The Geologic Time Scale
... Early Earth was probably uniform After heating, molten iron and nickel sank to form the core Lighter minerals flowed up to form mantle and crust ...
... Early Earth was probably uniform After heating, molten iron and nickel sank to form the core Lighter minerals flowed up to form mantle and crust ...
Seafloor Spreading
... • These plate boundaries are the sites of most earthquakes, volcanoes, and young mountain ranges. • Compared to continental crust, ocean crust is thinner and denser. New ocean crust continues to form at mid-ocean ridges. 2.1m Many processes of the rock cycle are consequences of plate dynamics. These ...
... • These plate boundaries are the sites of most earthquakes, volcanoes, and young mountain ranges. • Compared to continental crust, ocean crust is thinner and denser. New ocean crust continues to form at mid-ocean ridges. 2.1m Many processes of the rock cycle are consequences of plate dynamics. These ...
Internal Structure of the Earth File
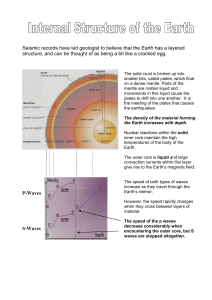
... smaller bits, called plates, which float on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. ...
... smaller bits, called plates, which float on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. ...
ag earth science - Sonoma Valley High School
... Who created the theory of continental drift? What are two pieces of evidence that helped to prove the theory of continental drift? What was the super-continent called in the continental drift theory? What evidence was used to form the plate tectonics theory? How does Continental Drift and Plate Tect ...
... Who created the theory of continental drift? What are two pieces of evidence that helped to prove the theory of continental drift? What was the super-continent called in the continental drift theory? What evidence was used to form the plate tectonics theory? How does Continental Drift and Plate Tect ...
plate tectonics webquest3
... 3. Use the map (click above) to view where earth's major mountain chains are located. 4. Label these areas with green carrots in a chain (^^^^^^) on your world map. EARTHQUAKES 5. Use the map (click link above) to view where on earth earthquakes happen most often. 6. Color these areas on your world ...
... 3. Use the map (click above) to view where earth's major mountain chains are located. 4. Label these areas with green carrots in a chain (^^^^^^) on your world map. EARTHQUAKES 5. Use the map (click link above) to view where on earth earthquakes happen most often. 6. Color these areas on your world ...
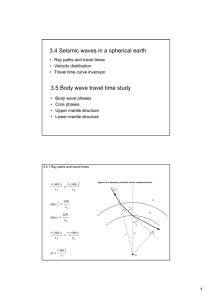
3.4 Seismic waves in a spherical earth 3.5 Body wave travel time study
... Upper mantle structure Lower mantle structure ...
... Upper mantle structure Lower mantle structure ...
Document
... released radiates in all directions from its source, the focus (or hypocenter) Energy propagates in the form of seismic (elastic) waves Sensitive instruments (seismometers) around the world record the event ...
... released radiates in all directions from its source, the focus (or hypocenter) Energy propagates in the form of seismic (elastic) waves Sensitive instruments (seismometers) around the world record the event ...
Earth`s+Layers+Worksheet+PowerPoint
... Outer Core Lower pressure allows the outer core to remain liquid & move around inner core causes Earth’s magnetic field Made up of metals Temperature and pressure are lower in the ...
... Outer Core Lower pressure allows the outer core to remain liquid & move around inner core causes Earth’s magnetic field Made up of metals Temperature and pressure are lower in the ...
Chapter 20 – Mountain Building
... • Oceanic-Continental Convergent boundary: - Oceanic crust is subducted under continental crust. - Subducted oceanic crust melts. - Magma rises upward forming a volcanic mountain range on the continental crust. Example: Andes Mountains, South America ...
... • Oceanic-Continental Convergent boundary: - Oceanic crust is subducted under continental crust. - Subducted oceanic crust melts. - Magma rises upward forming a volcanic mountain range on the continental crust. Example: Andes Mountains, South America ...
SCIENCE TEST1 (VWILLIAMSSCIENCETEST1)
... 22. Which is a device that is used to gather information about formations on the ocean bottom? A. sonar B. radar C. MRI D. laser 23. Which landform results when one of Earth's plates slides past another? A. faults B. plateaus C. mountains D. deltas 24. Volcanoes are formed from A. hot gases pushing ...
... 22. Which is a device that is used to gather information about formations on the ocean bottom? A. sonar B. radar C. MRI D. laser 23. Which landform results when one of Earth's plates slides past another? A. faults B. plateaus C. mountains D. deltas 24. Volcanoes are formed from A. hot gases pushing ...
Tectonics and Sea Floor Spreading
... The theory of Plate Tectonics explains most observable geological features on the surface of the Earth as the result of a major, unified pattern of large scale horizontal motions, involving the shallowest portions of the planet. In turns, motions of the “plates” thus defined at the surface of the Ea ...
