chapter 14 - TeamCFA school
... CORE CASE STUDY: The crucial importance of rare-earth metals. Few people have heard of rare-earth metals and oxides that are crucial to the major technologies that support today’s lifestyles and economies. Without affordable supplies of rare-earth metals, industrialized nations could not develop the ...
... CORE CASE STUDY: The crucial importance of rare-earth metals. Few people have heard of rare-earth metals and oxides that are crucial to the major technologies that support today’s lifestyles and economies. Without affordable supplies of rare-earth metals, industrialized nations could not develop the ...
Salahaddin University College of Science Geology Department
... 39) You finda rock that hasa fine-grained composition. Looking at it carefully, you see what appear to be clam shell fragments in it.This rock is most likely: A. Intrusive igneous B. Extrusive igneous C. Sedimentary D. Metamorphic 40) For magma to become lava, it has to: A. Come to the Earth’s surfa ...
... 39) You finda rock that hasa fine-grained composition. Looking at it carefully, you see what appear to be clam shell fragments in it.This rock is most likely: A. Intrusive igneous B. Extrusive igneous C. Sedimentary D. Metamorphic 40) For magma to become lava, it has to: A. Come to the Earth’s surfa ...
Nonrenewable Mineral Resources
... many metals. This is known as the materials revolution. For example, development of silicon and ceramics may replace the need for as much metal. SCIENCE FOCUS: The nanotechnology revolution. Nanotechnology involves the manipulation of atoms and molecules to create materials. The technology is very p ...
... many metals. This is known as the materials revolution. For example, development of silicon and ceramics may replace the need for as much metal. SCIENCE FOCUS: The nanotechnology revolution. Nanotechnology involves the manipulation of atoms and molecules to create materials. The technology is very p ...
File
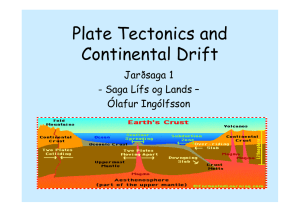
... The plates move on a plastic-like layer of the mantle, an area called the asthenosphere. o The rigid plates of the lithosphere float and move around on the asthenosphere like rafts. When plates move, they can interact in several ways. Movement along any plate boundary means that changes must happen ...
... The plates move on a plastic-like layer of the mantle, an area called the asthenosphere. o The rigid plates of the lithosphere float and move around on the asthenosphere like rafts. When plates move, they can interact in several ways. Movement along any plate boundary means that changes must happen ...
chapter15earthquakes..
... 18: The Elastic Rebound Theory states that earthquakes are caused by (c) the snapping back of rocks when they break under great forces. 19: As seismic waves pass from the crust to the mantle, they (b) speed up. 20: Which of the following would an earthquake affect the least? (a) a building in the sh ...
... 18: The Elastic Rebound Theory states that earthquakes are caused by (c) the snapping back of rocks when they break under great forces. 19: As seismic waves pass from the crust to the mantle, they (b) speed up. 20: Which of the following would an earthquake affect the least? (a) a building in the sh ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... 4. Is the Outer Core a liquid or a solid? 5. The Earth Bowl graham cracker or Rice Krispies layer represents the Earth’s ________, which is 20 ______ deep. 6. Although the Earth Bowl is made of cool gelatin, the center of the earth is actually extremely ...
... 4. Is the Outer Core a liquid or a solid? 5. The Earth Bowl graham cracker or Rice Krispies layer represents the Earth’s ________, which is 20 ______ deep. 6. Although the Earth Bowl is made of cool gelatin, the center of the earth is actually extremely ...
Plates move apart.
... as the African Plate splits apart. This huge valley is thousands of kilometers long and as much as 1800 meters (5900 ft) deep. ...
... as the African Plate splits apart. This huge valley is thousands of kilometers long and as much as 1800 meters (5900 ft) deep. ...
Geochronology and provenance analysis of basement and clastic
... continental margin by a deformed suture zone (the Pujilf fault zone). Mafic basement rocks (Pallatanga Unit) yield oceanic plateau geochemical signatures and probably forrn part of the Caribbean Oceanic Plateau, implying a late Cretaceous age (Spikings et al., 2001; Kerr et al., 2002). The Pallatang ...
... continental margin by a deformed suture zone (the Pujilf fault zone). Mafic basement rocks (Pallatanga Unit) yield oceanic plateau geochemical signatures and probably forrn part of the Caribbean Oceanic Plateau, implying a late Cretaceous age (Spikings et al., 2001; Kerr et al., 2002). The Pallatang ...
3.2 Origins of Biodiversity - Amazing World of Science with Mr. Green
... Evolution is the cumulative, gradual change in the genetic characteristics of successive generations of a species or race of an organism, ultimately giving rise to species or races different from the common ...
