Bisgaier 1998
... lipolysis cannot be underestimated as a major source of these particles. The enhanced catabolism of triglyceriderich lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase is a potential mechanism by which increased phospholipid may form nascent HDL or be transferred to existing HDL pools (13). Possibly the differentia ...
... lipolysis cannot be underestimated as a major source of these particles. The enhanced catabolism of triglyceriderich lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase is a potential mechanism by which increased phospholipid may form nascent HDL or be transferred to existing HDL pools (13). Possibly the differentia ...
Solubilizing Excipients in Oral and Injectable Formulations
... molecules in solution. These noncovalent bulk and specific solubility-enhancing interactions are the basis of the phenomenon that “like dissolves like” and include van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, dipole–dipole and ion–dipole interactions, and in certain cases favorable electromagnetic intera ...
... molecules in solution. These noncovalent bulk and specific solubility-enhancing interactions are the basis of the phenomenon that “like dissolves like” and include van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, dipole–dipole and ion–dipole interactions, and in certain cases favorable electromagnetic intera ...
September 2006 - Highmark Blue Shield
... Direct Renin Inhibitors This policy pertains to the products categorized as direct renin inhibitors. Aliskeren (Tekturna®) is currently the only product available within this therapeutic category. Aliskeren is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with o ...
... Direct Renin Inhibitors This policy pertains to the products categorized as direct renin inhibitors. Aliskeren (Tekturna®) is currently the only product available within this therapeutic category. Aliskeren is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with o ...
(NSAIDs) classification, diagnosis and management
... history of adverse reactions precipitated with ASA and/or other NSAID. In patients without clear history, provocation tests are necessary to confirm or exclude hypersensitivity (26). In recent years, new in vitro testing methods have been proposed, but their usefulness for the diagnosis of NSAIDs hy ...
... history of adverse reactions precipitated with ASA and/or other NSAID. In patients without clear history, provocation tests are necessary to confirm or exclude hypersensitivity (26). In recent years, new in vitro testing methods have been proposed, but their usefulness for the diagnosis of NSAIDs hy ...
Useful Medications for Oral Conditions
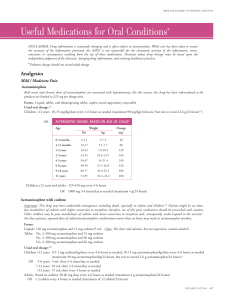
... Important: The drug requires acidic pH in the stomach to disintegrate and dissolve for oral absorption; therefore, absorption is decreased by medications that increase gastric pH. Also, prescribe with caution for patients taking other medications metabolized by CYP enzymes because fluconazole is a h ...
... Important: The drug requires acidic pH in the stomach to disintegrate and dissolve for oral absorption; therefore, absorption is decreased by medications that increase gastric pH. Also, prescribe with caution for patients taking other medications metabolized by CYP enzymes because fluconazole is a h ...
digoxin - DavisPlus
... ated with digoxin include miscalculation of pediatric doses and insufficient monitoring of digoxin levels. Have second practitioner independently check original order and dose calculations. Monitor therapeutic drug levels. For rapid digitalization, the initial dose is higher than the maintenance dos ...
... ated with digoxin include miscalculation of pediatric doses and insufficient monitoring of digoxin levels. Have second practitioner independently check original order and dose calculations. Monitor therapeutic drug levels. For rapid digitalization, the initial dose is higher than the maintenance dos ...
Please Highlight this Area and Add your Main Title
... methamphetamine following acute (Day 1) and repeated (Day 4) administrations. The 1.0 mg/kg prazosin dose attenuated the hyperactive effect of methamphetamine without disrupting activity in unpaired control mice. These results are consistent with previous studies that have reported that prazosin dos ...
... methamphetamine following acute (Day 1) and repeated (Day 4) administrations. The 1.0 mg/kg prazosin dose attenuated the hyperactive effect of methamphetamine without disrupting activity in unpaired control mice. These results are consistent with previous studies that have reported that prazosin dos ...
The Risk of Using Poppy Seed Tea Made from Several Varieties
... sumers [7]. Unfortunately, there are death cases reported worldwide because of the overdoses found in poppy seed tea. One of the cases found on the internet showed that the overdose appeared when using 1.5 kg of poppy seeds for obtaining the tea. Furthermore, it was an unexpected and undesired effec ...
