3.8 Rocks and Processes of the Rock Cycle
... The rock beneath the Earth’s surface is sometimes heated to high enough temperatures that it melts to create magma. Different magmas have different composition and contain whatever elements were in the rock or rocks that melted. Magmas also contain gases. The main elements are the same as the elemen ...
... The rock beneath the Earth’s surface is sometimes heated to high enough temperatures that it melts to create magma. Different magmas have different composition and contain whatever elements were in the rock or rocks that melted. Magmas also contain gases. The main elements are the same as the elemen ...
Types of Rocks
... What can heat and pressure do to rocks? • Because of the extreme heat and pressure: – Crystals can change shape and size – Chemicals can combine and create new minerals – Rocks can have striped or swirls because of minerals melting and pressure – An entirely new rock can be formed that looks nothin ...
... What can heat and pressure do to rocks? • Because of the extreme heat and pressure: – Crystals can change shape and size – Chemicals can combine and create new minerals – Rocks can have striped or swirls because of minerals melting and pressure – An entirely new rock can be formed that looks nothin ...
CHAPTER 2CROCKS AND MINERALS C A FIRST LOOK
... 4. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more elements in specific proportions, and it has a distinct set of physical (and chemical) properties. 5. A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic, solid element or compound having definite chemical composition and a regular, characteristic cry ...
... 4. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more elements in specific proportions, and it has a distinct set of physical (and chemical) properties. 5. A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic, solid element or compound having definite chemical composition and a regular, characteristic cry ...
Rocks and Minerals
... Intrusive Rock Bodies Plutonic • Less dense magmas rise through the crust • Rising magmas slowly cool – Viscosity increases – Density increases ...
... Intrusive Rock Bodies Plutonic • Less dense magmas rise through the crust • Rising magmas slowly cool – Viscosity increases – Density increases ...
Unit 5_Lesson 109_Review
... Using the notes from above, answer the questions below 1.) What branch of science would you be studying if you were blowing up chemicals? A.) Life ...
... Using the notes from above, answer the questions below 1.) What branch of science would you be studying if you were blowing up chemicals? A.) Life ...
CHAPTER 2CROCKS AND MINERALS C A FIRST LOOK
... 4. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more elements in specific proportions, and it has a distinct set of physical (and chemical) properties. 5. A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic, solid element or compound having definite chemical composition and a regular, characteristic cry ...
... 4. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more elements in specific proportions, and it has a distinct set of physical (and chemical) properties. 5. A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic, solid element or compound having definite chemical composition and a regular, characteristic cry ...
VOYAGE OF THE CONTINENTS AFRICA ORIGINS Script
... layers, horizontal layers. Normally these sediments rest on basement rocks such as granites. And the granites normally rest on mantle but not here in Vredefort. These quartzites that have been turned vertical. In fact what time of us believe, is in entire 36 km sequence of rocks have been turned on ...
... layers, horizontal layers. Normally these sediments rest on basement rocks such as granites. And the granites normally rest on mantle but not here in Vredefort. These quartzites that have been turned vertical. In fact what time of us believe, is in entire 36 km sequence of rocks have been turned on ...
Deep seismic reflection profiling of Archean cratons
... • By analogy with modern examples, mantle reflections are often interpreted as indicators of subduction ...
... • By analogy with modern examples, mantle reflections are often interpreted as indicators of subduction ...
Sedimentary cover of the Ankara Mélange: role of the Upper
... overthrusting the western basin margin, as part of major thrust faults affecting the area. However, new mapping shows that convergence increases northwards, with only high-angle reverse faulting of Palaeocene age being observed in the south. Although the basin fill is commonly reverse-faulted and lo ...
... overthrusting the western basin margin, as part of major thrust faults affecting the area. However, new mapping shows that convergence increases northwards, with only high-angle reverse faulting of Palaeocene age being observed in the south. Although the basin fill is commonly reverse-faulted and lo ...
Geology: Fluids in the lower crust following Mendocino triple
... Geodynamic and plate tectonic models for the Mendocino triple junction, a fault-fault-trench triple junction in northwestern California, predict a slab-free zone south of the triple junction in which asthenospheric mantle upwells to the base of the crust. A variety of geological and geophysical data ...
... Geodynamic and plate tectonic models for the Mendocino triple junction, a fault-fault-trench triple junction in northwestern California, predict a slab-free zone south of the triple junction in which asthenospheric mantle upwells to the base of the crust. A variety of geological and geophysical data ...
2How Is Continental Movement Explained by Plate Tectonics?
