Sequence of events in an Earthquake
... Days or weeks may occur before a major earthquake or earthquakes occur. There are often many little shocks, or tremors, that occur called foreshocks. They are the result of pressure building the tectonic plates. ...
... Days or weeks may occur before a major earthquake or earthquakes occur. There are often many little shocks, or tremors, that occur called foreshocks. They are the result of pressure building the tectonic plates. ...
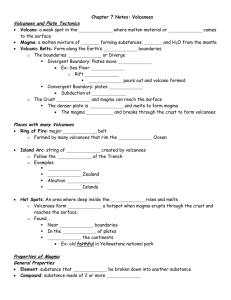
Chapter 7 Notes: Volcanoes Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano Magma
... Magma: a molten mixture of ________ forming substances, ________ and H2O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s _______________ boundaries o The boundaries _______________ or Diverge Divergent Boundary: Plates move _______________ Ex: Sea Floor _______________ o Rift ____________ ...
... Magma: a molten mixture of ________ forming substances, ________ and H2O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s _______________ boundaries o The boundaries _______________ or Diverge Divergent Boundary: Plates move _______________ Ex: Sea Floor _______________ o Rift ____________ ...
EGU2017-5486 - CO Meeting Organizer
... of a layer of eclogites 15-20 km thick. These mafic rocks which are denser than mantle peridotites pertain to the crust by their composition. Together with crystalline rocks 14 km thick located above the Moho they form the crystalline crust with the thickness 30-35 km which is typical of many contin ...
... of a layer of eclogites 15-20 km thick. These mafic rocks which are denser than mantle peridotites pertain to the crust by their composition. Together with crystalline rocks 14 km thick located above the Moho they form the crystalline crust with the thickness 30-35 km which is typical of many contin ...
History of Earth Part 2 SG AK
... 1,300 km long and in places tens of kilometers wide, slices through two thirds of the length of California. Along it, the Pacific Plate has been grinding horizontally past the North American Plate for 10 million years, at an average rate of about 5 cm/yr ...
... 1,300 km long and in places tens of kilometers wide, slices through two thirds of the length of California. Along it, the Pacific Plate has been grinding horizontally past the North American Plate for 10 million years, at an average rate of about 5 cm/yr ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics CK12
... • On the map in Figure 1.3, the arrows show the directions that the plates are going. The Atlantic has a midocean ridge, where seafloor spreading is taking place. The Pacific Ocean has many deep sea trenches, where subduction is taking place. What is the future of the Atlantic plate? What is the fut ...
... • On the map in Figure 1.3, the arrows show the directions that the plates are going. The Atlantic has a midocean ridge, where seafloor spreading is taking place. The Pacific Ocean has many deep sea trenches, where subduction is taking place. What is the future of the Atlantic plate? What is the fut ...
Tutorial Problems 1. Where Do Earthquakes Happen? 2. Where do
... Answers to Tutorial Problems 1. Earthquakes occur all the time all over the world, both along plate edges and along faults. Most earthquakes occur along the edge of the oceanic and continental plates. The earth's crust (the outer layer of the planet) is made up of several pieces, called plates. Ear ...
... Answers to Tutorial Problems 1. Earthquakes occur all the time all over the world, both along plate edges and along faults. Most earthquakes occur along the edge of the oceanic and continental plates. The earth's crust (the outer layer of the planet) is made up of several pieces, called plates. Ear ...
Full-Text - Journal of Tethys
... The rocks studied have porphyritic texture and phenocrysts with plagioclase, sanidine, amphibole, biotite and quartz. Based on geochemical data and multi elements pattern, these rocks are medium to high K calc-alkaline suite and show LILE and LREE enriched normalized multi-element patterns, and Nb a ...
... The rocks studied have porphyritic texture and phenocrysts with plagioclase, sanidine, amphibole, biotite and quartz. Based on geochemical data and multi elements pattern, these rocks are medium to high K calc-alkaline suite and show LILE and LREE enriched normalized multi-element patterns, and Nb a ...
Hawaii Hotspot: Annotated Teacher Edition
... Why? The Pacific plate is the largest tectonic plate on the globe. One of its most striking features is the 6,000 km-long Hawaiian-Emperor Seamount chain. We use the ages of volcanic rocks to study the history of the chain, its formation above a hotspot, and motion of the Pacific plate over the last ...
... Why? The Pacific plate is the largest tectonic plate on the globe. One of its most striking features is the 6,000 km-long Hawaiian-Emperor Seamount chain. We use the ages of volcanic rocks to study the history of the chain, its formation above a hotspot, and motion of the Pacific plate over the last ...
Structure of the Earth - South Kingstown High School Home Page
... Continental Drift: All continents were once a part of a single supercontinent and they’ve moved ...
... Continental Drift: All continents were once a part of a single supercontinent and they’ve moved ...
Chapters 9-12 Take-Home Quiz
... a. an isolated area of active volcanism, especially one away from a plate boundary b. an area of intensive earthquake activity c. an area in which subduction is causing partial melting d. a zone of continent-continent collision ...