... sumers [7]. Unfortunately, there are death cases reported worldwide because of the overdoses found in poppy seed tea. One of the cases found on the internet showed that the overdose appeared when using 1.5 kg of poppy seeds for obtaining the tea. Furthermore, it was an unexpected and undesired effec ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) ISSN: 2278-3008.
... The drug optimization can be achieved through Chronopharmacology. Chronopharmacology is the Science that deals with the variations in the pharmacological actions of various drugs over a period of 24 hours of the day. The biochemical, physiological and pathological variations of the 24 hour period in ...
... The drug optimization can be achieved through Chronopharmacology. Chronopharmacology is the Science that deals with the variations in the pharmacological actions of various drugs over a period of 24 hours of the day. The biochemical, physiological and pathological variations of the 24 hour period in ...
Efficacy of Lidocaine Iontophoresis Using Either Alternating or Direct
... electrodes at t, and T is the period of the square wave. However, there have been fewer studies in which the efficacy of AC-IOP is compared with that of DCIOP, which is widely used. Yan et al. reported the good correlations between phenylalanine and mannitol transport across human epidermal membra ...
... electrodes at t, and T is the period of the square wave. However, there have been fewer studies in which the efficacy of AC-IOP is compared with that of DCIOP, which is widely used. Yan et al. reported the good correlations between phenylalanine and mannitol transport across human epidermal membra ...
“Robo-Tripping”: Dextromethorphan Abuse and its Anesthetic
... Logan BK, Goldfogel G, Hamilton R, Kuhlman J. Five deaths resulting from abuse of dextromethorphan sold over the internet. ...
... Logan BK, Goldfogel G, Hamilton R, Kuhlman J. Five deaths resulting from abuse of dextromethorphan sold over the internet. ...
Glucophage (metformin)
... abdominal distress. There may be associated hypothermia, hypotension and resistance bradyarrhythmias with more marked acidosis. The patient and the patient’s physician must be aware of the possible importance of such symptoms and the patient should be instructed to notify the physician immediately i ...
... abdominal distress. There may be associated hypothermia, hypotension and resistance bradyarrhythmias with more marked acidosis. The patient and the patient’s physician must be aware of the possible importance of such symptoms and the patient should be instructed to notify the physician immediately i ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... Over the years, Cannabis remains the most widely used illicit drug worldwide due to its affordability and availability [2]. Besides, cannabis is a major controversial drug as there are numerous conflicting and controversial reports concerning its psychological and physiological effects [3]. Many rep ...
... Over the years, Cannabis remains the most widely used illicit drug worldwide due to its affordability and availability [2]. Besides, cannabis is a major controversial drug as there are numerous conflicting and controversial reports concerning its psychological and physiological effects [3]. Many rep ...
etoposide injection usp
... or the formation of free radicals. Pharmacokinetics: On intravenous administration, the disposition of etoposide is best described as a biphasic process with a distribution half-life of about 1.5 hours and terminal elimination half-life ranging from 4 to 11 hours. Total body clearance values range f ...
... or the formation of free radicals. Pharmacokinetics: On intravenous administration, the disposition of etoposide is best described as a biphasic process with a distribution half-life of about 1.5 hours and terminal elimination half-life ranging from 4 to 11 hours. Total body clearance values range f ...
Useful Medications for Oral Conditions
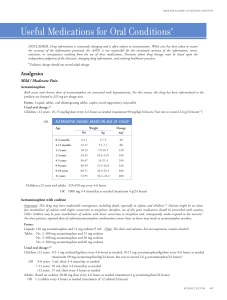
... Important: The drug requires acidic pH in the stomach to disintegrate and dissolve for oral absorption; therefore, absorption is decreased by medications that increase gastric pH. Also, prescribe with caution for patients taking other medications metabolized by CYP enzymes because fluconazole is a h ...
... Important: The drug requires acidic pH in the stomach to disintegrate and dissolve for oral absorption; therefore, absorption is decreased by medications that increase gastric pH. Also, prescribe with caution for patients taking other medications metabolized by CYP enzymes because fluconazole is a h ...
SINAREST Tablet/Syrup
... Chlorpheniramine maleate. Paracetamol produces analgesia by elevation of the pain threshold and antipyretic effect through action on the hypothalamic heatregulating center. Paracetamol is equal to aspirin in analgesic and antipyretic effectiveness, and it is unlikely to produce many of the side effe ...
