PH109 Exploring the Uiverse, Test #4, Spring, 1999
... 14. It is unlikely that astronauts will ever pass through black holes because a) they do not really exist b) they are too small to hold a person c) they cannot be found because they are black and cannot be seen d) tidal forces would rip them apart 15. In the simulation we saw in class, what was the ...
... 14. It is unlikely that astronauts will ever pass through black holes because a) they do not really exist b) they are too small to hold a person c) they cannot be found because they are black and cannot be seen d) tidal forces would rip them apart 15. In the simulation we saw in class, what was the ...
In a mass spectrometer, charged particles are injected into a
... above the position where U 238 does U 235 has an atomic weight of 235 atomic mass units. U 238 instead have an atomic weight of 238 atomic mass units. ...
... above the position where U 238 does U 235 has an atomic weight of 235 atomic mass units. U 238 instead have an atomic weight of 238 atomic mass units. ...
Lecture powerpoint
... masses, measured in kilograms, to the force, measured in newtons. In the SI system of units, G has the value 6.67 × 10−11 N m2/kg2. ...
... masses, measured in kilograms, to the force, measured in newtons. In the SI system of units, G has the value 6.67 × 10−11 N m2/kg2. ...
amanda`sGravity and Free Fall
... How does it work? Why do objects fall to the ground? What keeps the planets in motion in the sky? ...
... How does it work? Why do objects fall to the ground? What keeps the planets in motion in the sky? ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... If the ending force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the object may change – it may either ...
... If the ending force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the object may change – it may either ...
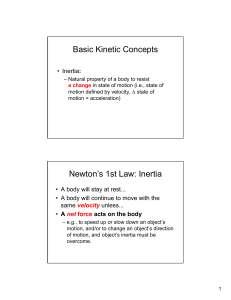
Basic Kinetic
... • Like it or not, there is a force of attraction between you and the person sitting next to you. – However, this force is so small that you don’t notice it. – When one of the objects is the earth (with its huge mass), the force of attraction (i.e. gravity) is very significant. ...
... • Like it or not, there is a force of attraction between you and the person sitting next to you. – However, this force is so small that you don’t notice it. – When one of the objects is the earth (with its huge mass), the force of attraction (i.e. gravity) is very significant. ...
Ch. 26.5: The Expanding Universe
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hVApTLE7Csc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FhfnqboacV0&NR=1 ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hVApTLE7Csc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FhfnqboacV0&NR=1 ...
Skills Worksheet
... 11. Describe the relationship between motion and a reference point. When an object is in motion, the reference point is an object that appears to stay in place. ______________________________________________________________ 12. How is it possible to be accelerating and traveling at a constant speed? ...
... 11. Describe the relationship between motion and a reference point. When an object is in motion, the reference point is an object that appears to stay in place. ______________________________________________________________ 12. How is it possible to be accelerating and traveling at a constant speed? ...
Study Guide for Ch 6 Test Newtons Laws
... light and color, developed early versions of his three laws of motion, and gained new insights into the nature of planetary motion. Fear of criticism stifles scientist When Cambridge reopened in 1667, Newton was given a minor position at Trinity and began his academic career. His studies in optics l ...
... light and color, developed early versions of his three laws of motion, and gained new insights into the nature of planetary motion. Fear of criticism stifles scientist When Cambridge reopened in 1667, Newton was given a minor position at Trinity and began his academic career. His studies in optics l ...
Introduction and Kinematics
... Extract the equations • Calculate the net force along every component for every part of the system. Be sure to pay attention to signs. • Do this by calculating the components of all the forces against the coordinate system. • Set this total equal to ma (this could be zero). If the acceleration is do ...
... Extract the equations • Calculate the net force along every component for every part of the system. Be sure to pay attention to signs. • Do this by calculating the components of all the forces against the coordinate system. • Set this total equal to ma (this could be zero). If the acceleration is do ...
Section 12.2 Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion IPLS
... shows that mass and weight are proportional, doubling the mass of an false object will not affect its weight. 15. On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is only about one sixth that on Earth. Will an object weigh more or less on the moon than it ...
... shows that mass and weight are proportional, doubling the mass of an false object will not affect its weight. 15. On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is only about one sixth that on Earth. Will an object weigh more or less on the moon than it ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.