further force and motion considerations
... – Acceleration = change of velocity Force over a period of time causes a change of momentum over that time. – Average net force over a period of time = m(Vf – Vi) Therefore changing momentum over a short period of time generates a greater force than over a longer period of time – When landing from a ...
... – Acceleration = change of velocity Force over a period of time causes a change of momentum over that time. – Average net force over a period of time = m(Vf – Vi) Therefore changing momentum over a short period of time generates a greater force than over a longer period of time – When landing from a ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
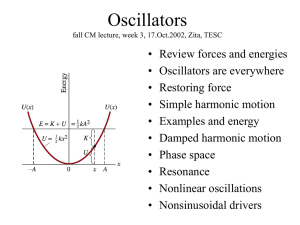
... Total mechanical energy E = T + V is conserved in the absence of dissipative forces: Kinetic T = (1/2) m v2 = p2 /(2m), Potential energy V = - F dx ...
... Total mechanical energy E = T + V is conserved in the absence of dissipative forces: Kinetic T = (1/2) m v2 = p2 /(2m), Potential energy V = - F dx ...
Worksheet
... a) in the same direction as motion b) only on objects that are not in motion c) in the opposite direction of the motion d) in both directions 5. The friction on an object moving through water or air is ____________. a) fluid friction b) rolling friction c) sliding friction d) static friction 6. The ...
... a) in the same direction as motion b) only on objects that are not in motion c) in the opposite direction of the motion d) in both directions 5. The friction on an object moving through water or air is ____________. a) fluid friction b) rolling friction c) sliding friction d) static friction 6. The ...
Gravity
... force of 30 N on a Happy Face with a mass of 100 kg. If the friction is 15 N, how fast did the chihuahua accelerate the Happy Face? 2. If the chihuahua pushes too far and they both fall off the edge of the table, which one accelerates faster? ...
... force of 30 N on a Happy Face with a mass of 100 kg. If the friction is 15 N, how fast did the chihuahua accelerate the Happy Face? 2. If the chihuahua pushes too far and they both fall off the edge of the table, which one accelerates faster? ...
12.2 Newton`s 1st and 2nd Laws of Motion
... continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
... continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
AP Physics 1 * Unit 2
... A mass, m1 = 3.00kg, is resting on a frictionless horizontal table is connected to a cable that passes over a pulley and then is fastened to a hanging mass, m2 = 11.0 kg as shown below. Find the acceleration of each mass and the tension in the cable. ...
... A mass, m1 = 3.00kg, is resting on a frictionless horizontal table is connected to a cable that passes over a pulley and then is fastened to a hanging mass, m2 = 11.0 kg as shown below. Find the acceleration of each mass and the tension in the cable. ...
Form 3 Science Test Test 6: Force, energy and motion Total: 50
... mass and for acceleration. B The formula for force is F = x where F stands for force, stands for momentum and for acceleration. C The formula for force is F = x where F stands for force, stands for mass and for altitude. D The formula for force is F = x where F stands for friction, stands for mass a ...
... mass and for acceleration. B The formula for force is F = x where F stands for force, stands for momentum and for acceleration. C The formula for force is F = x where F stands for force, stands for mass and for altitude. D The formula for force is F = x where F stands for friction, stands for mass a ...
Chapter 3 - Cloudfront.net
... • The same laws of physics that govern the motion of the planets and stars controls the motion of objects here on earth like the motion of cars… • Mechanics: the study of objects in motion ...
... • The same laws of physics that govern the motion of the planets and stars controls the motion of objects here on earth like the motion of cars… • Mechanics: the study of objects in motion ...
Earthquakes - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Why is the moment magnitude scale used today by geologists to measure earthquakes? • The moment magnitude scale determines the total energy released by an earthquake • This scale uses a electronic seismograph that can measure earthquakes that are big or small, and near or far • Geologist examine mo ...
... Why is the moment magnitude scale used today by geologists to measure earthquakes? • The moment magnitude scale determines the total energy released by an earthquake • This scale uses a electronic seismograph that can measure earthquakes that are big or small, and near or far • Geologist examine mo ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... Two weights, each with mass m, are connected with a massless string and suspended from two massless, frictionless pulleys in a gravitational field as shown above. Denote the length of string from pulley A to mass A by x. The length of string from pulley B to mass B is L − x, where L is fixed by the ...
... Two weights, each with mass m, are connected with a massless string and suspended from two massless, frictionless pulleys in a gravitational field as shown above. Denote the length of string from pulley A to mass A by x. The length of string from pulley B to mass B is L − x, where L is fixed by the ...
Work is a force that moves through a distance
... 5. 1N equals 1kgm/s2. What is a Dyne equal to? 6 How much force is required to accelerate a 1800kg car at 3.00m/s/s? 7. What is the weight of the 1800kg car in question G? 8. What is the difference between mass and weight? 9. What unit is weight measured in? 10. What is inertia? 11. What do automobi ...
... 5. 1N equals 1kgm/s2. What is a Dyne equal to? 6 How much force is required to accelerate a 1800kg car at 3.00m/s/s? 7. What is the weight of the 1800kg car in question G? 8. What is the difference between mass and weight? 9. What unit is weight measured in? 10. What is inertia? 11. What do automobi ...