Document
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
Earth Materials
... first movement occurs during an earthquake • Epicenter: The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus (this is usually the location reported in the media) ...
... first movement occurs during an earthquake • Epicenter: The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus (this is usually the location reported in the media) ...
Lecture-18-11
... The previous image shows a system that is underdamped – it goes through multiple oscillations before coming to rest. A critically damped system is one that relaxes back to the equilibrium position without oscillating and in minimum time; an overdamped system will also not oscillate but is damped so ...
... The previous image shows a system that is underdamped – it goes through multiple oscillations before coming to rest. A critically damped system is one that relaxes back to the equilibrium position without oscillating and in minimum time; an overdamped system will also not oscillate but is damped so ...
the vector product - Tennessee State University
... impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed.”) ...
... impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed.”) ...
earthquake - EPaathSala
... earthquake, the larger the amplitude of ground motion at a given distance. He calibrated his scale of magnitudes using measured maximum amplitudes of shear waves on seismometers particularly sensitive to shear waves with periods of about one second. The records had to be obtained from a specific kin ...
... earthquake, the larger the amplitude of ground motion at a given distance. He calibrated his scale of magnitudes using measured maximum amplitudes of shear waves on seismometers particularly sensitive to shear waves with periods of about one second. The records had to be obtained from a specific kin ...
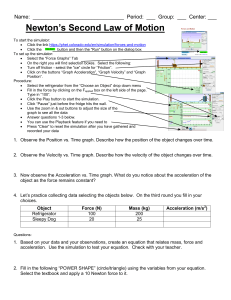
Phy221 E1Review
... d. Draw motion graphs from lab data or other representations of motion and interpret the meaning of coordinates, intercepts, slope and area. e. Given an equation describing the motion of an object, utilize differentiation and/or integration to represent the other kinematic variables as functions of ...
... d. Draw motion graphs from lab data or other representations of motion and interpret the meaning of coordinates, intercepts, slope and area. e. Given an equation describing the motion of an object, utilize differentiation and/or integration to represent the other kinematic variables as functions of ...
mDv
... In an inelastic collision (things stick together), m1v1 + m2v2 = (m1 + m2)vf If I throw a 2 kg clay ball forward at 10 m/s, and my friend throws a 1 kg clay ball forward at 20 m/s, what will their speed be when they hit and stick together? For work to occur, only the force that is parallel to the m ...
... In an inelastic collision (things stick together), m1v1 + m2v2 = (m1 + m2)vf If I throw a 2 kg clay ball forward at 10 m/s, and my friend throws a 1 kg clay ball forward at 20 m/s, what will their speed be when they hit and stick together? For work to occur, only the force that is parallel to the m ...
Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Product of Earth`s Internal Fire
... cause regolith to slip and cliffs to collapse. The sudden shaking and disturbance of water-saturated sediment and regolith can turn seemingly solid ground to a liquid mass similar to quicksand (liquefaction). Earthquakes generate seismic sea waves, called tsunami, which have been particularly destru ...
... cause regolith to slip and cliffs to collapse. The sudden shaking and disturbance of water-saturated sediment and regolith can turn seemingly solid ground to a liquid mass similar to quicksand (liquefaction). Earthquakes generate seismic sea waves, called tsunami, which have been particularly destru ...
Crustal Interactions Midterm Rev
... displacement of features in this area? 1) vertical lifting of surface rock 2) folding of surface rock 3) down-warping of the crust 4) movement along a transform fault 11 Which diagram of rock layers represents the best evidence of crustal movement? ...
... displacement of features in this area? 1) vertical lifting of surface rock 2) folding of surface rock 3) down-warping of the crust 4) movement along a transform fault 11 Which diagram of rock layers represents the best evidence of crustal movement? ...
+x - SeyedAhmad.com
... F ma kx • Acceleration is a maximum at the end points and it is zero at the center of oscillation. ...
... F ma kx • Acceleration is a maximum at the end points and it is zero at the center of oscillation. ...
MOTION
... rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
... rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
Unit 4 - BIOMECHANICS
... Examples: Sprinter accelerates down a track or hockey player quickly veers to go around another player. ...
... Examples: Sprinter accelerates down a track or hockey player quickly veers to go around another player. ...
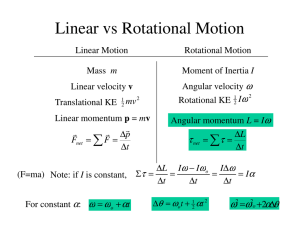
Linear vs Rotational Motion ∑ ω
... Disk 1 is rotating freely and has angular velocity ωi and moment of inertia I1 about its symmetry axis, as shown. It drops onto disk 2 of moment of inertia I2, initially at rest. Because of kinetic friction, the two disks eventually attain a common angular velocity ωf. (a) What is ωf? (b) What is th ...
... Disk 1 is rotating freely and has angular velocity ωi and moment of inertia I1 about its symmetry axis, as shown. It drops onto disk 2 of moment of inertia I2, initially at rest. Because of kinetic friction, the two disks eventually attain a common angular velocity ωf. (a) What is ωf? (b) What is th ...