Rocks and Culture
... • Igneous rocks are: “plutonic” or “volcanic” based on grain size. In plutonic rocks, all grains are in the visible size range. In volcanics the smallest grains cannot be seen without magnification. The rock on the right had to be magnified for you to be able to see the small grains. ...
... • Igneous rocks are: “plutonic” or “volcanic” based on grain size. In plutonic rocks, all grains are in the visible size range. In volcanics the smallest grains cannot be seen without magnification. The rock on the right had to be magnified for you to be able to see the small grains. ...
Chapter 5
... general shape and structure A mountain system is a group of adjacent mountain ranges A mountain belt is a group of mountain systems ...
... general shape and structure A mountain system is a group of adjacent mountain ranges A mountain belt is a group of mountain systems ...
Sedimentary rock
... • Oceanic ridges are continuous elevated zones on the floor of all major ocean basins. The rifts at the crest of ridges represent divergent plate boundaries. ...
... • Oceanic ridges are continuous elevated zones on the floor of all major ocean basins. The rifts at the crest of ridges represent divergent plate boundaries. ...
Tectonic Framework of the Willamette Valley (Josh Troyer)
... Near the end of the Cretaceous period (~66 Ma), a volcanic island arc formed over a hot spot on the Kula and Juan de Fuca (Farallon) plates. As subduction continued, this island arc collided with the North American plate and was accreted to the continental margin. The basalts of the Siletz River Vo ...
... Near the end of the Cretaceous period (~66 Ma), a volcanic island arc formed over a hot spot on the Kula and Juan de Fuca (Farallon) plates. As subduction continued, this island arc collided with the North American plate and was accreted to the continental margin. The basalts of the Siletz River Vo ...
UNIT 10 Plate Tectonics Study Guide
... - Oceanic divergent zones or spreading centers are located within ocean basins and involve only the oceanic crust. - Found along this zone is the Earth’s longest mountain chain (found mostly underwater). -Oceanic divergent zones (or the mid-oceanic mountains found on the ocean seafloor) are probably ...
... - Oceanic divergent zones or spreading centers are located within ocean basins and involve only the oceanic crust. - Found along this zone is the Earth’s longest mountain chain (found mostly underwater). -Oceanic divergent zones (or the mid-oceanic mountains found on the ocean seafloor) are probably ...
Study Guide Rocks and Minerals Vocabulary: Cleavage rocks
... What are the characteristics of sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks? How can you identify a type of rock using these characteristics? ...
... What are the characteristics of sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks? How can you identify a type of rock using these characteristics? ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Name
... 10. T or F: Volcanoes and earthquakes form in similar areas. They are often found on the same plate boundaries. True False Possible essay/extended response questions: Explain the process of convection currents in the mantle and predict what would happen if Earth’s core cooled down in the future. ...
... 10. T or F: Volcanoes and earthquakes form in similar areas. They are often found on the same plate boundaries. True False Possible essay/extended response questions: Explain the process of convection currents in the mantle and predict what would happen if Earth’s core cooled down in the future. ...
Evolution and the History of Life
... when 90 percent of marine organisms and 75 percent of terrestrial organisms became extinct. • Mesozoic Era – 248 mya to 65 mya –dominated by dinosaurs and other reptiles, and birds until their mass extinction when the era ended. Age of the Reptiles. • Cenozoic Era – 65 mya to now – dominated by mamm ...
... when 90 percent of marine organisms and 75 percent of terrestrial organisms became extinct. • Mesozoic Era – 248 mya to 65 mya –dominated by dinosaurs and other reptiles, and birds until their mass extinction when the era ended. Age of the Reptiles. • Cenozoic Era – 65 mya to now – dominated by mamm ...
Rock Star 101
... •Grains you can see (speckled) •Crystalline (sparkly fresh surfaces) •Hard •No layers, no holes ...
... •Grains you can see (speckled) •Crystalline (sparkly fresh surfaces) •Hard •No layers, no holes ...
volcanoes 101 - AlmaMiddleSchoolScience
... leaving a trial of volcanoes in a plate would be Yellowstone or the Hawaiian islands. Hawaii sits on the Pacific Plate which is moving to the northwest. There is a hot spot on the earth’s core causing magma to rise. The plume is located in the mantle, and is rising. The plate moves over the hot spot ...
... leaving a trial of volcanoes in a plate would be Yellowstone or the Hawaiian islands. Hawaii sits on the Pacific Plate which is moving to the northwest. There is a hot spot on the earth’s core causing magma to rise. The plume is located in the mantle, and is rising. The plate moves over the hot spot ...
