SwissRe - Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences
... Earthquakes occur where earthquakes occur, and… Earthquakes occur where seismometers exist ...
... Earthquakes occur where earthquakes occur, and… Earthquakes occur where seismometers exist ...
7a earthquakes
... A strike-slip fault is formed where two parts of the earth’s crust (plates) slide past each other. ...
... A strike-slip fault is formed where two parts of the earth’s crust (plates) slide past each other. ...
Topics covered in PH111 - Rose
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
Notes on Earthquakes and Earth`s interior - earth
... B. What are the different layers of the Earth and their properties? (ESRT pg. 10) 1. The Crust- is a solid layer, which consists of continental and oceanic crust. This layer is relatively thin compared to the other layers. a) Continental crust is made of Granite, which is a low-density igneous rock ...
... B. What are the different layers of the Earth and their properties? (ESRT pg. 10) 1. The Crust- is a solid layer, which consists of continental and oceanic crust. This layer is relatively thin compared to the other layers. a) Continental crust is made of Granite, which is a low-density igneous rock ...
earthquakes II
... cm) wide. Attach pieces together with clear adhesive tape to form a long strip. Insert the strip of paper into the slits so the ends of the strip extend out of the slits. Attach two rubber bands around the box so the bands are stretched wide to the sides of the other two slits. Place a fine tip mark ...
... cm) wide. Attach pieces together with clear adhesive tape to form a long strip. Insert the strip of paper into the slits so the ends of the strip extend out of the slits. Attach two rubber bands around the box so the bands are stretched wide to the sides of the other two slits. Place a fine tip mark ...
Essential Questions - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... opposite side of the Earth, where no waves are detected by a seismograph. 6. What causes an earthquake to occur? An EQ occurs due to the breaking and/or shifting of rock beneath the Earth’s surface. 7. Can Earthquakes be predicted? Why or why not? No, there is no way to know exactly when the rock w ...
... opposite side of the Earth, where no waves are detected by a seismograph. 6. What causes an earthquake to occur? An EQ occurs due to the breaking and/or shifting of rock beneath the Earth’s surface. 7. Can Earthquakes be predicted? Why or why not? No, there is no way to know exactly when the rock w ...
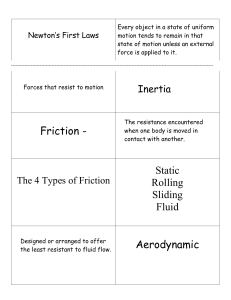
Cut squares along dotted line then fold in half to make flashcard
... One Newton is the amount of force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s/s. ...
... One Newton is the amount of force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s/s. ...
Ch. 4-Newton`s 1st law
... motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. ...
... motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. ...
Chapter 8- Earthquakes
... plate boundaries: normal faults, reverse faults, and strike-slip faults. ...
... plate boundaries: normal faults, reverse faults, and strike-slip faults. ...
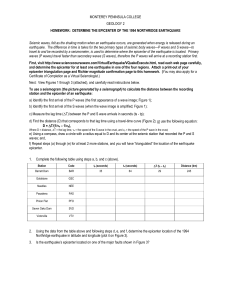
The Northridge Earthquake
... HOMEWORK: DETERMINE THE EPICENTER OF THE 1994 NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE Seismic waves, felt as the shaking motion when an earthquake occurs, are generated when energy is released during an earthquake. The difference in time is takes for the two primary types of seismic body waves—P waves and S waves—to ...
... HOMEWORK: DETERMINE THE EPICENTER OF THE 1994 NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE Seismic waves, felt as the shaking motion when an earthquake occurs, are generated when energy is released during an earthquake. The difference in time is takes for the two primary types of seismic body waves—P waves and S waves—to ...
1) A car starts to accelerate from rest with a=0
... 6) Robert and Paul pull a crate of 50 kg as indicated in the figure. Robert pulls with a force of 80N and Paul with a force of 60N. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the crate if the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.10? a) 1.0 m/s2 Paul 60N b) 1.8 m/s2 c) 2.0 m/s2 top d) 2.8 m/s2 vie ...
... 6) Robert and Paul pull a crate of 50 kg as indicated in the figure. Robert pulls with a force of 80N and Paul with a force of 60N. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the crate if the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.10? a) 1.0 m/s2 Paul 60N b) 1.8 m/s2 c) 2.0 m/s2 top d) 2.8 m/s2 vie ...
Earthquake Jeopardy
... Earthquake Safety for 600 An area along a fault where relatively few earthquakes have occurred recently but where strong earthquakes have occurred in the past. ...
... Earthquake Safety for 600 An area along a fault where relatively few earthquakes have occurred recently but where strong earthquakes have occurred in the past. ...
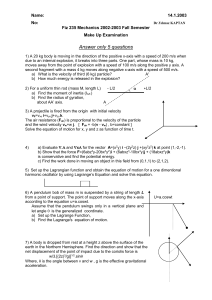
Fiz 235 Mechanics 2002
... Answer only 5 questions 1) A 20 kg body is moving in the direction of the positive x-axis with a speed of 200 m/s when due to an internal explosion, it breaks into three parts. One part, whose mass is 10 kg, moves away from the point of explosion with a speed of 100 m/s along the positive y axis. A ...
... Answer only 5 questions 1) A 20 kg body is moving in the direction of the positive x-axis with a speed of 200 m/s when due to an internal explosion, it breaks into three parts. One part, whose mass is 10 kg, moves away from the point of explosion with a speed of 100 m/s along the positive y axis. A ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... P-waves arrive first, then S waves, the Surface waves (love and rayleigh) ...
... P-waves arrive first, then S waves, the Surface waves (love and rayleigh) ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide
... 3. Which wave travels the fastest? P-wave 4. Which wave is the surface wave? L-wave 5. Which measure the magnitude “strength” of an earthquake? Richter Scale 6. Which measure the height of the waves, time, and the epicenter? (hint: paper) seismogram 7. Which is the breaking point “below the surface” ...
... 3. Which wave travels the fastest? P-wave 4. Which wave is the surface wave? L-wave 5. Which measure the magnitude “strength” of an earthquake? Richter Scale 6. Which measure the height of the waves, time, and the epicenter? (hint: paper) seismogram 7. Which is the breaking point “below the surface” ...
Chp_ 13-2 notes - South Pointe Middle
... around another object in space. • Centripetal force is the unbalanced force that makes an object move in a circular path around another object. • Gravity provides the centripetal force on the planets and their moons that keeps them in orbit ...
... around another object in space. • Centripetal force is the unbalanced force that makes an object move in a circular path around another object. • Gravity provides the centripetal force on the planets and their moons that keeps them in orbit ...
Listening Closely to ‘See’ Into the Earth
... and are equipped with a seismometer and a hydrophone. They can detect Earth motions in both vertical and horizontal directions, and can even record small, short-period earthquakes, such as those associated with hydrothermal vent activity. In typical experiments using short-period OBSs, large numbers ...
... and are equipped with a seismometer and a hydrophone. They can detect Earth motions in both vertical and horizontal directions, and can even record small, short-period earthquakes, such as those associated with hydrothermal vent activity. In typical experiments using short-period OBSs, large numbers ...