Building a simple seismometer
... Seismometers operate on the principle of inertia, i.e. a body at rest will tend to remain that way unless a force is applied to make it move. An ideal seismometer would be a mass floating just above the ground. When the ground moves (due to the vibrations caused by an earthquake) the mass remains st ...
... Seismometers operate on the principle of inertia, i.e. a body at rest will tend to remain that way unless a force is applied to make it move. An ideal seismometer would be a mass floating just above the ground. When the ground moves (due to the vibrations caused by an earthquake) the mass remains st ...
The Tech Museum Web Quest 1. a) What instrument measures
... c) When was the first of these instruments invented? ________________________________ 2. The movement of plates along faults is not smooth; instead, the plates move in ____________ and cause ______________________. 3. About how deep do faults go into the earth? ______________________________________ ...
... c) When was the first of these instruments invented? ________________________________ 2. The movement of plates along faults is not smooth; instead, the plates move in ____________ and cause ______________________. 3. About how deep do faults go into the earth? ______________________________________ ...
Dynamic Crust Part 1
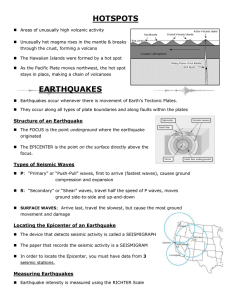
... Fault: Break in the rock of Earth’s lithosphere along which there has been displacement (movement). Seismic Waves: Vibrational energy that radiates through Earth from an earthquake. Focus: One of two fixed points that determine the shape and position of an ellipse; an earthquake’s point of origin wi ...
... Fault: Break in the rock of Earth’s lithosphere along which there has been displacement (movement). Seismic Waves: Vibrational energy that radiates through Earth from an earthquake. Focus: One of two fixed points that determine the shape and position of an ellipse; an earthquake’s point of origin wi ...
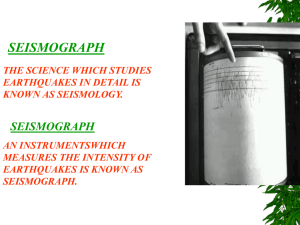
Seismographs - Ring of Fire Science
... station but not the direction of the epicenter. To determine the exact location of the epicenter of an earthquake a scientist must first determine the time lapse between the arrival of the P waves and S waves at three stations. Scientists determining the distance they were from the focus of an earth ...
... station but not the direction of the epicenter. To determine the exact location of the epicenter of an earthquake a scientist must first determine the time lapse between the arrival of the P waves and S waves at three stations. Scientists determining the distance they were from the focus of an earth ...
QR-6 Earthquakes and the Earth`s Interior Answer each of the
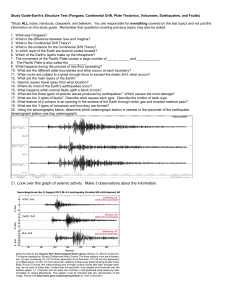
... 9. Briefly describe the triangulation method used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake. 10. Describe the differences between the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, Richter Scale, and the moment magnitude scale. 11. How much more energy does an earthquake measuring 7.0 on the Richter Scale rel ...
... 9. Briefly describe the triangulation method used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake. 10. Describe the differences between the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, Richter Scale, and the moment magnitude scale. 11. How much more energy does an earthquake measuring 7.0 on the Richter Scale rel ...
Felix Waldhauser, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Title
... plate tectonic processes. The location of earthquakes within the Earth’s crust and mantle are the fundamental parameters used in a wide range of research areas, including earthquake physics, the structure and dynamics of the Earth’s interior, and seismic hazards. Yet, the accuracy with which we know ...
... plate tectonic processes. The location of earthquakes within the Earth’s crust and mantle are the fundamental parameters used in a wide range of research areas, including earthquake physics, the structure and dynamics of the Earth’s interior, and seismic hazards. Yet, the accuracy with which we know ...
Document
... FAULTS Fault, in geology, is a fracture in the Earth's crust along which a section of the crust has been displaced relative to another section, in response to forces of tension or compression as a result of tectonic movement. This movement may be in a vertical or horizontal direction, or a combinat ...
... FAULTS Fault, in geology, is a fracture in the Earth's crust along which a section of the crust has been displaced relative to another section, in response to forces of tension or compression as a result of tectonic movement. This movement may be in a vertical or horizontal direction, or a combinat ...
Document
... vibrations or oscillations, rapid and more or less powerful, of the earth's crust, caused by the unexpected movement of the rock mass in subsoil. This displacement is generated by tectonics force that cause the release of energy in an internal point of the Earth said hypocenter; starting from the fr ...
... vibrations or oscillations, rapid and more or less powerful, of the earth's crust, caused by the unexpected movement of the rock mass in subsoil. This displacement is generated by tectonics force that cause the release of energy in an internal point of the Earth said hypocenter; starting from the fr ...
Gr. 8 NOTES: EARTHQUAKES Name: Pages 325 - 327
... 1. Give 3 expressions used to describe the phenomenon by which the Earth’s crust moves. . _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is a seismic wave, how are they formed & what do they cause? _______________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. Give 3 expressions used to describe the phenomenon by which the Earth’s crust moves. . _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is a seismic wave, how are they formed & what do they cause? _______________________________________________________________ ...
Name Date Pd _____ VIDEO: EARTHQUAKES (Bill Nye) 1. ha
... 2. The earth’s surface is made of ________________________ plates that are floating on molten rock. 3. The cracks are called __________________. 4. Scientists measure the movement of the earth’s crust with a ___________________________. 5. The record of the earth’s movement made with a seismometer i ...
... 2. The earth’s surface is made of ________________________ plates that are floating on molten rock. 3. The cracks are called __________________. 4. Scientists measure the movement of the earth’s crust with a ___________________________. 5. The record of the earth’s movement made with a seismometer i ...