... map. Where are most of these boundaries located? The top picture on the right shows how plates move at a spreading boundary and what the result can be. The Great Rift Valley in Africa is one place where new crust is being added to the earth's surface. As the crust builds up, it forms a wider and dee ...
... map. Where are most of these boundaries located? The top picture on the right shows how plates move at a spreading boundary and what the result can be. The Great Rift Valley in Africa is one place where new crust is being added to the earth's surface. As the crust builds up, it forms a wider and dee ...
Study Guide
... 2. Scientists called _________________________, study earthquakes around the world. Earthquakes are measured using an instrument called a ________________________. The scale which measures the strength of the earthquake is known as the __________________ scale. ...
... 2. Scientists called _________________________, study earthquakes around the world. Earthquakes are measured using an instrument called a ________________________. The scale which measures the strength of the earthquake is known as the __________________ scale. ...
File
... tell much about how much is in the core versus how much has been lost to space," making sulfur virtually impossible to directly measure. [Photo Timeline: How the Earth Formed] To track and quantify the elusive sulfur, the researchers looked to copper isotopes (atoms of the same element with differen ...
... tell much about how much is in the core versus how much has been lost to space," making sulfur virtually impossible to directly measure. [Photo Timeline: How the Earth Formed] To track and quantify the elusive sulfur, the researchers looked to copper isotopes (atoms of the same element with differen ...
Make sure you label your diagrams and use arrows to show
... Wash your hands before starting this lab! Only handle your own cake and brownie piece! Do not put the cake or brownie on the table…always place the models on your paper towel. 1) Calculate the density of your slice of cake and brownie. ...
... Wash your hands before starting this lab! Only handle your own cake and brownie piece! Do not put the cake or brownie on the table…always place the models on your paper towel. 1) Calculate the density of your slice of cake and brownie. ...
ASSIGNMENT – JANUARY 3RD – READ AND ANSWER
... From where does the word "Metamorphic" come from? What is another name for igneous rock? What makes igneous rocks? AND How does igneous rock form below ground? Explain the different uses for igneous rocks. How do we use minerals every day? ...
... From where does the word "Metamorphic" come from? What is another name for igneous rock? What makes igneous rocks? AND How does igneous rock form below ground? Explain the different uses for igneous rocks. How do we use minerals every day? ...
Plate Tectonics PhET
... Now go to the “Plate Motion” tab. Under “View, check “Both,” “Show Labels,” and “Show Sea Water.” Experiment with different types of crust at the plate boundary. Note the following vocabulary terms: ...
... Now go to the “Plate Motion” tab. Under “View, check “Both,” “Show Labels,” and “Show Sea Water.” Experiment with different types of crust at the plate boundary. Note the following vocabulary terms: ...
Jeopardy
... During the rock cycle, a collision between two continental plates could force one plate down toward the heat of the mantle, producing this type of rock. ...
... During the rock cycle, a collision between two continental plates could force one plate down toward the heat of the mantle, producing this type of rock. ...
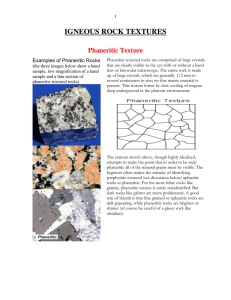
Igneous Rock Textures
... The last textural term is reserved for pyroclastic rocks, those blown out into the atmosphere during violent volcanic eruptions. These rocks are collectively termed fragmental. If you examine a fragmental volcanic rock closely you can see why. You will note that it is comprised of numerous grains or ...
... The last textural term is reserved for pyroclastic rocks, those blown out into the atmosphere during violent volcanic eruptions. These rocks are collectively termed fragmental. If you examine a fragmental volcanic rock closely you can see why. You will note that it is comprised of numerous grains or ...
File
... which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash. Examples of composite volcanoes include Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount St. Helens in Washington State. ...
... which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash. Examples of composite volcanoes include Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount St. Helens in Washington State. ...
a floating body displaces its own weight of water Crust and mantle
... around with must have occurred to Airy. You can see the analogy between ice and water in his conceptualization of mountain highlands being compensated by deep mountain roots shown below. ...
... around with must have occurred to Airy. You can see the analogy between ice and water in his conceptualization of mountain highlands being compensated by deep mountain roots shown below. ...
What is an earthquake?
... • Used to describe both sudden slip on a fault, and the resulting ground shaking and radiated seismic energy caused by the slip • Caused by volcanic or magmatic activity, • Caused by other sudden stress changes in the earth. ...
... • Used to describe both sudden slip on a fault, and the resulting ground shaking and radiated seismic energy caused by the slip • Caused by volcanic or magmatic activity, • Caused by other sudden stress changes in the earth. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.