... The theory of Plate Tectonics explains most observable geological features on the surface of the Earth as the result of a major, unified pattern of large scale horizontal motions, involving the shallowest portions of the planet. In turns, motions of the “plates” thus defined at the surface of the Ea ...
What Rock Is It?
... ocks are made up of one or more minerals, such as quartz, feldspar, calcite, and gypsum. Depending on how they formed, rocks are classified into three families: volcanic, or igneous rocks; layered, or sedimentary rocks; and changed, or metamorphic rocks. Volcanic rock forms from hot lava that flow ...
... ocks are made up of one or more minerals, such as quartz, feldspar, calcite, and gypsum. Depending on how they formed, rocks are classified into three families: volcanic, or igneous rocks; layered, or sedimentary rocks; and changed, or metamorphic rocks. Volcanic rock forms from hot lava that flow ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
HNRS 228 Astrobiology Chap.4 Geology Bennett et al.
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
HNRS 228 Astrobiology Chap.4 Geology Bennett et al.
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
... Plate tectonics, or movement of the plates, is driven by convection within the asthenosphere Molten material wells up at oceanic rifts, producing seafloor spreading, and is returned to the asthenosphere in subduction zones As one end of a plate is subducted back into the asthenosphere, it helps ...
049555507X_131304 - ASB
... The Three Types of Plate Boundaries Convergent Boundaries Convergent boundaries are places where two plates collide There are three types of convergent boundaries. An oceanic-oceanic boundary is where two oceanic plates collide, one ocean plate will subduct beneath the margin of the other plate ...
... The Three Types of Plate Boundaries Convergent Boundaries Convergent boundaries are places where two plates collide There are three types of convergent boundaries. An oceanic-oceanic boundary is where two oceanic plates collide, one ocean plate will subduct beneath the margin of the other plate ...
High School Science Proficiency Review #3 Earth Science
... E.12.C.2 Students understand the concept of plate tectonics including the evidence that supports it (structural, geophysical and ...
... E.12.C.2 Students understand the concept of plate tectonics including the evidence that supports it (structural, geophysical and ...
docx: Earth`s Interior Pre Assessment
... c. Both a. and b. are true. d. Neither a. nor b. are true. 27. Which element makes up most of the Earth’s inner and outer cores? a. Silicon b. Oxygen c. Nitrogen d. Iron 28. The Northern Lights are caused when ______________________________. a. Greenhouse gases build up in the atmosphere and give of ...
... c. Both a. and b. are true. d. Neither a. nor b. are true. 27. Which element makes up most of the Earth’s inner and outer cores? a. Silicon b. Oxygen c. Nitrogen d. Iron 28. The Northern Lights are caused when ______________________________. a. Greenhouse gases build up in the atmosphere and give of ...
Seafloor Spreading
... – Subduction occurs when one of the two converging plates descends beneath the other. – A subduction zone forms when one oceanic plate, which has become denser as a result of cooling, descends below another plate creating a deep-sea trench. – The subducted plate descends into the mantle and melts. – ...
... – Subduction occurs when one of the two converging plates descends beneath the other. – A subduction zone forms when one oceanic plate, which has become denser as a result of cooling, descends below another plate creating a deep-sea trench. – The subducted plate descends into the mantle and melts. – ...
Chapter 8 - SchoolRack
... Lapilli - which means “little stones” in Italian, are pebble like bits of pyroclastic material between 2 and 64mm in diameter Volcanic Ash - consist of particles that are less than 2mm in ...
... Lapilli - which means “little stones” in Italian, are pebble like bits of pyroclastic material between 2 and 64mm in diameter Volcanic Ash - consist of particles that are less than 2mm in ...
ES Chapter 17
... – Subduction occurs when one of the two converging plates descends beneath the other. – A subduction zone forms when one oceanic plate, which has become denser as a result of cooling, descends below another plate creating a deep-sea trench. – The subducted plate descends into the mantle and melts. – ...
... – Subduction occurs when one of the two converging plates descends beneath the other. – A subduction zone forms when one oceanic plate, which has become denser as a result of cooling, descends below another plate creating a deep-sea trench. – The subducted plate descends into the mantle and melts. – ...
Exemplar Response
... Any type of rock can be made into an igneous rock if it melts. Igneous rocks come from magma, deep within Earth’s surface that has cooled. If it cools very quickly it might make pumice. If it cools very slowly, rocks with visible minerals in them. Metamorphic rocks can form from all three types of r ...
... Any type of rock can be made into an igneous rock if it melts. Igneous rocks come from magma, deep within Earth’s surface that has cooled. If it cools very quickly it might make pumice. If it cools very slowly, rocks with visible minerals in them. Metamorphic rocks can form from all three types of r ...
Mantle downwelling Modes of mantle convection
... Physics and chemistry of the Earth’s interior – Mantle downwelling ...
... Physics and chemistry of the Earth’s interior – Mantle downwelling ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.