* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth Layers and PT study guide ANSWERS
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
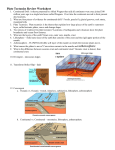
Name: Earth’s Layers and Plate Tectonics Study Guide Part 2 1. What are the three layers of the Earth? List all three and provide descriptions and facts about each layer. Mantle – 67% of Earth’s mass Crust – Extremely thin (less than 1%), outermost layer Core – Made of iron and nickel, central portion 2. What are the five layers of the Earth? List and describe. Lithosphere – Outermost layer made of the crust and rigid upper portion of the mantle, divided into tectonic plates Asthenosphere – “Plastic” layer, solid rock that flows very slowly Mesosphere – Strong lower part of the mantle, extends from the asthenosphere into the core Outer Core – Liquid layer that surrounds the inner core Inner Core – Solid, dense layer of the core 3. What is the basis of three layers? What is the basis of five layers? (In other words, why are they divided that way?) The basis of the three layers in composition (make up of the layers) while the basis of the five layers is physical properties. 4. What are some differences between continental and oceanic crust? Oceanic Crust – dense, primarily made of basalt Continental Crust – less dense, primarily made of granite 5. Why does oceanic crust sit lower than continental crust? The oceanic crust sits lower than continental crust because the density of oceanic crust is greater due to the type of rock (basalt) 6. What are tectonic plates? Tectonic plates are pieces of the lithosphere that consists of the crust and outermost portion of the mantle. These plates form boundaries where geologic events/landforms such as earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain ranges, trenches, and mid-ocean ridges occur. 7. What are the characteristics of the asthenosphere? The asthenosphere flows directly under the lithosphere and is the “plastic” layer that causes the plate motion. 8. How do scientists know about the inside of the Earth? What technology do they use? Scientists use seismic waves to study the various layers of the Earth. 9. Name: Describe Wegener’s theory on Continental drift and the evidence he used to come up with the theory. Wegener believed that all of the continents must have been connected to form one landmass and slowly drifted apart. His evidence included fossils on separate continents and the puzzle pieces that the different continents formed. 10. What did Earth look like 300 million years ago? What was the landmass called? 300 million years ago Earth was one large landmass with all of the continents connected. This landmass is called Pangaea. 11. What is the “Tectonics theory”? “Tectonics theory” states that pieces of the lithosphere are in constant motion on top of the asthenosphere. Additionally, “tectonics theory” is supported by evidence such as sea-floor spreading, trenches, volcanoes, and earthquakes. 12. List the three types of boundaries and explain how crust moves for each. 1. Divergent – The plates move away from one another (divide) 2. Convergent – The plates collide 3. Transform – The plates slide past one another 13.What landforms occur at each boundary? Name the boundary and list the landforms. Divergent – Mid-ocean ridge, rift valley Convergent – Trenches, mountains Transform – Faults 14. What are the three different causes of plate motion? List and describe all three. Convection – Hot rock rises and cool rock sinks causing a current in the mantle. Ridge push – Plate motion due to gravity Slab pull – Plate motion due to the density of the crust during subduction 15.Describe sea-floor spreading and the landforms that are created. Sea-floor spreading occurs at mid-ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is created through volcanic activity. Sea-floor spreading creates new oceanic crust and rift valleys. 16. What is the evidence of sea-floor spreading? Think about the age of rocks. The rock samples that are taken closest to the mid-ocean ridge are the youngest and the rock samples taken farther from the mid-ocean ridge are older. 17.What is subduction and on what type of boundary does subduction occur? Subduction occurs when one plate is forced below another plate. Subduction occurs along convergent boundaries. Name: 18. During subduction what plate will sink? During subduction the plate that has the greatest density will sink. 19. Does subduction occur at a continental-continental convergent boundary? Why not? Subduction does not occur at a large rate at continental-continental boundaries because of the similarities in composition and density. Additionally, the two plates are pushed upwards to form mountains. 20.What landform is created when two continental crusts collide? Mountains 21. In every oceanic convergent boundary (continental or oceanic) there will be specific landforms. List them and describe. Continental – Oceanic boundary: Trenches, volcanoes, and mountains Oceanic – Oceanic boundary: Trenches, island arcs, and volcanoes Continental – Continental: Mountains 22. What are the 3 possible driving forces of plate tectonics? Convection currents, ridge push, slab pull 23.Describe how convection currents in the asthenosphere cause the lithosphere to move. Hot magma becomes less dense and rises, cooler magma becomes more density and sinks (Density and Temperature cause convection currents) 24.Identify different plate boundaries on your seafloor map. Where are some divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries and transform boundaries?