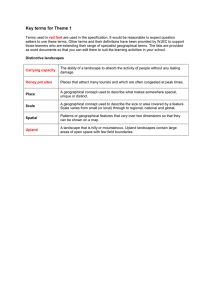
Key terms - Component 1 Word Document | GCSE
... Places that attract many tourists and which are often congested at peak times. ...
... Places that attract many tourists and which are often congested at peak times. ...
plate tectonics - Canvas by Instructure
... • The lithosphere is thin below mid-ocean ridges and thick below continents. • Earth’s tectonic plates are large pieces of the lithosphere that fit together like the pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle. • The layer of Earth below the lithosphere, called the asthenosphere, is so hot that it behaves li ...
... • The lithosphere is thin below mid-ocean ridges and thick below continents. • Earth’s tectonic plates are large pieces of the lithosphere that fit together like the pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle. • The layer of Earth below the lithosphere, called the asthenosphere, is so hot that it behaves li ...
Invitation and - FSU GK-12 Contact Information
... 2. How can rocks be moving like butter in the mantle? They are molten because they are under extreme heat and pressure. 3. What would happen to those mantle rocks if they made it to the much cooler surface of the earth? They would harden and crystallize to form the rocks we are familiar with. 4. So ...
... 2. How can rocks be moving like butter in the mantle? They are molten because they are under extreme heat and pressure. 3. What would happen to those mantle rocks if they made it to the much cooler surface of the earth? They would harden and crystallize to form the rocks we are familiar with. 4. So ...
Earth as a System
... beneath the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it – about 200 km thick ...
... beneath the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it – about 200 km thick ...
Chapter 14 Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources
... Tectonic plates have rearranged the earth’s continents and ocean basins over millions of years like pieces of a gigantic jigsaw puzzle. The plates have three types of boundaries. Natural hazards such as earthquakes and volcanoes are likely to be found at plate boundaries. ...
... Tectonic plates have rearranged the earth’s continents and ocean basins over millions of years like pieces of a gigantic jigsaw puzzle. The plates have three types of boundaries. Natural hazards such as earthquakes and volcanoes are likely to be found at plate boundaries. ...
1st Sem (unit I)
... chemistry of the nickel iron core of bodies having a similar composition to that of the earth. 2. Natural sources a. Vulcanicity: Some geologists on the basis of upwelling and spread of hot and liquid lava on the earth‟s surface during volcanic eruptions believe that there is at least a layer below ...
... chemistry of the nickel iron core of bodies having a similar composition to that of the earth. 2. Natural sources a. Vulcanicity: Some geologists on the basis of upwelling and spread of hot and liquid lava on the earth‟s surface during volcanic eruptions believe that there is at least a layer below ...
How are rocks formed?
... 6. Goes through the process of heat and pressure 7. Goes through the process of compaction and cementation 8. Consist of Intrusive and extrusive rocks 9. Can change into other rocks, can be foliated and go through chemical changes • 10. Can go through the process weathering and erosion ...
... 6. Goes through the process of heat and pressure 7. Goes through the process of compaction and cementation 8. Consist of Intrusive and extrusive rocks 9. Can change into other rocks, can be foliated and go through chemical changes • 10. Can go through the process weathering and erosion ...
Ch. 7.2 Volcanic Eruptions
... Only a few hundred meters high at most; very steep sides. Result from explosive eruptions of solid fragments. ...
... Only a few hundred meters high at most; very steep sides. Result from explosive eruptions of solid fragments. ...
Determining the Age of Rocks
... Continental Drift Theory All continents were once joined together in a single landmass (supercontinent) called Pangea Fossil evidence supports the Continental Drift Theory. Fossils from a fernlike plant Glossopteris have been found in Africa, South America, Australia, and Antarctica. The seeds ...
... Continental Drift Theory All continents were once joined together in a single landmass (supercontinent) called Pangea Fossil evidence supports the Continental Drift Theory. Fossils from a fernlike plant Glossopteris have been found in Africa, South America, Australia, and Antarctica. The seeds ...
Andean margin
... • Low-angle subduction zones, great distance from trench to active arc. • Magmatic events produce large composite batholiths, with superunits and units which individually show mafic to acid (primitive to mature) compositional trends. • Very large volumes of magma are emplaced into the crust, and can ...
... • Low-angle subduction zones, great distance from trench to active arc. • Magmatic events produce large composite batholiths, with superunits and units which individually show mafic to acid (primitive to mature) compositional trends. • Very large volumes of magma are emplaced into the crust, and can ...
Determining the Age of Rocks
... Continental Drift Theory All continents were once joined together in a single landmass (supercontinent) called Pangea Fossil evidence supports the Continental Drift Theory. Fossils from a fernlike plant Glossopteris have been found in Africa, South America, Australia, and Antarctica. The seeds ...
... Continental Drift Theory All continents were once joined together in a single landmass (supercontinent) called Pangea Fossil evidence supports the Continental Drift Theory. Fossils from a fernlike plant Glossopteris have been found in Africa, South America, Australia, and Antarctica. The seeds ...
Document
... 14. What is found at the boundaries of a terrane? _______________________________________________________________ 15. Describe the magnetic properties of a terrane. _______________________________________________________________ 16. What happens when a tectonic plate carrying a terrane subducts unde ...
... 14. What is found at the boundaries of a terrane? _______________________________________________________________ 15. Describe the magnetic properties of a terrane. _______________________________________________________________ 16. What happens when a tectonic plate carrying a terrane subducts unde ...
