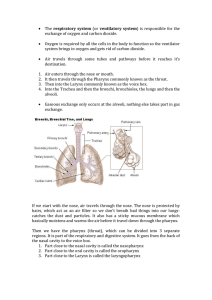
You Can’t Have One Without the Other
... system and other body systems. Design an experiment to demonstrate the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems. Summarize the relationship between oxygen debt and muscular contractions. Create labeled drawings of the lungs and diaphragm during inhalation and exhalation. ...
... system and other body systems. Design an experiment to demonstrate the relationship between the circulatory and respiratory systems. Summarize the relationship between oxygen debt and muscular contractions. Create labeled drawings of the lungs and diaphragm during inhalation and exhalation. ...
Untitled - englishcorner.sg
... A whale breathes in oxygen through its spouting holes ... and dives under while holding its breath. The oxygen is sent to the lungs and exchanged for carbon dioxide. Now, because of its body-heat the carbon dioxide becomes warm. As the whale surfaces, it spouts the warm steam. The spouted steam hits ...
... A whale breathes in oxygen through its spouting holes ... and dives under while holding its breath. The oxygen is sent to the lungs and exchanged for carbon dioxide. Now, because of its body-heat the carbon dioxide becomes warm. As the whale surfaces, it spouts the warm steam. The spouted steam hits ...
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Did you ever wonder why it is that we
... miscarriages, premature births, and small babies. Another concern is the risk of second hand smoke. Scientific testing shows that people with heart and lung disease or with allergies can be made sick by inhaling second hand smoke. So, more than 1/2 the states have made laws prohibiting smoking in pu ...
... miscarriages, premature births, and small babies. Another concern is the risk of second hand smoke. Scientific testing shows that people with heart and lung disease or with allergies can be made sick by inhaling second hand smoke. So, more than 1/2 the states have made laws prohibiting smoking in pu ...
respiratory test
... 3. The largest layer of cartilage on the larynx, the thyroid cartilage, is commonly called the Adam’s apple. ...
... 3. The largest layer of cartilage on the larynx, the thyroid cartilage, is commonly called the Adam’s apple. ...
*Reflects the NEW 2014 Standards Updates! 1 There are 35 phyla of
... Endothermic animals must eat much more often than ectothermic animals since it takes energy to maintain a constant body temperature. For example, a lion must eat its weight in food every seven to ten days. Cold-blooded (ectothermic) animals- including fish, amphibians, and reptiles, which have an ...
... Endothermic animals must eat much more often than ectothermic animals since it takes energy to maintain a constant body temperature. For example, a lion must eat its weight in food every seven to ten days. Cold-blooded (ectothermic) animals- including fish, amphibians, and reptiles, which have an ...
Acc_Bio_Resp_Quiz_Quiz_Trade
... ~ CO2 is high in the capillary, so it diffuses into the alveolus where there is a lower concentration ~ O2 is high in the alveolus, so it diffuses into the capillary where there is a lower concentration 22. Why is carbon monoxide gas dangerous? ~Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin more readily than ...
... ~ CO2 is high in the capillary, so it diffuses into the alveolus where there is a lower concentration ~ O2 is high in the alveolus, so it diffuses into the capillary where there is a lower concentration 22. Why is carbon monoxide gas dangerous? ~Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin more readily than ...
CHAPTER 47 Respiratory System
... 6. Air entering the Nose passes into the NASAL CAVITY. The Nasal Cavity is richly supplied with arteries, veins, and capillaries, which bring nutrients and water to its cells. 7. As air pushes back from the Nasal Cavity, it enters the PHARYNX. The Pharynx is located in the back of the mouth and serv ...
... 6. Air entering the Nose passes into the NASAL CAVITY. The Nasal Cavity is richly supplied with arteries, veins, and capillaries, which bring nutrients and water to its cells. 7. As air pushes back from the Nasal Cavity, it enters the PHARYNX. The Pharynx is located in the back of the mouth and serv ...
principal structures (student review)
... The trachea branches out into the 2 main bronchi- right and left.Branches into the two main bronchi which is plural for bronchus. The bronchi look like an upside down tree. Big tree trunk (trachea) branches into 2 smaller primary branches- Bronchi, which eventually branch out into Bronchioles. Branc ...
