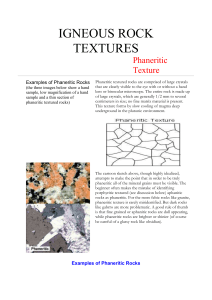
igneous rock textures
... Aphanitic texture consists of small crystals that cannot be seen by the eye with or hand lens. The entire rock is made up of small crystals, which are generally less than 1/2 mm in size. This texture results from rapid cooling in volcanic or hypabyssal (shallow subsurface) environments. ...
... Aphanitic texture consists of small crystals that cannot be seen by the eye with or hand lens. The entire rock is made up of small crystals, which are generally less than 1/2 mm in size. This texture results from rapid cooling in volcanic or hypabyssal (shallow subsurface) environments. ...
Unit C – The Changing Earth(pages 292 – 401)
... Hutton noticed vertical columns beneath horizontal strata Layers of unconformity where there was no apparent pattern Hypothesized vertical columns used to be horizontal but were tilted and followed by periods of erosions and finally more sediments ...
... Hutton noticed vertical columns beneath horizontal strata Layers of unconformity where there was no apparent pattern Hypothesized vertical columns used to be horizontal but were tilted and followed by periods of erosions and finally more sediments ...
Part 1: Describing differences between oceanic
... Type of Boundary? What is the effect/outcome of this plate movement? Divergent Convergent Transform Example 2: Drag 2 old oceanic crusts onto the screen. Drag the plate in the direction of the RED arrow. Draw it! Type of Boundary? What is the effect/outcome of this plate movement? Divergent ...
... Type of Boundary? What is the effect/outcome of this plate movement? Divergent Convergent Transform Example 2: Drag 2 old oceanic crusts onto the screen. Drag the plate in the direction of the RED arrow. Draw it! Type of Boundary? What is the effect/outcome of this plate movement? Divergent ...
3rd grade grade layers of the earth
... Enduring Understanding: Science process skills of inquiry are used to learn about the world around us. The earth is made of layers. Natural forces shape the earth. Arkansas Frameworks: ...
... Enduring Understanding: Science process skills of inquiry are used to learn about the world around us. The earth is made of layers. Natural forces shape the earth. Arkansas Frameworks: ...
Crustal Interactions Midterm Rev
... traveling to seismic stations C and D. 7 An observer discovers shallow-water marine fossils in rock strata at an elevation of 5,000 meters. What is the best explanation for this observation? 1) The level of the ocean was once 5,000 meters higher. 2) Violent earthquakes caused crustal subsidence. 3) ...
... traveling to seismic stations C and D. 7 An observer discovers shallow-water marine fossils in rock strata at an elevation of 5,000 meters. What is the best explanation for this observation? 1) The level of the ocean was once 5,000 meters higher. 2) Violent earthquakes caused crustal subsidence. 3) ...
What is a Volcano? - ric0003livingstoneprimaryschool
... What is a volcanic eruption? A volcano erupts when hot melted rock (magma), gas and other debris is pushed up through the Earth’s crust. Volcanoes are essentially vents on the Earths surface from which fiery power in the form of molten rock, debris, and gases can escape from deep within the earth’s ...
... What is a volcanic eruption? A volcano erupts when hot melted rock (magma), gas and other debris is pushed up through the Earth’s crust. Volcanoes are essentially vents on the Earths surface from which fiery power in the form of molten rock, debris, and gases can escape from deep within the earth’s ...
Chapter 5 Fast Changes on Earth: Earthquakes
... Plates (248) – gigantic slabs of rock making up the crust Fault (249) – where the plates come together Earthquake (249) – movement in the Earth’s crust that are caused by a sudden shift in the Earth’s plates Tsunami (252) – giant waves caused by earthquakes on the ocean floor What are earthquakes? M ...
... Plates (248) – gigantic slabs of rock making up the crust Fault (249) – where the plates come together Earthquake (249) – movement in the Earth’s crust that are caused by a sudden shift in the Earth’s plates Tsunami (252) – giant waves caused by earthquakes on the ocean floor What are earthquakes? M ...
Intro 1-2-3-4
... 3. Mesosphere - rigid but not as hard as lithosphere • higher temp than asthenosphere, but not molten because of compression pressure • 4950km thick ...
... 3. Mesosphere - rigid but not as hard as lithosphere • higher temp than asthenosphere, but not molten because of compression pressure • 4950km thick ...
Plate Tectonics Subduction zone Magma Taupo volcanic
... As the Pacific plate is forced down into the mantle, the oceanic crust, which caps the Pacific plate, begins to heat up. Under increasing pressure and temperature, the former crustal material undergoes chemical reactions and molten magma is formed. This magma is very hot and contains gases making it ...
... As the Pacific plate is forced down into the mantle, the oceanic crust, which caps the Pacific plate, begins to heat up. Under increasing pressure and temperature, the former crustal material undergoes chemical reactions and molten magma is formed. This magma is very hot and contains gases making it ...
