How Australia was formed – Geographical
... super-continent of Gondwanaland. Other present-day continents which formed part of Gondwanaland are Africa, Antarctica, South America and some southern parts of the Asian continent. The existence of Gondwanaland was first discovered during the late 19th century by an Austrian geologist named Eduard ...
... super-continent of Gondwanaland. Other present-day continents which formed part of Gondwanaland are Africa, Antarctica, South America and some southern parts of the Asian continent. The existence of Gondwanaland was first discovered during the late 19th century by an Austrian geologist named Eduard ...
Unit 3 Vocabulary
... Uplifted Mountain - forms when large regions rise vertically with very little deformation Convergent tending to move toward one point or approaching each other Earthquake - causes vibrations in the ground that result from movement along breaks in Earth’s lithosphere Epicenter - location directly abo ...
... Uplifted Mountain - forms when large regions rise vertically with very little deformation Convergent tending to move toward one point or approaching each other Earthquake - causes vibrations in the ground that result from movement along breaks in Earth’s lithosphere Epicenter - location directly abo ...
No Slide Title
... Name of the theory developed by Alfred Wagner to explain the movement of continents. ...
... Name of the theory developed by Alfred Wagner to explain the movement of continents. ...
Plate Tectonics Vocab
... The amount of mass of a substance in a given volume (Density = mass/volume) Denser sinks, less dense floats/rises ...
... The amount of mass of a substance in a given volume (Density = mass/volume) Denser sinks, less dense floats/rises ...
Plate Tectonics_notes student
... A _____________ that all the continents were once joined together in ____________ _________________________. Pangaea is the name Wegener gave to the supercontinent. The word comes from the Greek word meaning, “_________________.” It was centered where _______________ is today and reached from pole t ...
... A _____________ that all the continents were once joined together in ____________ _________________________. Pangaea is the name Wegener gave to the supercontinent. The word comes from the Greek word meaning, “_________________.” It was centered where _______________ is today and reached from pole t ...
WHAT IS A PLATE? The surface of the Earth is broken up into large
... warm. Pitch, used for roads, can be brittle when struck with a hammer, but still flow very slowly, just as ice does when a glacier moves downhill. The temperature gradient of the Earth means that, at a certain depth in the upper mantle, peridotite will behave like this too. This occurs when peri ...
... warm. Pitch, used for roads, can be brittle when struck with a hammer, but still flow very slowly, just as ice does when a glacier moves downhill. The temperature gradient of the Earth means that, at a certain depth in the upper mantle, peridotite will behave like this too. This occurs when peri ...
The Earth`s Layers and Plate Tectonics Study Guide #1 Unit 3
... broken into many pieces called plates plates "float" on the soft, plastic mantle Continental plates sit on top of the much denser Oceanic Plates ...
... broken into many pieces called plates plates "float" on the soft, plastic mantle Continental plates sit on top of the much denser Oceanic Plates ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... motions provide the mechanisms by which mantle rocks melt to generate magma. __________________ • Rising magma can form ________________in an ocean (Aleutian Islands). ...
... motions provide the mechanisms by which mantle rocks melt to generate magma. __________________ • Rising magma can form ________________in an ocean (Aleutian Islands). ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... conclusion to draw from this evidence? a. Mesosaurus migrated across the ocean from location X to location Y. b. The continents of South America and Africa were joined when Mesosaurus lived. c. The present climates at locations X and Y are similar. 10. A chain of volcanoes commonly forms when a. a c ...
... conclusion to draw from this evidence? a. Mesosaurus migrated across the ocean from location X to location Y. b. The continents of South America and Africa were joined when Mesosaurus lived. c. The present climates at locations X and Y are similar. 10. A chain of volcanoes commonly forms when a. a c ...
Plate Tectonics - bvsd.k12.pa.us
... 1. During the 1940s and 1950s, scientists began using radar on moving ships to map large areas of the ocean floor in detail. ...
... 1. During the 1940s and 1950s, scientists began using radar on moving ships to map large areas of the ocean floor in detail. ...
1 - Ridgefield School District
... 1. During the 1940s and 1950s, scientists began using radar on moving ships to map large areas of the ocean floor in detail. ...