... a. an isolated area of active volcanism, especially one away from a plate boundary b. an area of intensive earthquake activity c. an area in which subduction is causing partial melting d. a zone of continent-continent collision ...
Astro ch 20
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Earth`s Layers
... Processes that affect Earth’s surface are often a result of what’s going on inside Earth. But what’s inside Earth? This question is very difficult to answer, because geologists are unable to see deep inside Earth. But geologists have found other methods to study the interior of Earth. Geologists hav ...
... Processes that affect Earth’s surface are often a result of what’s going on inside Earth. But what’s inside Earth? This question is very difficult to answer, because geologists are unable to see deep inside Earth. But geologists have found other methods to study the interior of Earth. Geologists hav ...
Primary Middle Phase - Volcano Session Notes
... • Three pairs will be asked at random • As a group we will decide whose description most Volcanologist-like! ...
... • Three pairs will be asked at random • As a group we will decide whose description most Volcanologist-like! ...
D38 Beneath Earth*s Surface
... small pieces of magma and ash into the air. • The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. • Often cinder cones form on the sides of larger volcanoes. ...
... small pieces of magma and ash into the air. • The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. • Often cinder cones form on the sides of larger volcanoes. ...
LP - BioFolio
... Which is the thickest layer of the Earth? A. Inner core B. Outer core C. Mantle D. Crust Which is the thinnest layer of the Earth? A. Inner core B. Outer core C. Mantle D. Crust ...
... Which is the thickest layer of the Earth? A. Inner core B. Outer core C. Mantle D. Crust Which is the thinnest layer of the Earth? A. Inner core B. Outer core C. Mantle D. Crust ...
Microsoft Word - APES Chapter 16 Study Guide
... • Tectonic plates produce mountains. • Tectonic plates produce volcanoes. • Tectonic plates produce ocean trenches. • Tectonic plates are composed of crust and core. • Tectonic plates move on the asthenosphere. 11. Name the boundary where the tectonic plates move apart in opposite directions. 12. Na ...
... • Tectonic plates produce mountains. • Tectonic plates produce volcanoes. • Tectonic plates produce ocean trenches. • Tectonic plates are composed of crust and core. • Tectonic plates move on the asthenosphere. 11. Name the boundary where the tectonic plates move apart in opposite directions. 12. Na ...
When did the Andes mountains form?
... highest mountain chain in the world after the Himalayas already near their present elevation 14 million years ago. Dr Evenstar said: "It seems highly likely that the The Andes have been a mountain chain for much Andes have gone up slowly over at least the last 30 longer than previously thought, new ...
... highest mountain chain in the world after the Himalayas already near their present elevation 14 million years ago. Dr Evenstar said: "It seems highly likely that the The Andes have been a mountain chain for much Andes have gone up slowly over at least the last 30 longer than previously thought, new ...
UNIT 5: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... 3. Magma forms over subduction zones due the release of __________________ from the subducting plate. This lowers the _____________________ _____________________ of the surrounding crustal rock, causing it to melt. 4. The magma that feeds “subduction zone volcanoes” comes from the crust, and is hig ...
... 3. Magma forms over subduction zones due the release of __________________ from the subducting plate. This lowers the _____________________ _____________________ of the surrounding crustal rock, causing it to melt. 4. The magma that feeds “subduction zone volcanoes” comes from the crust, and is hig ...
Chapter 2 - TeacherWeb
... helped determine where ocean basins are located. Tectonic plates move changing the position of the continents. ...
... helped determine where ocean basins are located. Tectonic plates move changing the position of the continents. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... produced along the oceanic ridge system. • Two oceanic plates pull apart • Mantle material and new lavas rise up to fill the gap • Large quantities of basaltic magma are produced ...
... produced along the oceanic ridge system. • Two oceanic plates pull apart • Mantle material and new lavas rise up to fill the gap • Large quantities of basaltic magma are produced ...
3 DYNAMIC SURFACE OF THE EARTH MODULE - 2
... place upwardly. After reaching about 100 kms below the surface that current gets diverged leading to split into the upper part. The molten material penetrates into the split and thus creation of new surface and the draft of the mammoth plate in opposition direction. It happens below the mid-oceanic ...
... place upwardly. After reaching about 100 kms below the surface that current gets diverged leading to split into the upper part. The molten material penetrates into the split and thus creation of new surface and the draft of the mammoth plate in opposition direction. It happens below the mid-oceanic ...
HazardsModuleoutline 86.50KB 2017-03-29 12
... To be able to describe the biological, geological and climatological evidence for the theory of continental drift as proposed by Alfred Wegener. To know and understand what palaeomagnetism is and how it supports the theory of plate tectonics. To be able to explain how the discovery and study of the ...
... To be able to describe the biological, geological and climatological evidence for the theory of continental drift as proposed by Alfred Wegener. To know and understand what palaeomagnetism is and how it supports the theory of plate tectonics. To be able to explain how the discovery and study of the ...
Grade 8 Chapter 2 : Notes
... helped determine where ocean basins are located. Tectonic plates move changing the position of the continents. ...
... helped determine where ocean basins are located. Tectonic plates move changing the position of the continents. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.