Jeopardy - Fair Lawn Schools
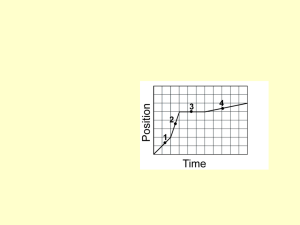
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
Homework Week 6
... with a net force of 1 N. What is the book's acceleration? 3. Calculate the momentum of a 16-kg bicycle traveling north at 3 m/s. 4. Calculate the momentum of a 12-kg bicycle traveling east at 2 m/s. 5. Calculate the acceleration of a bus whose speed changes from 7 m/s to 16 m/s over a period of 5 s. ...
... with a net force of 1 N. What is the book's acceleration? 3. Calculate the momentum of a 16-kg bicycle traveling north at 3 m/s. 4. Calculate the momentum of a 12-kg bicycle traveling east at 2 m/s. 5. Calculate the acceleration of a bus whose speed changes from 7 m/s to 16 m/s over a period of 5 s. ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 7: Newton`s Laws
... God said, Let Newton be! And all was light.” Alexander Pope (1688-1744) ...
... God said, Let Newton be! And all was light.” Alexander Pope (1688-1744) ...
Unit 2 Section 4 Notes Newton`s Laws of Motion
... because gravity exists everywhere in the universe; it is the force of attraction between 2 objects due to mass. Astronauts in orbit experience apparent weightlessness because they are in free fall. The astronauts and vehicle are falling toward Earth with the same acceleration. ...
... because gravity exists everywhere in the universe; it is the force of attraction between 2 objects due to mass. Astronauts in orbit experience apparent weightlessness because they are in free fall. The astronauts and vehicle are falling toward Earth with the same acceleration. ...
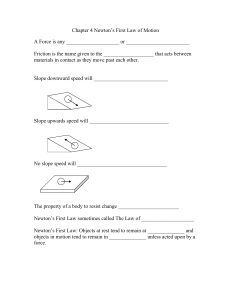
Activity - Newtons First Law File
... Answer the following questions and take good notes when necessary. This assignment will work well as a study guide if done neatly and properly. The solutions to this assignment will be posted on Moodle later – be sure to check your answers to the ...
... Answer the following questions and take good notes when necessary. This assignment will work well as a study guide if done neatly and properly. The solutions to this assignment will be posted on Moodle later – be sure to check your answers to the ...
Chapter 12
... Tides result in a net force which slows Earth’s rotation and speeds the Moon’s orbital velocity. ...
... Tides result in a net force which slows Earth’s rotation and speeds the Moon’s orbital velocity. ...
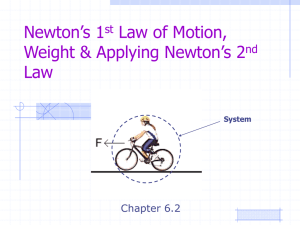
Newton`s 2nd Law - Moore Public Schools
... A force of 20 N acts upon a 5 kg block. Calculate the acceleration of the object. ...
... A force of 20 N acts upon a 5 kg block. Calculate the acceleration of the object. ...
What is Newton`s Second Law of Motion? http://www.glencoe.com
... Force and Newton's Laws What is Newton's Second Law of Motion? Force is a push or pull on an object. Net force is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton's second law of motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the force. Accelera ...
... Force and Newton's Laws What is Newton's Second Law of Motion? Force is a push or pull on an object. Net force is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton's second law of motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the force. Accelera ...
Conceptual Physics
... Volume is a measure of how much ________________ and object occupies. ________________ is the quantity of matter in an object. Mass is measured in _________________________________. __________________ is the force of gravity on an object. Relationship between mass and weight: W = mg Where: ...
... Volume is a measure of how much ________________ and object occupies. ________________ is the quantity of matter in an object. Mass is measured in _________________________________. __________________ is the force of gravity on an object. Relationship between mass and weight: W = mg Where: ...
Document
... d. Copernicus e. Tycho Brahe f. Kepler’s 3 Laws of Planetary Motion i. Kepler’s 3rd law equation g. Galileo i. Discoveries ii. Dialogo and Trial h. Modern Astronomy ...
... d. Copernicus e. Tycho Brahe f. Kepler’s 3 Laws of Planetary Motion i. Kepler’s 3rd law equation g. Galileo i. Discoveries ii. Dialogo and Trial h. Modern Astronomy ...
X Final Review
... 8. If a12kg object has 5,000J of gravitational potential energy, how high above the ground is it? ...
... 8. If a12kg object has 5,000J of gravitational potential energy, how high above the ground is it? ...
Document
... (provides a numerical value) for the amount of matter (protons and neutrons) that it contains. • Weight is a measure of the force exerted on a body by gravity, which is directly related to the amount of mass and acceleration due to gravity. • Mass is the same everywhere in the universe, while weight ...
... (provides a numerical value) for the amount of matter (protons and neutrons) that it contains. • Weight is a measure of the force exerted on a body by gravity, which is directly related to the amount of mass and acceleration due to gravity. • Mass is the same everywhere in the universe, while weight ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 10. If the same force is applied to an object with a large mass, it will have a _______________________ acceleration. 11. If the same force is applied to an object with a small mass, it will have a _______________________ acceleration. ...
... 10. If the same force is applied to an object with a large mass, it will have a _______________________ acceleration. 11. If the same force is applied to an object with a small mass, it will have a _______________________ acceleration. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.