Shake, Rattle, and Roll the Earth
... - some igneous rock contains iron - a record of these switches occur in the rock - surrounding the Mid-ocean ridges (places where new crust is formed) • Heatflow measurements - measurement are highest at areas of new sea floor creation - decreases as one moves away from these points ...
... - some igneous rock contains iron - a record of these switches occur in the rock - surrounding the Mid-ocean ridges (places where new crust is formed) • Heatflow measurements - measurement are highest at areas of new sea floor creation - decreases as one moves away from these points ...
Top driven asymmetric mantle convection
... mechanisms governing plate tectonics and mantle convection. Mantle convection models fail to integrate plate kinematics and thermodynamics of the mantle. We computed the volume of the plates lost along subduction zones, which is about 306 km3/yr (±15). Mass balance predicts that slabs are compensate ...
... mechanisms governing plate tectonics and mantle convection. Mantle convection models fail to integrate plate kinematics and thermodynamics of the mantle. We computed the volume of the plates lost along subduction zones, which is about 306 km3/yr (±15). Mass balance predicts that slabs are compensate ...
Earthquake BINGO
... Rupture (crack) at surface People hurt Streams/rivers diverted Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale Richter Scale Mountain ridges line up Shapes of continents match Mid Atlantic Ridge S-Wave Convergent ...
... Rupture (crack) at surface People hurt Streams/rivers diverted Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale Richter Scale Mountain ridges line up Shapes of continents match Mid Atlantic Ridge S-Wave Convergent ...
Chapter 3 Geosphere
... 15km-300km thick. Includes crust and uppermost layer of mantle. Divided into tectonic plates. ...
... 15km-300km thick. Includes crust and uppermost layer of mantle. Divided into tectonic plates. ...
Benchmark 3 Study Guide
... 15. What geological event takes place at transform boundaries?_________________________________________ 16. What geological features are created at convergent boundaries with subduction?_______________________ 17. What causes plate tectonic movement?__________________________________________________ ...
... 15. What geological event takes place at transform boundaries?_________________________________________ 16. What geological features are created at convergent boundaries with subduction?_______________________ 17. What causes plate tectonic movement?__________________________________________________ ...
notes for geologofe - sciencepowerpoint.com
... Hexagonal. (Four axes, three are equal in length and lie at an angle of 120° from each other). Triclinic: (3 axis, all unequal and none at 90° angles). Orthorhombic: (All axis unequal in length, and 90° degrees from each other). Monoclinic:All axis unequal in length. Two of them are at right ...
... Hexagonal. (Four axes, three are equal in length and lie at an angle of 120° from each other). Triclinic: (3 axis, all unequal and none at 90° angles). Orthorhombic: (All axis unequal in length, and 90° degrees from each other). Monoclinic:All axis unequal in length. Two of them are at right ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... in red). The boundary layer is a zone across which the transition in rheology and heat transfer mechanism occurs (in green). The thickness of the boundary layer is exaggerated here for clarity: it is probably less than half the thickness of the lithosphere. ...
... in red). The boundary layer is a zone across which the transition in rheology and heat transfer mechanism occurs (in green). The thickness of the boundary layer is exaggerated here for clarity: it is probably less than half the thickness of the lithosphere. ...
Quiz 1 Rocks and Plates
... B. two, converging, oceanic plates meeting head-on and piling up into a mid-ocean ridge C. a divergent boundary where the continental plate changes to an oceanic plate D. a deep, vertical fault along which two plates slide past one another in opposite directions Mount St. Helens and the other Cascad ...
... B. two, converging, oceanic plates meeting head-on and piling up into a mid-ocean ridge C. a divergent boundary where the continental plate changes to an oceanic plate D. a deep, vertical fault along which two plates slide past one another in opposite directions Mount St. Helens and the other Cascad ...
8.1 powerpoint
... and Earth’s gravity. It became a glowing ball of melted rock. • Dense materials sank toward the center and less dense moved toward the surface • Layers were formed—core, mantle, crust ...
... and Earth’s gravity. It became a glowing ball of melted rock. • Dense materials sank toward the center and less dense moved toward the surface • Layers were formed—core, mantle, crust ...
Plate Tectonic Mapping Assignment
... Identify each plate boundary using the specific colours . a. Divergent = blue b. Convergent ocean-ocean =orange c. Convergent ocean-continental= red d. Convergent continental- continental=brown e. Transform=green Label where you would expect to find large mountain ranges with rows of brown triangles ...
... Identify each plate boundary using the specific colours . a. Divergent = blue b. Convergent ocean-ocean =orange c. Convergent ocean-continental= red d. Convergent continental- continental=brown e. Transform=green Label where you would expect to find large mountain ranges with rows of brown triangles ...
