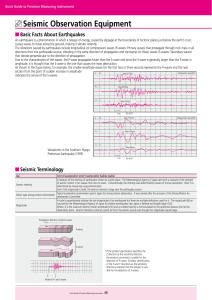
Seismic Observation Equipment
... Typical acceleration seismometer used in Japan for strong motion observation. It was named after the acronym of the Strong Motion AcSMAC type strong-motion seismometer celerometer Committee. A scale to quantitatively indicate the size (magnitude) of an earthquake but there are multiple definitions u ...
... Typical acceleration seismometer used in Japan for strong motion observation. It was named after the acronym of the Strong Motion AcSMAC type strong-motion seismometer celerometer Committee. A scale to quantitatively indicate the size (magnitude) of an earthquake but there are multiple definitions u ...
Document
... 3. L-Waves are Surface waves. They are the slowest earthquake waves. L-Waves are always last to arrive. They travel along the surface of the earth, not down into it. They usually create the most damage because they are nearer to the surface. ...
... 3. L-Waves are Surface waves. They are the slowest earthquake waves. L-Waves are always last to arrive. They travel along the surface of the earth, not down into it. They usually create the most damage because they are nearer to the surface. ...
Earthquakes
... Normal and the thrust faulting are examples of dip slip, where the displacement along the fault is in the direction of dip and movement on them involves a vertical component. ...
... Normal and the thrust faulting are examples of dip slip, where the displacement along the fault is in the direction of dip and movement on them involves a vertical component. ...
Algebra - Militant Grammarian
... SHM. If the frequency is 10.0 vibrations per second and the amplitude is 4.0 mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get f ...
... SHM. If the frequency is 10.0 vibrations per second and the amplitude is 4.0 mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get f ...
Earthquake Test Study Guide
... 6) Which seismic wave has a push-pull movement? 7) Which seismic wave has a wriggling side to side motion? 8) Which seismic wave causes the most damage during an earthquake? 9) Which seismic wave does not travel through liquids? 10) Which seismic wave travels through the all layers of the Earth? 11) ...
... 6) Which seismic wave has a push-pull movement? 7) Which seismic wave has a wriggling side to side motion? 8) Which seismic wave causes the most damage during an earthquake? 9) Which seismic wave does not travel through liquids? 10) Which seismic wave travels through the all layers of the Earth? 11) ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
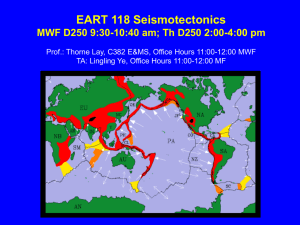
EART 118 Seismotectonics
... Polarity of first P-wave arrival varies between seismic stations in different directions. First motion is compression for stations located such that material near the fault moves ``toward'' the station, or dilatation, where motion is ``away from'' the station. When a P wave arrives at a seismometer ...
... Polarity of first P-wave arrival varies between seismic stations in different directions. First motion is compression for stations located such that material near the fault moves ``toward'' the station, or dilatation, where motion is ``away from'' the station. When a P wave arrives at a seismometer ...
Earthquakes
... Earthquakes and Tectonic Plates! • Plate boundaries occur in three sections: o Circum~ Pacific Belt. o Mediterranean Belt. o Himalayan Belt. ...
... Earthquakes and Tectonic Plates! • Plate boundaries occur in three sections: o Circum~ Pacific Belt. o Mediterranean Belt. o Himalayan Belt. ...
Newton 1 and 2 P. 2 - Adams Science News
... According to newton's first law, the state of motion of an object doesn't change as long as the net force acting on it is zero. Example “if you throw a baseball in space it will continue at the same velocity forever. ...
... According to newton's first law, the state of motion of an object doesn't change as long as the net force acting on it is zero. Example “if you throw a baseball in space it will continue at the same velocity forever. ...
Earthquake Quiz - cohort6science
... _______________11. The type of stress that pushes rock together causing a collision is tension. _______________12. The focus is the point on the Earth’s surface where an earthquake begins. _______________13. Compression is a type of stress that causes the Earth’s landforms to change shape. _________ ...
... _______________11. The type of stress that pushes rock together causing a collision is tension. _______________12. The focus is the point on the Earth’s surface where an earthquake begins. _______________13. Compression is a type of stress that causes the Earth’s landforms to change shape. _________ ...
Year 8 Tectonics
... Sections of the earth that move about and cause earthquakes and volcanoes. A great force of nature, such as an earthquake or volcano, which is a threat or a danger to people. ...
... Sections of the earth that move about and cause earthquakes and volcanoes. A great force of nature, such as an earthquake or volcano, which is a threat or a danger to people. ...
Newton`s Laws Vocabulary
... change in the motion of an object Acceleration – change of velocity or speed Velocity – the rate of speed with which something happens Speed – rate of motion Friction – the resistance of movement on surfaces that touch. Mass – the amount of matter in an object ...
... change in the motion of an object Acceleration – change of velocity or speed Velocity – the rate of speed with which something happens Speed – rate of motion Friction – the resistance of movement on surfaces that touch. Mass – the amount of matter in an object ...
Name: Notes - 4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a
... B. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on Earth? C. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on the Moon? 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12 ...
... B. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on Earth? C. What is the weight of a 1.0 kg mass on the Moon? 10. What is the difference between mass and weight? 11. Bathroom Scales A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12 ...
Earthquakes Seismic Waves Day 1
... Seismograph: instrument used to measure and record seismic wave magnitude. Magnitude: amount of energy released. Mercalli Scale: descriptive scale (containing 12 steps) to measure level of damage from an earthquake. Richter Scale: measures magnitude (strength) of earthquake by the size of the seismi ...
... Seismograph: instrument used to measure and record seismic wave magnitude. Magnitude: amount of energy released. Mercalli Scale: descriptive scale (containing 12 steps) to measure level of damage from an earthquake. Richter Scale: measures magnitude (strength) of earthquake by the size of the seismi ...