Respiratory System - Napa Valley College
... Consist of a series of tubes that transport air in an out of the lungs. Function is to supply oxygen to the body cells and to transport carbon dioxide which is produced by the body cells into the atmosphere There are two forms of respiration exchange ...
... Consist of a series of tubes that transport air in an out of the lungs. Function is to supply oxygen to the body cells and to transport carbon dioxide which is produced by the body cells into the atmosphere There are two forms of respiration exchange ...
Reece9e_Lecture_C26
... o Humans and bacteria share a common ancestor that lived more than 3 billion years ago. o Fossils and genetic evidence indicate that this ancestor was a single-celled prokaryote. o Even though bacteria have changed little in their morphology since that common ancestor, there has been 3 billion years ...
... o Humans and bacteria share a common ancestor that lived more than 3 billion years ago. o Fossils and genetic evidence indicate that this ancestor was a single-celled prokaryote. o Even though bacteria have changed little in their morphology since that common ancestor, there has been 3 billion years ...
- Jerry Zucker Middle School Of Science
... 2. What are the 2 groups in which we can classify these phyla? Vertebrates and invertebrates 3. What are the 6 characteristics all animals share? Bodies are multi-cellular; heterotrophs; obtain food and oxygen; keep internal conditions in balance (homeostasis); they move; they reproduce 4. What are ...
... 2. What are the 2 groups in which we can classify these phyla? Vertebrates and invertebrates 3. What are the 6 characteristics all animals share? Bodies are multi-cellular; heterotrophs; obtain food and oxygen; keep internal conditions in balance (homeostasis); they move; they reproduce 4. What are ...
Lung Structure PowerPoint slides Unit 1 VCE Biology
... • Not much carbon dioxide is in atmospheric air – it only makes up a tiny percentage ...
... • Not much carbon dioxide is in atmospheric air – it only makes up a tiny percentage ...
Diaphragm (sheet of muscle)
... •Breathing (ventilation) is normally an involuntary process. •The brain controls the rate of breathing ...
... •Breathing (ventilation) is normally an involuntary process. •The brain controls the rate of breathing ...
class10-science-notes
... Lymph- Extracellular fluid similar to plasma but colourless with lesser protein. Function of lymph- (i) Transportation of digested & absorbed fats from the small intestine. (ii) Drains excess fluid from the intercellular spaces back in the blood. Higher animals- E.g., birds, mammals. (i) Oxyge ...
... Lymph- Extracellular fluid similar to plasma but colourless with lesser protein. Function of lymph- (i) Transportation of digested & absorbed fats from the small intestine. (ii) Drains excess fluid from the intercellular spaces back in the blood. Higher animals- E.g., birds, mammals. (i) Oxyge ...
Panspermia and Horizontal Gene Transfer
... Among Eukaryotes, the situation is reminiscent of that for prokaryotes a decade ago – examples of evolution by HGT are already too numerous to keep count. One of the most salient examples is the immune system of jawed vertebrates. In 1998, a team at Yale wrote, “We owe the repertoire of our immune s ...
... Among Eukaryotes, the situation is reminiscent of that for prokaryotes a decade ago – examples of evolution by HGT are already too numerous to keep count. One of the most salient examples is the immune system of jawed vertebrates. In 1998, a team at Yale wrote, “We owe the repertoire of our immune s ...
Background Metabolism shapes the cellular energy budget in
... Metabolism shapes the cellular energy budget in response to physiological demands and changing environments, ultimately affecting many cellular functions. Cells use gene regulatory networks to coordinate and adapt the activity of multiple metabolic pathways. Understanding the interplay between compl ...
... Metabolism shapes the cellular energy budget in response to physiological demands and changing environments, ultimately affecting many cellular functions. Cells use gene regulatory networks to coordinate and adapt the activity of multiple metabolic pathways. Understanding the interplay between compl ...
Support and Movement
... Responsiveness – reaction to a change Growth – increase in body size; no change in shape Reproduction – production ...
... Responsiveness – reaction to a change Growth – increase in body size; no change in shape Reproduction – production ...
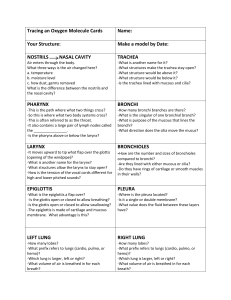
Tracing an Oxygen Molecule Cards Name
... -You will need to make four. Where are they found in the respiratory system? -What is the purpose of the cilia? -What is the purpose of the mucous? -How do they work together? ...
... -You will need to make four. Where are they found in the respiratory system? -What is the purpose of the cilia? -What is the purpose of the mucous? -How do they work together? ...
Test Review – Ch
... 26. What an energy acquiring process? What is an energy releasing process? Obtain chemical energy in photosynthesis by producing glucose. Release energy in glucose during cell respiration 27. Why might plants photosynthesize more in the summer months than in the winter? More chlorophyll present to a ...
... 26. What an energy acquiring process? What is an energy releasing process? Obtain chemical energy in photosynthesis by producing glucose. Release energy in glucose during cell respiration 27. Why might plants photosynthesize more in the summer months than in the winter? More chlorophyll present to a ...
Chapter 23: The Respiratory System
... Contraction of the diaphragm, the main inspiratory muscle, and external intercostal muscles increases the size of the thoracic cavity The intrapleural (intrathoracic) pressure decreases so that the lungs expand Expansion of the lungs decreases alveolar pressure so that air moves along the pressure g ...
... Contraction of the diaphragm, the main inspiratory muscle, and external intercostal muscles increases the size of the thoracic cavity The intrapleural (intrathoracic) pressure decreases so that the lungs expand Expansion of the lungs decreases alveolar pressure so that air moves along the pressure g ...
Molecular Modeling
... Hemoglobin that is tied up as (HbCO) can be regenerated and is not available for oxygen transport for the life of that particular red blood cell. In this way (CO) effectively poisens the hemoglobin oxygen transport system. Hemoglobin has a greater affinity for (CO) than for molecular oxygen. ...
... Hemoglobin that is tied up as (HbCO) can be regenerated and is not available for oxygen transport for the life of that particular red blood cell. In this way (CO) effectively poisens the hemoglobin oxygen transport system. Hemoglobin has a greater affinity for (CO) than for molecular oxygen. ...
Animals - Mt. SAC
... increase surface area and decrease evaporation • Terrestrial animals may use only 1% 2% of its energy to obtain oxygen ...
... increase surface area and decrease evaporation • Terrestrial animals may use only 1% 2% of its energy to obtain oxygen ...
Study Guide: Unit Test – Digestion, Respiratory, Circulatory Systems
... 18. Where is urine stored until it can be eliminated? in the urinary bladder 19. What occurs in the stomach? Acid kills most of the bacteria swallowed with food. ...
... 18. Where is urine stored until it can be eliminated? in the urinary bladder 19. What occurs in the stomach? Acid kills most of the bacteria swallowed with food. ...
Honors Biology - WordPress.com
... 1. Fours pairs of walking legs 2. A cephalothoras instead of separate head and thorax 3. Usually have four pairs of simple eyes 4. No antennae 5. Respiration done through organs known as “book lungs.” ...
... 1. Fours pairs of walking legs 2. A cephalothoras instead of separate head and thorax 3. Usually have four pairs of simple eyes 4. No antennae 5. Respiration done through organs known as “book lungs.” ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... (out of the plasma), resulting in decreased plasma glucose levels. This system is an example of the physiological principle of a. homeostasis. b. ...
... (out of the plasma), resulting in decreased plasma glucose levels. This system is an example of the physiological principle of a. homeostasis. b. ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.