Seafloor Spreading
... that there are both age and magnetic patterns in the seafloor. This provided more evidence that plates both exist and move. It resulted in the development of the theory of plate tectonics, which describes the motions of plates and the interactions between them that occur at plate boundaries. The new ...
... that there are both age and magnetic patterns in the seafloor. This provided more evidence that plates both exist and move. It resulted in the development of the theory of plate tectonics, which describes the motions of plates and the interactions between them that occur at plate boundaries. The new ...
Chapter 4
... plate moves over the hot spot a series of volcanoes are produced. This gives geologists a wonderful view of the movement of a plate through time with the distribution of volcanoes indicating the direction of motion and their ages revealing the rate at which the plate was moving. One of the most stri ...
... plate moves over the hot spot a series of volcanoes are produced. This gives geologists a wonderful view of the movement of a plate through time with the distribution of volcanoes indicating the direction of motion and their ages revealing the rate at which the plate was moving. One of the most stri ...
Overview of Information about the Broad River watershed
... Geological relationships exposed along the route of days 6 & 7 are illustrated in the attached map and portrayed in a geological cross section in Figure 8. The route on these last two days carries the Appalachian transect to the Coastal Plain. It begins on Day 6 at Clark Hill Dam within the Savannah ...
... Geological relationships exposed along the route of days 6 & 7 are illustrated in the attached map and portrayed in a geological cross section in Figure 8. The route on these last two days carries the Appalachian transect to the Coastal Plain. It begins on Day 6 at Clark Hill Dam within the Savannah ...
Volcanic landforms
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
Volcanoes
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
... Volcanic eruptions can develop into three different types of volcanic mountains, depending on the nature of the volcanic material. A shield cone is a volcanic mountain that is built almost entirely of lava flow. The slopes of a shield cone volcano are very gentle and rounded like a warrior's shield. ...
Landforms
... plate edges. When plates rub against each other, Earth’s crust cracks and chips under the pressure. These cracks are called faults. When the crust moves along faults, great amounts of energy are released in the form of earthquakes. Earthquakes cause dramatic changes to the surface of the earth. ...
... plate edges. When plates rub against each other, Earth’s crust cracks and chips under the pressure. These cracks are called faults. When the crust moves along faults, great amounts of energy are released in the form of earthquakes. Earthquakes cause dramatic changes to the surface of the earth. ...
File
... • What Do Hot Spots Form? A hot spot often produces a long chain of volcanoes. •How do hot spots Form? A hot spot forms from Mantle Plumes, or areas of the mantle that are hotter then others ...
... • What Do Hot Spots Form? A hot spot often produces a long chain of volcanoes. •How do hot spots Form? A hot spot forms from Mantle Plumes, or areas of the mantle that are hotter then others ...
Lecture_Ch06 - earthjay science
... • voluminous mantle material rises and melts to form mafic magma • crust above hot spots melts to produce intermediate and felsic magma Example: Hawaiian Islands—or Emperor-Hawaiian Seamount Chain >80 volcanoes—progressively younger from N to S (80 mya to now), change in age along the chain has been ...
... • voluminous mantle material rises and melts to form mafic magma • crust above hot spots melts to produce intermediate and felsic magma Example: Hawaiian Islands—or Emperor-Hawaiian Seamount Chain >80 volcanoes—progressively younger from N to S (80 mya to now), change in age along the chain has been ...
Chapter 9
... dense rocks. Islands—Formed by undersea volcanoes erupting over many years. This builds up undersea mountains that eventually protrude above sea level. Mountain ranges—Formed where two plates are colliding. The stress on the surface causes the crust to buckle upward, forming a mountain range. Rift v ...
... dense rocks. Islands—Formed by undersea volcanoes erupting over many years. This builds up undersea mountains that eventually protrude above sea level. Mountain ranges—Formed where two plates are colliding. The stress on the surface causes the crust to buckle upward, forming a mountain range. Rift v ...
Ch 10 - Mr. Neason`s Earth Science
... Highly viscous magma slows the upward movement of expanding gases. The gases collect in bubble and pockets that increase in size until they eject magma from the volcano in an explosive eruption. Volcanic Material Depending on the type of eruption, volcanoes may produce lava flows or eject pyroclasti ...
... Highly viscous magma slows the upward movement of expanding gases. The gases collect in bubble and pockets that increase in size until they eject magma from the volcano in an explosive eruption. Volcanic Material Depending on the type of eruption, volcanoes may produce lava flows or eject pyroclasti ...
Activity Sheet: Grades 6-8 - Washington State Parks and Recreation
... d. More than _____________ of the earth’s volcanoes on land form above areas where one plate dives beneath another. These areas are known as _________________________________________. e. About ________________beneath your feet, rocks along the subduction zone _____________________________ forming __ ...
... d. More than _____________ of the earth’s volcanoes on land form above areas where one plate dives beneath another. These areas are known as _________________________________________. e. About ________________beneath your feet, rocks along the subduction zone _____________________________ forming __ ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.