DID YOU KNOW? www.geolsoc.org.uk/volcanoes
... move away from each other or collide. At divergent plate boundaries, oceanic plates move away cools to form new crust. That means most volcanic activity occurs under the sea. Where there is a lot of activity from each other and hot magma rises and, volcanic material can build up above sea level, for ...
... move away from each other or collide. At divergent plate boundaries, oceanic plates move away cools to form new crust. That means most volcanic activity occurs under the sea. Where there is a lot of activity from each other and hot magma rises and, volcanic material can build up above sea level, for ...
What Erupts from a Volcano?
... • Subduction Produces Magma As descending oceanic crust scrapes past the continental crust, the temperature and pressure increase. ...
... • Subduction Produces Magma As descending oceanic crust scrapes past the continental crust, the temperature and pressure increase. ...
Plate Tectonic Theory
... As the cold air flows over the warm lake water, the warm water heats the air's bottom layer as lake moisture evaporates into the cold air. Since warm air is lighter or less dense than cold air, the heated air rises and begins to cool. As the air cools, the moisture that evaporated into it condenses ...
... As the cold air flows over the warm lake water, the warm water heats the air's bottom layer as lake moisture evaporates into the cold air. Since warm air is lighter or less dense than cold air, the heated air rises and begins to cool. As the air cools, the moisture that evaporated into it condenses ...
TECTONIC PLATES
... help locate tectonic plate boundaries. Earthquakes are particularly useful in this way. When tectonic plates push against each other at convergent boundaries or slide against each other at transform boundaries, pressure builds. Eventually, enough pressure builds up and the plates suddenly slip. This ...
... help locate tectonic plate boundaries. Earthquakes are particularly useful in this way. When tectonic plates push against each other at convergent boundaries or slide against each other at transform boundaries, pressure builds. Eventually, enough pressure builds up and the plates suddenly slip. This ...
Plate Tectonics study guide
... 10. This is a picture of a Convergent boundary. 11. Volcanoes occur here because a more dense plate is meeting up with a less dense plate. 12. The oceanic crust is denser than the continental crust. That is why the oceanic crust sub ducts under the continental crust. Fill in the blanks 13. Two conti ...
... 10. This is a picture of a Convergent boundary. 11. Volcanoes occur here because a more dense plate is meeting up with a less dense plate. 12. The oceanic crust is denser than the continental crust. That is why the oceanic crust sub ducts under the continental crust. Fill in the blanks 13. Two conti ...
Name - Cobb Learning
... a. Wash your hands or use hand sanitizer. b. Cover your work area with a square of wax paper or foil. c. Your teacher will add icing for you to use to represent the asthenosphere. Spread the asthenosphere about .5 cm thick on the wax paper. 2. Model 1: Divergent Plate Boundaries, Oceanic/Oceanic a. ...
... a. Wash your hands or use hand sanitizer. b. Cover your work area with a square of wax paper or foil. c. Your teacher will add icing for you to use to represent the asthenosphere. Spread the asthenosphere about .5 cm thick on the wax paper. 2. Model 1: Divergent Plate Boundaries, Oceanic/Oceanic a. ...
Key to Cornell notes for Understanding Rock Rock A mixture of
... A sill forms when magma goes between the rock layers Laccoliths form when enough magma flows between the rocks layers, they are pushed up. A dike forms when magma flows in cracks that cut through rock layers A pluton is balloon shaped intrusions Batholiths form when many plutons converge into one im ...
... A sill forms when magma goes between the rock layers Laccoliths form when enough magma flows between the rocks layers, they are pushed up. A dike forms when magma flows in cracks that cut through rock layers A pluton is balloon shaped intrusions Batholiths form when many plutons converge into one im ...
e-Science Teachers Pack - Faculty of Sciences
... Learning outcomes: The continents are situated upon an unstable, dynamic and always moving crust; this movement lead to the formation and destruction of the Pangea and Gondwana supercontinents The isotopes in zircon can be used as fingerprints to past geological processes; highlighting what the ...
... Learning outcomes: The continents are situated upon an unstable, dynamic and always moving crust; this movement lead to the formation and destruction of the Pangea and Gondwana supercontinents The isotopes in zircon can be used as fingerprints to past geological processes; highlighting what the ...
Plate Tectonics
... He was a German geophysicist remembered most for his theory of continental drift. His theory stated continents are slowly drifting around the Earth and was not accepted at the time. ...
... He was a German geophysicist remembered most for his theory of continental drift. His theory stated continents are slowly drifting around the Earth and was not accepted at the time. ...
Sample
... backgrounds that range widely in terms of their levels of exposure to geology. Many students have not had prior geology courses and therefore, have little knowledge of the processes that form resources; many others have had courses in physical geology that focused on Earth’s surface processes with l ...
... backgrounds that range widely in terms of their levels of exposure to geology. Many students have not had prior geology courses and therefore, have little knowledge of the processes that form resources; many others have had courses in physical geology that focused on Earth’s surface processes with l ...
Earth`s Layers Online Activity http://homepage.mac.com/cohora/ext
... 8. The Inner core is under so much pressure it does not move like a liquid, it Write the temperature of the center of the Earth. 9. A scientist who studies rocks is called a ____________________________________. What does a Geomorphologist study? ...
... 8. The Inner core is under so much pressure it does not move like a liquid, it Write the temperature of the center of the Earth. 9. A scientist who studies rocks is called a ____________________________________. What does a Geomorphologist study? ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.























