chapter2
... The Three Types of Plate Boundaries Convergent Boundaries Convergent boundaries are places where two plates collide There are three types of convergent boundaries. An oceanic-oceanic boundary is where two oceanic plates collide, one ocean plate will subduct beneath the margin of the other plate ...
... The Three Types of Plate Boundaries Convergent Boundaries Convergent boundaries are places where two plates collide There are three types of convergent boundaries. An oceanic-oceanic boundary is where two oceanic plates collide, one ocean plate will subduct beneath the margin of the other plate ...
Constructing the Costa Rica-Nicaragua
... subducting plates changes along the length of the subduction zone. This inclination influences the position of volcanoes, the location of mountains, and the direction in which the mantle underneath the plate moves. Whereas two-dimensional models are limited to one slice of a 3D earth, 3D models allo ...
... subducting plates changes along the length of the subduction zone. This inclination influences the position of volcanoes, the location of mountains, and the direction in which the mantle underneath the plate moves. Whereas two-dimensional models are limited to one slice of a 3D earth, 3D models allo ...
20150511082662
... 20) Magma with [high Silica content, [high Viscosity, and [low temperatures cause volcanoes to have Explosive Eruptions. 21) The Pocket of Magma underneath the Volcano is called _____________ a) pipe b) crater c) magma chamber d) central vent ...
... 20) Magma with [high Silica content, [high Viscosity, and [low temperatures cause volcanoes to have Explosive Eruptions. 21) The Pocket of Magma underneath the Volcano is called _____________ a) pipe b) crater c) magma chamber d) central vent ...
Getting to Know: Where Earthquakes Occur
... earthquakes are shallow, especially those that occur at divergent plate boundaries. However, some earthquakes can occur at extreme depths in Earth’s crust. In fact, some earthquakes occur so far below Earth’s surface that they cannot be detected at the surface. Scientists classify earthquakes by the ...
... earthquakes are shallow, especially those that occur at divergent plate boundaries. However, some earthquakes can occur at extreme depths in Earth’s crust. In fact, some earthquakes occur so far below Earth’s surface that they cannot be detected at the surface. Scientists classify earthquakes by the ...
LAURENTIA j20 Geosynclinal theory < Hall, Dana - e
... Great thicknesses of sediments are typical of continental margins. These and their holding trough that as a unit is destined to be, is being, or was folded orogenically, is called a geosyncline (Figure j20.1). Hans Stille in 1940 called the continentward part of a geosyncline with shallow-water quar ...
... Great thicknesses of sediments are typical of continental margins. These and their holding trough that as a unit is destined to be, is being, or was folded orogenically, is called a geosyncline (Figure j20.1). Hans Stille in 1940 called the continentward part of a geosyncline with shallow-water quar ...
Topic/Objective: ______ _____ Full Name: __________ Class: __
... _Transform boundaries________________ (side by side movement) Effects of Metamorphism on rocks impurities_______ such as _holes___ and _fossils____ are destroyed _pore space___ between grains is lost due to _compression_______ Rock __density_________ increases _Minerals crystals______ are flattened, ...
... _Transform boundaries________________ (side by side movement) Effects of Metamorphism on rocks impurities_______ such as _holes___ and _fossils____ are destroyed _pore space___ between grains is lost due to _compression_______ Rock __density_________ increases _Minerals crystals______ are flattened, ...
Volcanoes, Plutons, and Igneous Rocks Lab – Answer Sheet
... 19a. What is the scale (in km) and contour interval of this map? (Use a ruler to determine how large 10 km is). 19b. What is the highest elevation in feet at the top of Mauna Loa? _________________________ ...
... 19a. What is the scale (in km) and contour interval of this map? (Use a ruler to determine how large 10 km is). 19b. What is the highest elevation in feet at the top of Mauna Loa? _________________________ ...
FREE Sample Here - College Test bank
... A. The mass of a substance per unit volume B. A measure of weight C. The mass of a substance multiplied by its percentage volume of water D. A measure of volume E. The volume occupied by a particular substance in relation to that of water ...
... A. The mass of a substance per unit volume B. A measure of weight C. The mass of a substance multiplied by its percentage volume of water D. A measure of volume E. The volume occupied by a particular substance in relation to that of water ...
FREE Sample Here
... A. The mass of a substance per unit volume B. A measure of weight C. The mass of a substance multiplied by its percentage volume of water D. A measure of volume E. The volume occupied by a particular substance in relation to that of water ...
... A. The mass of a substance per unit volume B. A measure of weight C. The mass of a substance multiplied by its percentage volume of water D. A measure of volume E. The volume occupied by a particular substance in relation to that of water ...
C:\Users\jmhemzac\Desktop\2017 spring\121 final rev S17f.wpd
... (human) perspective of earth events (e.g., time frame for volcanic eruptions) More on the “big picture” – you should be able to discuss: – why do continents and mid-ocean ridges (notably in the Atlantic Ocean) have the shapes that we see? how are these shapes related to the history of plate tectonic ...
... (human) perspective of earth events (e.g., time frame for volcanic eruptions) More on the “big picture” – you should be able to discuss: – why do continents and mid-ocean ridges (notably in the Atlantic Ocean) have the shapes that we see? how are these shapes related to the history of plate tectonic ...