... Evolution is the cumulative, gradual change in the genetic characteristics of successive generations of a species or race of an organism, ultimately giving rise to species or races different from the common ...
Origin of the Universe
... 11. Currently made of N2 (78%), O2 (21%), and Others (Ar, CO2, etc.) 12. Source materials include water from comets, vapor from volcanoes, and chemical weathering of rocks 13. Is greatly influenced by the photosynthesis of plants 14. Originally one homogeneous mass of hot rock and metal 15. Original ...
... 11. Currently made of N2 (78%), O2 (21%), and Others (Ar, CO2, etc.) 12. Source materials include water from comets, vapor from volcanoes, and chemical weathering of rocks 13. Is greatly influenced by the photosynthesis of plants 14. Originally one homogeneous mass of hot rock and metal 15. Original ...
1-1 PowerPoint - West Branch Schools
... observations (because of extreme temperature conditions) they rely on indirect methods of observations. • FYI: The deepest level reached was at a gold mine in South Africa (Depth of 3.8km) You would need to travel 1,600 times that depth to reach the center of the Earth, or approximately 6,000km. ...
... observations (because of extreme temperature conditions) they rely on indirect methods of observations. • FYI: The deepest level reached was at a gold mine in South Africa (Depth of 3.8km) You would need to travel 1,600 times that depth to reach the center of the Earth, or approximately 6,000km. ...
AQA A Revision Guide – The Restless Earth
... temperature. The newly molten rock is lighter that that which surrounds it, so it will rise towards the surface and cause volcanoes on the Earth's surface. The continental crust is crumpled by the collision of the two plates creating Fold Mountains. Constructive (Tensional) Plate Boundary (volcanoes ...
... temperature. The newly molten rock is lighter that that which surrounds it, so it will rise towards the surface and cause volcanoes on the Earth's surface. The continental crust is crumpled by the collision of the two plates creating Fold Mountains. Constructive (Tensional) Plate Boundary (volcanoes ...
Student Study Guide
... There are …………….main plates or sections of the earth’s crust (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 6 ...
... There are …………….main plates or sections of the earth’s crust (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 6 ...
SGES 1302 Lecture14
... Once partial melting produces magma, the magma rises towards the Earth surface due to its bouyancy (less dense than the surrounding rocks). A magma’s ability to rise is large controlled by its fluidity (viscosity), which is governed by its temperature and composition. Increasing temperature decrease ...
... Once partial melting produces magma, the magma rises towards the Earth surface due to its bouyancy (less dense than the surrounding rocks). A magma’s ability to rise is large controlled by its fluidity (viscosity), which is governed by its temperature and composition. Increasing temperature decrease ...
OCEAN BASIN FLOOR - ES-Emerald(2010
... SEAMOUNTS are isolated volcanic peaks which may rise hundreds of meters above the surrounding topography. ...
... SEAMOUNTS are isolated volcanic peaks which may rise hundreds of meters above the surrounding topography. ...
5-Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... of plant and animal fossils found on the matching coastlines of South America and Africa, which are now separated by the Atlantic Ocean. ...
... of plant and animal fossils found on the matching coastlines of South America and Africa, which are now separated by the Atlantic Ocean. ...
Layers of Earth
... How we know about the Earth’s structure • No one has been to the center of the Earth • We use information gathered from seismic waves (produced by earthquakes) to learn about the core of the Earth P-Wave shadow zone From the lack of S waves (which can’t pass through liquids) and a great slowing of ...
... How we know about the Earth’s structure • No one has been to the center of the Earth • We use information gathered from seismic waves (produced by earthquakes) to learn about the core of the Earth P-Wave shadow zone From the lack of S waves (which can’t pass through liquids) and a great slowing of ...
Rocks - luckeyscience
... • Rock formed by rock fragments that are cemented together; sometimes visible large fragments, sometimes small, fine ...
... • Rock formed by rock fragments that are cemented together; sometimes visible large fragments, sometimes small, fine ...
how the rock was formed
... Example: gneiss formed from rearrangement of minerals in granite into ...
... Example: gneiss formed from rearrangement of minerals in granite into ...
QR-6 Earthquakes and the Earth`s Interior Answer each of the
... 7. List the major differences between P,S, and surface waves. 8. Which types of seismic waves tend to cause the greatest destruction to buildings? 9. Briefly describe the triangulation method used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake. 10. Describe the differences between the Modified Mercalli ...
... 7. List the major differences between P,S, and surface waves. 8. Which types of seismic waves tend to cause the greatest destruction to buildings? 9. Briefly describe the triangulation method used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake. 10. Describe the differences between the Modified Mercalli ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.