Volcanoes Webquest - Mrs. Gomez`s Class
... **Remember: Magna rises because it is less dense than the solid rock around it. 8. There are many structures within a volcano. Using the website http://www.volcanolive.com/ click on “volcanology” and then navigate to the glossary to define the following structures. a. magma chamber b. pipe c. vent c ...
... **Remember: Magna rises because it is less dense than the solid rock around it. 8. There are many structures within a volcano. Using the website http://www.volcanolive.com/ click on “volcanology” and then navigate to the glossary to define the following structures. a. magma chamber b. pipe c. vent c ...
Chapter 9: Causes of Volcanic Eruptions
... • Oceanic crust is subducted because it is denser and thinner than continental crust. ...
... • Oceanic crust is subducted because it is denser and thinner than continental crust. ...
The Layers of the EarthPowerPoint Fill-in-the
... The crust is composed of two rocks. The continental crust is mostly _______________. The oceanic crust is ________________. Basalt is much ___________________ than the granite. Because of this the ___________________ dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. The ___________________ is the ...
... The crust is composed of two rocks. The continental crust is mostly _______________. The oceanic crust is ________________. Basalt is much ___________________ than the granite. Because of this the ___________________ dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. The ___________________ is the ...
File
... 9. In addition to volcanoes, what also occurs frequently in the Pacific Ring of Fire? • earthquakes ...
... 9. In addition to volcanoes, what also occurs frequently in the Pacific Ring of Fire? • earthquakes ...
subduction zone
... The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. The word, tectonic, refers to ...
... The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. The word, tectonic, refers to ...
Exam 2 Review Sheet Handout Page
... 2) What is a mineral (definition)? 3) What is a mineraloid? 4) What is an atom? What is it composed of? 5) What is the atomic number? The atomic mass? 6) What is an isotope? 7) Be able to calculate the number of protons and neutrons if given the atomic number and/or the atomic mass number. Also, if ...
... 2) What is a mineral (definition)? 3) What is a mineraloid? 4) What is an atom? What is it composed of? 5) What is the atomic number? The atomic mass? 6) What is an isotope? 7) Be able to calculate the number of protons and neutrons if given the atomic number and/or the atomic mass number. Also, if ...
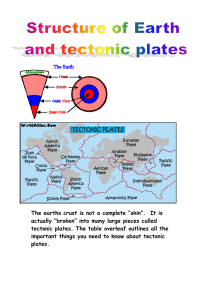
The earths crust is not a complete “skin”. It is actually “broken” into
... The earths crust is not a complete “skin”. It is actually “broken” into many large pieces called tectonic plates. The table overleaf outlines all the important things you need to know about tectonic plates. ...
... The earths crust is not a complete “skin”. It is actually “broken” into many large pieces called tectonic plates. The table overleaf outlines all the important things you need to know about tectonic plates. ...
Earth Layers and PT study guide ANSWERS
... Lithosphere – Outermost layer made of the crust and rigid upper portion of the mantle, divided into tectonic plates Asthenosphere – “Plastic” layer, solid rock that flows very slowly Mesosphere – Strong lower part of the mantle, extends from the asthenosphere into the core Outer Core – Liqui ...
... Lithosphere – Outermost layer made of the crust and rigid upper portion of the mantle, divided into tectonic plates Asthenosphere – “Plastic” layer, solid rock that flows very slowly Mesosphere – Strong lower part of the mantle, extends from the asthenosphere into the core Outer Core – Liqui ...
`I. True/False Questions: circle a “T” for true or “F” for false (10% total
... 2. (T F) The fundamental structure of silicate minerals is built upon the silicon-oxygen tetrahedron (SiO4). 3. (T F) After a theory has survived much scientific scrutiny, it may be elevated to hypothesis status. 4. (T F) Convergent plate tectonic boundaries are located where plates move toward one ...
... 2. (T F) The fundamental structure of silicate minerals is built upon the silicon-oxygen tetrahedron (SiO4). 3. (T F) After a theory has survived much scientific scrutiny, it may be elevated to hypothesis status. 4. (T F) Convergent plate tectonic boundaries are located where plates move toward one ...
Earth History – Study Guide Investigations: Sedimentary Rocks +
... 12. Name two other places where sediments can accumulate. 13. What type of rock is most easily broken down by carbonic acid? 14. What are the four natural forces that cause erosion? 15. Of the four from question 14, which is the most powerful natural force that causes erosion? 16. What are clastic r ...
... 12. Name two other places where sediments can accumulate. 13. What type of rock is most easily broken down by carbonic acid? 14. What are the four natural forces that cause erosion? 15. Of the four from question 14, which is the most powerful natural force that causes erosion? 16. What are clastic r ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.