... 1. During the 1940s and 1950s, scientists began using radar on moving ships to map large areas of the ocean floor in detail. ...
Plate Tectonic, Earthquakes, and Volcanoes Test Review
... What is Pangaea? How long ago had it formed? All continents were together in a giant supercontinent 245 million years ago. What sea surrounded Pangaea (means “all sea”)? Panthalassa ...
... What is Pangaea? How long ago had it formed? All continents were together in a giant supercontinent 245 million years ago. What sea surrounded Pangaea (means “all sea”)? Panthalassa ...
Plate Tectonics
... Wegener theory, called continental drift, explained why identical animal fossils like that of mesorausaus were found on coastlines separated by vast oceans. The continental drift theory could also explain the matching of large geological features across continents. Sea floor spreading in turn was th ...
... Wegener theory, called continental drift, explained why identical animal fossils like that of mesorausaus were found on coastlines separated by vast oceans. The continental drift theory could also explain the matching of large geological features across continents. Sea floor spreading in turn was th ...
Name - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... w/ ____________. 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly __________________________. ...
... w/ ____________. 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly __________________________. ...
Review Sheet
... Be able to list & explain Wegener’s evidence for continental drift. Describe the relationship between volcanoes, earthquakes, & plate boundaries. List & describe evidence for the theory of Sea Floor Spreading. Explain convection currents & how they are related to density. List plate boundary informa ...
... Be able to list & explain Wegener’s evidence for continental drift. Describe the relationship between volcanoes, earthquakes, & plate boundaries. List & describe evidence for the theory of Sea Floor Spreading. Explain convection currents & how they are related to density. List plate boundary informa ...
2651-RDW Using SOLO to develop extended writing
... Describe the mantle as the zone between the crust and the core which is: • cold and rigid just below the crust • hot and non-rigid at greater depths and therefore able to move. Describe the theory of plate tectonics: • energy transfer involving convection currents in the semi-rigid mantle causing th ...
... Describe the mantle as the zone between the crust and the core which is: • cold and rigid just below the crust • hot and non-rigid at greater depths and therefore able to move. Describe the theory of plate tectonics: • energy transfer involving convection currents in the semi-rigid mantle causing th ...
Chapter 7
... Greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system Mechanism of spreading Decompression melting occurs as the lithosphere is pulled apart Large quantities of basaltic magma are produced ...
... Greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system Mechanism of spreading Decompression melting occurs as the lithosphere is pulled apart Large quantities of basaltic magma are produced ...
File
... • molten material beneath the Earth’s crust. • collects in a magma chamber beneath a volcano, and can then be injected into cracks in rocks or issue out of volcanoes in eruptions. • temperature of magma ranges between 700 C and ...
... • molten material beneath the Earth’s crust. • collects in a magma chamber beneath a volcano, and can then be injected into cracks in rocks or issue out of volcanoes in eruptions. • temperature of magma ranges between 700 C and ...
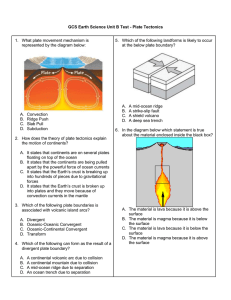
GCS Earth Science Unit B Test
... D. It states that the Earth’s crust is broken up into plates and they move because of convection currents in the mantle 3. Which of the following plate boundaries is associated with volcanic island arcs? A. B. C. D. ...
... D. It states that the Earth’s crust is broken up into plates and they move because of convection currents in the mantle 3. Which of the following plate boundaries is associated with volcanic island arcs? A. B. C. D. ...
Clouard_new_scientis..
... To back up their theory, the team built a model of the strain patterns across the Pacific plate using data from the ocean trenches and GPS readings of movement in the plate. Their model predicted a line where the crust was likely to tear and form volcanic islands and it matched the position of exist ...
... To back up their theory, the team built a model of the strain patterns across the Pacific plate using data from the ocean trenches and GPS readings of movement in the plate. Their model predicted a line where the crust was likely to tear and form volcanic islands and it matched the position of exist ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.