Case History: Asbestos Importance of Rocks and Minerals
... • Depending on the composition of magma • Felsic/granitic: silica-rich, typically related to continental crust, lighter colors, lower density • Intermediate/andesitic: 50:50 composition, commonly associated with convergent plate boundaries along the Pacific rim, eruptive volcanism • Mafic/basaltic: ...
... • Depending on the composition of magma • Felsic/granitic: silica-rich, typically related to continental crust, lighter colors, lower density • Intermediate/andesitic: 50:50 composition, commonly associated with convergent plate boundaries along the Pacific rim, eruptive volcanism • Mafic/basaltic: ...
Name Class___________ Date
... _____2. Which information would probably be least reliable for someone trying to identify a mineral sample? (1) streak (2) color (3) hardness _____3. In which type of rock is the fossil of a fern leaf most likely to be found? (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic ...
... _____2. Which information would probably be least reliable for someone trying to identify a mineral sample? (1) streak (2) color (3) hardness _____3. In which type of rock is the fossil of a fern leaf most likely to be found? (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic ...
Rocks and Landscapes of the Boonah District
... the forest and its transpiration has resulted in higher water pressures in the strata during high rainfall events, allowing the soft weathered rock to fail and move down hill in debris slides and earth flows. This is pronounced on slopes that fall in the same direction as the rock strata, which in t ...
... the forest and its transpiration has resulted in higher water pressures in the strata during high rainfall events, allowing the soft weathered rock to fail and move down hill in debris slides and earth flows. This is pronounced on slopes that fall in the same direction as the rock strata, which in t ...
Slide 1
... The word Volcano is derived from the name of the ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
... The word Volcano is derived from the name of the ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
Volcanoes - Ms. Buzanowski's 8th Grade Class
... Tephra – bits of rock or solidified lava dropping from the air Reservoir – where magma is stored Summit – highest point Vent - opening where lava flows ...
... Tephra – bits of rock or solidified lava dropping from the air Reservoir – where magma is stored Summit – highest point Vent - opening where lava flows ...
acting 101 homework check
... ACTING 101 HOMEWORK CHECK NUMBER THE SIDE OF YOUR ACTING 101 PAPER 1-10. WRITE LETTER OF CORRECT ANSWER ONLY! ...
... ACTING 101 HOMEWORK CHECK NUMBER THE SIDE OF YOUR ACTING 101 PAPER 1-10. WRITE LETTER OF CORRECT ANSWER ONLY! ...
~2.6 MB
... constrain deeper levels of fabric, present evidence for sub-slab trenchparallel flow of mantle material, and for a rapid reorientation of this flow at the northern edge of the Pacific plate. ...
... constrain deeper levels of fabric, present evidence for sub-slab trenchparallel flow of mantle material, and for a rapid reorientation of this flow at the northern edge of the Pacific plate. ...
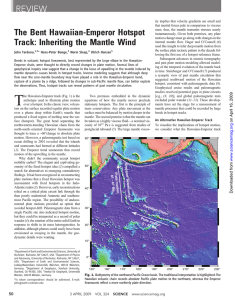
The Bent Hawaiian-Emperor Hotspot Track
... tabular upwelling; the plume source could conceivably move along-strike of the larger upwelling. Lateral heterogeneity in D′′ implies that some regions, such as “cusps” where dense material has been entrained, might serve to anchor the plume source (35). Together, these processes ...
... tabular upwelling; the plume source could conceivably move along-strike of the larger upwelling. Lateral heterogeneity in D′′ implies that some regions, such as “cusps” where dense material has been entrained, might serve to anchor the plume source (35). Together, these processes ...
Volcanoes
... Tephra – bits of rock or solidified lava dropping from the air Reservoir – where magma is stored Summit – highest point Vent - opening where lava flows ...
... Tephra – bits of rock or solidified lava dropping from the air Reservoir – where magma is stored Summit – highest point Vent - opening where lava flows ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... Beneath the lithosphere, in the upper mantle to a depth of about 600 km ...
... Beneath the lithosphere, in the upper mantle to a depth of about 600 km ...
Ch 4 PPT - Blountstown Middle School
... • The lithosphere is thin below mid-ocean ridges and thick below continents. • Earth’s tectonic plates are large pieces of the lithosphere that fit together like the pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle. • The layer of Earth below the lithosphere, called the asthenosphere, is so hot that it behaves like ...
... • The lithosphere is thin below mid-ocean ridges and thick below continents. • Earth’s tectonic plates are large pieces of the lithosphere that fit together like the pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle. • The layer of Earth below the lithosphere, called the asthenosphere, is so hot that it behaves like ...
Chapter 2 Landforms Geological History of California California`s
... o fluid mantle that moves very slowly o thin crust made of separate pieces (tectonic plates) that float over the mantle • the plates float atop the fluid mantle like cereal bits floa=ng in milk ...
... o fluid mantle that moves very slowly o thin crust made of separate pieces (tectonic plates) that float over the mantle • the plates float atop the fluid mantle like cereal bits floa=ng in milk ...
Interior Crust Hydrosphere Atmosphere Magnetosphere Tides
... Plate motion is driven by convection in the upper mantle. Mantle material in this zone is a very viscous liquid like glass ...
... Plate motion is driven by convection in the upper mantle. Mantle material in this zone is a very viscous liquid like glass ...
Slide 1
... Plate Tectonics theory that describes the formation, movement, and interactions of lithosphere sections that move over the athenosphere ...
... Plate Tectonics theory that describes the formation, movement, and interactions of lithosphere sections that move over the athenosphere ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.