... The trachea branches out into the 2 main bronchi- right and left.Branches into the two main bronchi which is plural for bronchus. The bronchi look like an upside down tree. Big tree trunk (trachea) branches into 2 smaller primary branches- Bronchi, which eventually branch out into Bronchioles. Branc ...
Chapter 14—Respiratory System. I. The Respiratory System. a
... i. Tidal Volume (TV)—normal, relaxed breathing. About 500 ml. ii. Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)—additional air volume that may be forcefully inhaled. About 3100 ml. iii. Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)—additional air volume that may be forcefully exhaled. About 1200 ml. iv. Vital Capacity (VC)—ER ...
... i. Tidal Volume (TV)—normal, relaxed breathing. About 500 ml. ii. Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)—additional air volume that may be forcefully inhaled. About 3100 ml. iii. Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)—additional air volume that may be forcefully exhaled. About 1200 ml. iv. Vital Capacity (VC)—ER ...
Document
... The fifth group - fats (butter and vegetable oil). The sixth group - sweet (sugar, honey, confectionery). In cases of various diseases it is limited to use certain food groups. For example, in the diets used in obesity, diabetes, eating sweets is severely limited or prohibited. ...
... The fifth group - fats (butter and vegetable oil). The sixth group - sweet (sugar, honey, confectionery). In cases of various diseases it is limited to use certain food groups. For example, in the diets used in obesity, diabetes, eating sweets is severely limited or prohibited. ...
APII Test 3 Guided Study
... 30. What are the concentrations and partial pressure of CO2 in the: lungs? Air? Body tissues? Blood? Plasma? Lymph? 31. What are the concentrations and partial pressure of O2 in the: lungs? Air? Body tissues? Blood? Plasma? Lymph? 32. What are some homeostatic imbalances that are cause by, or result ...
... 30. What are the concentrations and partial pressure of CO2 in the: lungs? Air? Body tissues? Blood? Plasma? Lymph? 31. What are the concentrations and partial pressure of O2 in the: lungs? Air? Body tissues? Blood? Plasma? Lymph? 32. What are some homeostatic imbalances that are cause by, or result ...
The circulatory system
... The levels of organization we start with Organs then the tissues , the cells that make the tissues. For this slide we chose the heart as demonstration for organs. One of the types of tissues that makes the heart is the cardiovascular(cardiac) muscle tissue. The cardiac muscle tissue is only foun ...
... The levels of organization we start with Organs then the tissues , the cells that make the tissues. For this slide we chose the heart as demonstration for organs. One of the types of tissues that makes the heart is the cardiovascular(cardiac) muscle tissue. The cardiac muscle tissue is only foun ...
Catch Up Biology Sample Chapter
... The function of the conducting portion of the respiratory system is to moisten, warm and clean inspired air before it is delivered to the respiratory portion of the system where gaseous exchange between air and blood takes place. Air is initially inspired through the nose and then passes through the ...
... The function of the conducting portion of the respiratory system is to moisten, warm and clean inspired air before it is delivered to the respiratory portion of the system where gaseous exchange between air and blood takes place. Air is initially inspired through the nose and then passes through the ...
Chapter 44 Gas Exchange and Circulation
... keep open circulatory system (hemocoel) perfused with oxygen. This system is limiting, though, and has prevented larger (modern) insects from evolving. ...
... keep open circulatory system (hemocoel) perfused with oxygen. This system is limiting, though, and has prevented larger (modern) insects from evolving. ...
Human Body Systems
... rest" heart rate on their chart. (Student pulse rate at rest will vary between 60 - 110 beats per minute. Adult rates are lower.) • Do some exercise such as running in place, jumping jacks, or other exercise for one minute. Stop and calculate pulse again over 15 seconds. Calculate the heart rate for ...
