Chapter: Chapter 5: Earthquakes and Earth`s Interior
... 12. _______ is the bouncing back of a wave from an interface between two mediums. REFLECTION 13. The theory that stress is continually built up along a fault and released when earthquake occurs is known as _______. ELASTIC REBOUND 14. The method of using data from three seismic stations to locate a ...
... 12. _______ is the bouncing back of a wave from an interface between two mediums. REFLECTION 13. The theory that stress is continually built up along a fault and released when earthquake occurs is known as _______. ELASTIC REBOUND 14. The method of using data from three seismic stations to locate a ...
Worksheet - 2
... g) Acceleration 2.Differences between a) Speed and velocity b) Uniform and Non-uniform speed c) Uniform and Non-uniform velocity d) Uniform acceleration and non-uniform acceleration 3. Define Uniform circular motion 4. What do you mean by the term retardation? Give an example 5. Describe the distanc ...
... g) Acceleration 2.Differences between a) Speed and velocity b) Uniform and Non-uniform speed c) Uniform and Non-uniform velocity d) Uniform acceleration and non-uniform acceleration 3. Define Uniform circular motion 4. What do you mean by the term retardation? Give an example 5. Describe the distanc ...
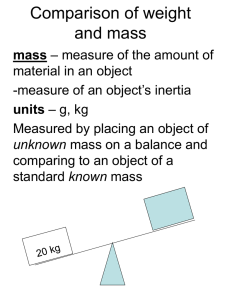
Comparison of weight and mass
... appear to be “weightless” because there is no normal force to balance gravitational force. ...
... appear to be “weightless” because there is no normal force to balance gravitational force. ...
Earthquakes - Science with Mrs. Lambert
... These waves move through Earth & will only pass through certain materials tells scientists what’s inside the Earth ...
... These waves move through Earth & will only pass through certain materials tells scientists what’s inside the Earth ...
Newton`s Second Law Pages 46-48
... • You are constantly accelerating; the net force is equal to zero. ...
... • You are constantly accelerating; the net force is equal to zero. ...
Resource from animation found at: http://www.iris.edu/hq/inclass
... as it did in Japan in 2011, the leading edge will lurch seaward, uplifting the seafloor, forming a mound of seawater that spreads out as a tsunami. The disaster of 1985 surprised seismologists who thought a subduction-zone earthquake would not produce such sudden ground motion, or strong acceleratio ...
... as it did in Japan in 2011, the leading edge will lurch seaward, uplifting the seafloor, forming a mound of seawater that spreads out as a tsunami. The disaster of 1985 surprised seismologists who thought a subduction-zone earthquake would not produce such sudden ground motion, or strong acceleratio ...
Document
... • A force directed toward the center of curved path • Centripetal acceleration is directed toward the center of a ...
... • A force directed toward the center of curved path • Centripetal acceleration is directed toward the center of a ...
Earthquake Vocabulary Part 2
... uppermost part of the mantle and is broken up into segments, or plates ...
... uppermost part of the mantle and is broken up into segments, or plates ...