... Chlorpheniramine maleate. Paracetamol produces analgesia by elevation of the pain threshold and antipyretic effect through action on the hypothalamic heatregulating center. Paracetamol is equal to aspirin in analgesic and antipyretic effectiveness, and it is unlikely to produce many of the side effe ...
Hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs
... history of adverse reactions precipitated with ASA and/or other NSAID. In patients without clear history, provocation tests are necessary to confirm or exclude hypersensitivity (26). In recent years, new in vitro testing methods have been proposed, but their usefulness for the diagnosis of NSAIDs hyp ...
... history of adverse reactions precipitated with ASA and/or other NSAID. In patients without clear history, provocation tests are necessary to confirm or exclude hypersensitivity (26). In recent years, new in vitro testing methods have been proposed, but their usefulness for the diagnosis of NSAIDs hyp ...
Fentanyl citrate - Therapeutic Goods Administration
... The multi-dose product consists of a 10 mL amber glass bottle with metering pump and dust cap, packed in a re-closable, child resistant outer plastic box. The evaluator considered that the child resistant box is far too difficult to open, requiring significant dexterity and strength. However, it is ...
... The multi-dose product consists of a 10 mL amber glass bottle with metering pump and dust cap, packed in a re-closable, child resistant outer plastic box. The evaluator considered that the child resistant box is far too difficult to open, requiring significant dexterity and strength. However, it is ...
Pharmacokinetic Interactions Between the Hepatitis C Virus
... BOC, RTV, and the HIV PIs: AUClast (area under the concentration–time curve from time 0 to the time of the last measurable sample); AUCτ (area under the concentration–time curve during a dosing interval τ); Cmax (maximum observed plasma concentration); Tmax (time to maximum observed plasma concentra ...
... BOC, RTV, and the HIV PIs: AUClast (area under the concentration–time curve from time 0 to the time of the last measurable sample); AUCτ (area under the concentration–time curve during a dosing interval τ); Cmax (maximum observed plasma concentration); Tmax (time to maximum observed plasma concentra ...
The History and Implications of Testing Thalidomide on
... models or predictive models for a specific disease or treatment must place the empirical evidence into the context of our current theories and philosophy of science. Any discussion of animal models in biomedical research should occur in the context of evolutionary biology, evolutionary developmental ...
... models or predictive models for a specific disease or treatment must place the empirical evidence into the context of our current theories and philosophy of science. Any discussion of animal models in biomedical research should occur in the context of evolutionary biology, evolutionary developmental ...
Pharmaceuticals: Focussing on Appropriate Utilization
... Indicators of pharmaceutical use within the current environment do not reflect a strategy for assessing the effectiveness or outcomes of prescription drugs. The assumption is that, other than death and other catastrophic events like heart attack or hip fracture, we have few population-based measures ...
... Indicators of pharmaceutical use within the current environment do not reflect a strategy for assessing the effectiveness or outcomes of prescription drugs. The assumption is that, other than death and other catastrophic events like heart attack or hip fracture, we have few population-based measures ...
PERCOCET Tablets Rx only Prescribing Information DESCRIPTION
... Metabolism and Elimination A high portion of oxycodone is N-dealkylated to noroxycodone during first-pass metabolism. Oxymorphone, is formed by the O-demethylation of oxycodone. The metabolism of oxycodone to oxymorphone is catalyzed by CYP2D6. Free and conjugated noroxycodone, free and conjugated o ...
... Metabolism and Elimination A high portion of oxycodone is N-dealkylated to noroxycodone during first-pass metabolism. Oxymorphone, is formed by the O-demethylation of oxycodone. The metabolism of oxycodone to oxymorphone is catalyzed by CYP2D6. Free and conjugated noroxycodone, free and conjugated o ...
Full-Text - Academic Journals
... extract that has a greater affinity with hemin maintains more hemin in solution and is thus more effective. This ...
... extract that has a greater affinity with hemin maintains more hemin in solution and is thus more effective. This ...
Effect of Khat chewing on the bioavailability of ampicillin and
... ampicillin bioavailability were substantially reduced by Khat chewing, except when the antibiotic was taken 2 h after chewing Khat (Table I). The reduction of ampicillin bioavailability was most pronounced when the drug was administered midway through the 4 h Khat chewing session (condition E). The ...
... ampicillin bioavailability were substantially reduced by Khat chewing, except when the antibiotic was taken 2 h after chewing Khat (Table I). The reduction of ampicillin bioavailability was most pronounced when the drug was administered midway through the 4 h Khat chewing session (condition E). The ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.