Tectonic Movement – Plates and Faults
... This is caused by the Earth's plates converging, diverging or transversing against one another. This causes the crust of the Earth to buckle and strain, generating incredible amounts of pressure that build up as time progresses and may conclude in the release of this energy. The crust is divided int ...
... This is caused by the Earth's plates converging, diverging or transversing against one another. This causes the crust of the Earth to buckle and strain, generating incredible amounts of pressure that build up as time progresses and may conclude in the release of this energy. The crust is divided int ...
Quiz 5 - Brooklyn College
... 12. A sill is a ______________ intrusion, whereas a dike is a ______________ intrusion. o ...
... 12. A sill is a ______________ intrusion, whereas a dike is a ______________ intrusion. o ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle. ...
... by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle. ...
Plate Boundaries
... India used to be an island, but about 15 million years ago it crashed into Asia (see map). As continental crust was pushing against continental crust the Himalayan mountain belt was pushed up. “Mountains” were also pushed down into the mantle as the normally 35 km thick crust is approximately ...
... India used to be an island, but about 15 million years ago it crashed into Asia (see map). As continental crust was pushing against continental crust the Himalayan mountain belt was pushed up. “Mountains” were also pushed down into the mantle as the normally 35 km thick crust is approximately ...
UNIT 10 Plate Tectonics Study Guide
... - Oceanic divergent zones or spreading centers are located within ocean basins and involve only the oceanic crust. - Found along this zone is the Earth’s longest mountain chain (found mostly underwater). -Oceanic divergent zones (or the mid-oceanic mountains found on the ocean seafloor) are probably ...
... - Oceanic divergent zones or spreading centers are located within ocean basins and involve only the oceanic crust. - Found along this zone is the Earth’s longest mountain chain (found mostly underwater). -Oceanic divergent zones (or the mid-oceanic mountains found on the ocean seafloor) are probably ...
Y8GeU4B Earthquake1 PPwk15
... but "great" earthquakes (those of magnitude 8.0 or greater). It is estimated that there several million temblors, most undetectable, happen every day. ...
... but "great" earthquakes (those of magnitude 8.0 or greater). It is estimated that there several million temblors, most undetectable, happen every day. ...
Building a Theory
... • Theory that is held with a very high degree of confidence and is comprehensive in scope. • Paradigm Shift – The replacement of an existing paradigm with a better paradigm. ...
... • Theory that is held with a very high degree of confidence and is comprehensive in scope. • Paradigm Shift – The replacement of an existing paradigm with a better paradigm. ...
+ t 1/2
... has been addressed by DePaolo using a combination of zircon crystallization ages and Nd model mantle extraction ages. His results indicate that 80% of the Earth's continental crust was formed by 1.6 Ga. Many younger crustal rocks must thus represent reworked older crust. ...
... has been addressed by DePaolo using a combination of zircon crystallization ages and Nd model mantle extraction ages. His results indicate that 80% of the Earth's continental crust was formed by 1.6 Ga. Many younger crustal rocks must thus represent reworked older crust. ...
Melting and Crystallisation
... different grain sizes are, as usual, due to the different rates of cooling which depends on the different situations under which the rocks cooled. Basalt is the most common of these mafic rocks. It is extruded from volcanoes and from long fissures (slits) at Earth’s surface. Basalt is produced at bo ...
... different grain sizes are, as usual, due to the different rates of cooling which depends on the different situations under which the rocks cooled. Basalt is the most common of these mafic rocks. It is extruded from volcanoes and from long fissures (slits) at Earth’s surface. Basalt is produced at bo ...
Fracking MEL - Temple University Sites
... pieces are tectonic plates, and the edges of the plates are called the plate boundaries. The plate boundaries are made up of many faults, and most of the earthquakes around the world occur on these faults. The edges of the plates are rough and get stuck, but the rest of the plate keeps moving. Becau ...
... pieces are tectonic plates, and the edges of the plates are called the plate boundaries. The plate boundaries are made up of many faults, and most of the earthquakes around the world occur on these faults. The edges of the plates are rough and get stuck, but the rest of the plate keeps moving. Becau ...
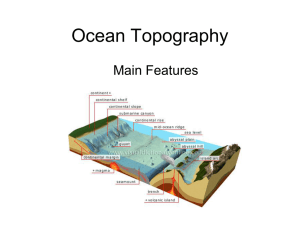
Ocean Topography
... • A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater mountain range, typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
... • A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater mountain range, typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. It is usually an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading. ...
How Earth*s Plates Move
... hundreds of feet over millions of years as the plates separated. This formed the Great Rift Valley. ...
... hundreds of feet over millions of years as the plates separated. This formed the Great Rift Valley. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.