Benchmark 1 Notes
... Unknown Equation- Use the variables in the Given and Unknown to determine which equation to use! Substitute Solve 4C: Projectile & Circular Motion Projectile Motion- an object in which gravity is the only force that acts on it! For a horizontally launched object, initial vertical velocit ...
... Unknown Equation- Use the variables in the Given and Unknown to determine which equation to use! Substitute Solve 4C: Projectile & Circular Motion Projectile Motion- an object in which gravity is the only force that acts on it! For a horizontally launched object, initial vertical velocit ...
Which will fall faster?
... • Will a lighter object fall faster or a heavier object? • Will a piece of paper fall faster or a text book? Why? • Lets try. ...
... • Will a lighter object fall faster or a heavier object? • Will a piece of paper fall faster or a text book? Why? • Lets try. ...
PHYS2330 Intermediate Mechanics Fall 2009 Final Exam
... This exam has two parts. Part I has 20 multiple choice questions, worth two points each. Part II consists of six relatively short problems, worth ten points each. The short problems can be worked out on the front page of the sheet provided, but use the back if you need more room. In any case please ...
... This exam has two parts. Part I has 20 multiple choice questions, worth two points each. Part II consists of six relatively short problems, worth ten points each. The short problems can be worked out on the front page of the sheet provided, but use the back if you need more room. In any case please ...
EarthScience_Topic 9-Properties of Earths Interior
... the left edge with the vertical axis (time). Be sure that most of the paper is hanging down below the graph. This is important. 2) Make a small, thin, and accurate mark on the paper at 0 time. Make another small, thin, and accurate, mark at 4:30 (4 minutes, 30 seconds). Your 2 marks are now 4:30 apa ...
... the left edge with the vertical axis (time). Be sure that most of the paper is hanging down below the graph. This is important. 2) Make a small, thin, and accurate mark on the paper at 0 time. Make another small, thin, and accurate, mark at 4:30 (4 minutes, 30 seconds). Your 2 marks are now 4:30 apa ...
SHM - MACscience
... force that tries to restore the object to its REST POSITION is PROPORTIONAL TO the DISPLACEMENT of the object. A pendulum and a mass on a spring both undergo this type of motion which can be described by a SINE WAVE or a COSINE WAVE depending upon the start position. Displacement x ...
... force that tries to restore the object to its REST POSITION is PROPORTIONAL TO the DISPLACEMENT of the object. A pendulum and a mass on a spring both undergo this type of motion which can be described by a SINE WAVE or a COSINE WAVE depending upon the start position. Displacement x ...
Motion: Forces and Cases of Motion
... The acceleration of an object is __________________ proportional to the net external ___________ acting on the object and _______________proportional to the object’s __________________. ...
... The acceleration of an object is __________________ proportional to the net external ___________ acting on the object and _______________proportional to the object’s __________________. ...
doc
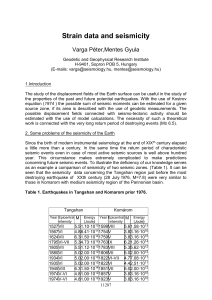
... Since the birth of modern instrumental seismology at the end of XIXth century elapsed a little more than a century. In the same time the return period of characteristic seismic events even in case of most active seismic sources is well above hundred year. This circumstance makes extremely complicate ...
... Since the birth of modern instrumental seismology at the end of XIXth century elapsed a little more than a century. In the same time the return period of characteristic seismic events even in case of most active seismic sources is well above hundred year. This circumstance makes extremely complicate ...
hp1f2013_class04_3d
... A tennis ball is hit at 50 mps at an angle of 5 degrees above the horizontal. The initial height is 2 m. Neglecting air drag, how far does the ball go before hitting the ground? Choose +x to be in the direction the ball starts at. Choose +y to be at right angles to that. Choose the origin to be the ...
... A tennis ball is hit at 50 mps at an angle of 5 degrees above the horizontal. The initial height is 2 m. Neglecting air drag, how far does the ball go before hitting the ground? Choose +x to be in the direction the ball starts at. Choose +y to be at right angles to that. Choose the origin to be the ...
Genetics Jeopardy
... while an object in motion tends to stay in motion, unless some outside force acts on it (Newton’s 1st Law) You must apply more force to move an object with greater mass. If you apply equal force to two objects, the one with greater mass will ...