... rest" heart rate on their chart. (Student pulse rate at rest will vary between 60 - 110 beats per minute. Adult rates are lower.) • Do some exercise such as running in place, jumping jacks, or other exercise for one minute. Stop and calculate pulse again over 15 seconds. Calculate the heart rate for ...
Scuba diving explained
... We have two lungs, one in the right side of our chest cage and one in the left (Figure l). Between them is the heart, a midline organ that tilts slightly to the left within the chest cage. (You can feel your heart beating by placing your finger tips under your left breast.) Although gas exchange tak ...
... We have two lungs, one in the right side of our chest cage and one in the left (Figure l). Between them is the heart, a midline organ that tilts slightly to the left within the chest cage. (You can feel your heart beating by placing your finger tips under your left breast.) Although gas exchange tak ...
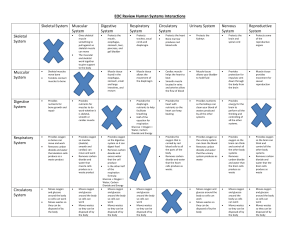
EOC Review Human Systems Interactions Skeletal System Muscular
... Cardiac musclehelps the heart to beat Smooth muscle located in veins and arteries allow the flow of blood ...
... Cardiac musclehelps the heart to beat Smooth muscle located in veins and arteries allow the flow of blood ...
Respiratory Assessment
... 53) Pulmonary ventilation involves the movement of air into and out of the lungs and is what is commonly called breathing. External respiration is the exchange of gases between the pulmonary blood and the alveoli. Respiratory gas transport is the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from th ...
... 53) Pulmonary ventilation involves the movement of air into and out of the lungs and is what is commonly called breathing. External respiration is the exchange of gases between the pulmonary blood and the alveoli. Respiratory gas transport is the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from th ...
Structure and Function
... Organisms have the ability to replace some cells that are worn out or damaged. As organisms grow and develop their body size and shape can change. This is called development. Reproduction All living things come from other living things. Reproduction is not necessary for the organism to survive (beca ...
... Organisms have the ability to replace some cells that are worn out or damaged. As organisms grow and develop their body size and shape can change. This is called development. Reproduction All living things come from other living things. Reproduction is not necessary for the organism to survive (beca ...
PowerPoint
... Respiratory Pigments Hemocyanin Most mollusks, some arthropods Copper ion Oxygenated—blue, deoxygenated—colorless Second most common pigment Myoglobin Found in muscle tissue Can store O2 for later use Amounts vary between species ...
... Respiratory Pigments Hemocyanin Most mollusks, some arthropods Copper ion Oxygenated—blue, deoxygenated—colorless Second most common pigment Myoglobin Found in muscle tissue Can store O2 for later use Amounts vary between species ...
Circulatory and excretory systems
... all the body cells.It also transports nutrients and water to the hole body.It`s divided in: * Plasma: Is a clear fluid wich transports nutrients and waste around the body. * Red blood cells: This carry oxygen from the lungs to all body cells. * White blood cells: This protect the body from germs and ...
... all the body cells.It also transports nutrients and water to the hole body.It`s divided in: * Plasma: Is a clear fluid wich transports nutrients and waste around the body. * Red blood cells: This carry oxygen from the lungs to all body cells. * White blood cells: This protect the body from germs and ...
Chapt09 Lecture 13ed Pt 3
... Exchange of gases in the body • Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. • The exchange of gases is dependent on diffusion. • Partial pressure is the amount of pressure each gas exerts (PCO2 or PO2). • Oxygen and carbon dioxide will diffuse from the area of higher to the area of lower partial pressu ...
... Exchange of gases in the body • Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. • The exchange of gases is dependent on diffusion. • Partial pressure is the amount of pressure each gas exerts (PCO2 or PO2). • Oxygen and carbon dioxide will diffuse from the area of higher to the area of lower partial pressu ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.