... while an object in motion tends to stay in motion, unless some outside force acts on it (Newton’s 1st Law) You must apply more force to move an object with greater mass. If you apply equal force to two objects, the one with greater mass will ...
Motion - Portland Jewish Academy
... 1. ________________________ put things into motion. 2. Forces are when something is __________________ or __________________. 3. When the scooter is put on the air track, what happen when he puts it on there & let’s go? 4. What does it take for it to move? 5. If there was enough track and enough air ...
... 1. ________________________ put things into motion. 2. Forces are when something is __________________ or __________________. 3. When the scooter is put on the air track, what happen when he puts it on there & let’s go? 4. What does it take for it to move? 5. If there was enough track and enough air ...
Chapter 8 Practice Test Name 1. A 30 kg object is set into orbit 7.5 x
... D. As a safety margin, the designer plans to make the rollercoaster go at twice the critical speed (twice as fast as you just calculated). At that speed, calculate the centripetal force on the rollercoaster. E. At that safer speed, calculate the normal force the track needs to provide at the highest ...
... D. As a safety margin, the designer plans to make the rollercoaster go at twice the critical speed (twice as fast as you just calculated). At that speed, calculate the centripetal force on the rollercoaster. E. At that safer speed, calculate the normal force the track needs to provide at the highest ...
Document
... An object moves with a velocity that is constant in magnitude and direction unless a non-zero net force acts on it. If an object is at rest then it will remain at rest or if it is moving along a straight line with uniform speed then it will continue to keep moving unless an external force is applied ...
... An object moves with a velocity that is constant in magnitude and direction unless a non-zero net force acts on it. If an object is at rest then it will remain at rest or if it is moving along a straight line with uniform speed then it will continue to keep moving unless an external force is applied ...
force
... Describe the relationship between: Force and acceleration: Directly Proportional Mass and acceleration: Inversely Proportional What is the rate of acceleration due to gravity? 9.8 m/s2 ...
... Describe the relationship between: Force and acceleration: Directly Proportional Mass and acceleration: Inversely Proportional What is the rate of acceleration due to gravity? 9.8 m/s2 ...
Newton`s 2nd Law Fill
... same instant, they’d both splash into the water at almost the same instant. This means their __________________ would be about the same. Would you have expected the bowling ball to hit the water first because it has more mass? It’s true that the force of ________________ would be greater on the bowl ...
... same instant, they’d both splash into the water at almost the same instant. This means their __________________ would be about the same. Would you have expected the bowling ball to hit the water first because it has more mass? It’s true that the force of ________________ would be greater on the bowl ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Life • Why would a truck take longer to accelerate when the driver hits the gas if it were loaded with bricks than if it were empty? • How might you design a car to achieve maximum acceleration? ...
... Life • Why would a truck take longer to accelerate when the driver hits the gas if it were loaded with bricks than if it were empty? • How might you design a car to achieve maximum acceleration? ...
Nature`s Forces, F due to Gravity, and Grav. Field
... Exercises 4.1 (Forces and Gravity) 1. Define a "force". _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2a Scientists believe that there are only four "natural" forces in the universe. These are: 1)______________________________________ 2) _____________________ ...
... Exercises 4.1 (Forces and Gravity) 1. Define a "force". _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2a Scientists believe that there are only four "natural" forces in the universe. These are: 1)______________________________________ 2) _____________________ ...
File
... or P-waves, travel the fastest, so they are the first to arrive at some other point on Earth’s crust. Secondary waves, or Swaves, arrive next and these tend to cause more damage than P-waves. Although they do not travel as far as primary waves and move at relatively low speeds, surface waves tend to ...
... or P-waves, travel the fastest, so they are the first to arrive at some other point on Earth’s crust. Secondary waves, or Swaves, arrive next and these tend to cause more damage than P-waves. Although they do not travel as far as primary waves and move at relatively low speeds, surface waves tend to ...
The student will demonstrate an understanding of motion, forces
... • You will use equipment to measure time and distance so that the motion of the object can be determined. • You will used data collected to calculate the speed of an object. • You will explain the results of applying a force to an object. ...
... • You will use equipment to measure time and distance so that the motion of the object can be determined. • You will used data collected to calculate the speed of an object. • You will explain the results of applying a force to an object. ...