Activity Sheet: Grades 6-8 - Washington State Parks and Recreation
... d. More than _____________ of the earth’s volcanoes on land form above areas where one plate dives beneath another. These areas are known as _________________________________________. e. About ________________beneath your feet, rocks along the subduction zone _____________________________ forming __ ...
... d. More than _____________ of the earth’s volcanoes on land form above areas where one plate dives beneath another. These areas are known as _________________________________________. e. About ________________beneath your feet, rocks along the subduction zone _____________________________ forming __ ...
File
... which the igneous rock crystallizes is a fluid, the ions that will form the minerals are able to move freely. The hotter the fluid the greater the movement and freedom, and the quicker the crystallization takes place. (Did you know that hot water freezes faster than cold? It does! The ice-resurfacin ...
... which the igneous rock crystallizes is a fluid, the ions that will form the minerals are able to move freely. The hotter the fluid the greater the movement and freedom, and the quicker the crystallization takes place. (Did you know that hot water freezes faster than cold? It does! The ice-resurfacin ...
Lassen Peak Is Sinking, And Volcanologists Don`t Know Why
... This can’t alone account for the sinking, especially the timing as it appears to have started over 70 years after the eruption ended. You might expect that the sinking would have happened soon after the eruption ended (because you’ve expelled all that volume of magma and volcanic gas). However, as I ...
... This can’t alone account for the sinking, especially the timing as it appears to have started over 70 years after the eruption ended. You might expect that the sinking would have happened soon after the eruption ended (because you’ve expelled all that volume of magma and volcanic gas). However, as I ...
earthquakes - Archway Chandler
... c. Fault – a crack resulting within the Earth’s crust as a result of the stress, usually along a plate boundary, i. Three types of faults 1. normal – caused by tension 2. reverse (thrust) – caused by compression 3. strike-slip – caused by shearing ...
... c. Fault – a crack resulting within the Earth’s crust as a result of the stress, usually along a plate boundary, i. Three types of faults 1. normal – caused by tension 2. reverse (thrust) – caused by compression 3. strike-slip – caused by shearing ...
Scotland`s Time Lords
... geometrical fit between South America and Africa suggested that they had been at one time joined and through time had drifted apart; the theory of continental drift. There was strong scientific evidence for this with identical, terrestrial fossils present on both continents however the scientific wo ...
... geometrical fit between South America and Africa suggested that they had been at one time joined and through time had drifted apart; the theory of continental drift. There was strong scientific evidence for this with identical, terrestrial fossils present on both continents however the scientific wo ...
2.isca-irjes-2014-01.. - International Science Congress Association
... carried out using two dimensional finite element modeling. With the current availability of computing technology, advanced numerical techniques and material models it would be an easy task to know the parameters effecting the transition from collision to subduction process between different tectonic ...
... carried out using two dimensional finite element modeling. With the current availability of computing technology, advanced numerical techniques and material models it would be an easy task to know the parameters effecting the transition from collision to subduction process between different tectonic ...
6th Grade UBD Unit 1
... h) Explain the effects of human activity on the erosion of the earth’s surface. i) Describe methods for conserving natural resources such as water, soil, and air. ...
... h) Explain the effects of human activity on the erosion of the earth’s surface. i) Describe methods for conserving natural resources such as water, soil, and air. ...
measuring the earth - Mepham Earth Science
... 7) CHANGES are EVENTS; All can be described in terms of "time and space (distance)". All changes require time and all require something to move a distance through space. a) Rate of change varies greatly. Some are fast (earthquakes). Some are slow (evolution). b) Changes may be cyclic; repeating agai ...
... 7) CHANGES are EVENTS; All can be described in terms of "time and space (distance)". All changes require time and all require something to move a distance through space. a) Rate of change varies greatly. Some are fast (earthquakes). Some are slow (evolution). b) Changes may be cyclic; repeating agai ...
Midterm Exam 1 Study Guide
... What did Alfred Wegener propose? Why were his ideas rejected? What was Pangaea? Name the layers of the earth (core, mantle, asthenosphere, etc.) How are these layers arranged? Describe the general idea of plate tectonics. What are the direct and indirect evidence for continental drift? What are the ...
... What did Alfred Wegener propose? Why were his ideas rejected? What was Pangaea? Name the layers of the earth (core, mantle, asthenosphere, etc.) How are these layers arranged? Describe the general idea of plate tectonics. What are the direct and indirect evidence for continental drift? What are the ...
Layers of Earth Notes
... • Intense heat causes the rocks to rise and then cool and sink. • The process is called convection, which causes the crust to move. • Average temperature 3000o © KeslerScience.com ...
... • Intense heat causes the rocks to rise and then cool and sink. • The process is called convection, which causes the crust to move. • Average temperature 3000o © KeslerScience.com ...
millenderdale
... a relatively hot and plastic state. Development of foliations between phases of intrusion implies that the site of intrusion was tectonically active. The textural evidence indicates that much of the hornblende in the ‘beerbachites' has replaced granoblastic pyroxene developed in original doleritic a ...
... a relatively hot and plastic state. Development of foliations between phases of intrusion implies that the site of intrusion was tectonically active. The textural evidence indicates that much of the hornblende in the ‘beerbachites' has replaced granoblastic pyroxene developed in original doleritic a ...
Actual Lesson Plan On Volcanoes
... Impact of the Ash- can generate lightning which can further ignite forest fires, cause human death from asphyxiation (suffocation), accumulate on plants and destroy them, and cover the surrounding towns costing them time and money to clear it away Impact on Climate- depending on the richness of the ...
... Impact of the Ash- can generate lightning which can further ignite forest fires, cause human death from asphyxiation (suffocation), accumulate on plants and destroy them, and cover the surrounding towns costing them time and money to clear it away Impact on Climate- depending on the richness of the ...
Summary and review
... What we are learning from GPS 1) Plate tectonic assumptions OK- but only to first order- Within plate deformation can be huge 2) How continents deform during orogenesisdiffuse? plate like? ...
... What we are learning from GPS 1) Plate tectonic assumptions OK- but only to first order- Within plate deformation can be huge 2) How continents deform during orogenesisdiffuse? plate like? ...
Fore-arc basin
... magma viscosity and gas content. – More silicic magmas in more evolved arcs - therefore greater explosive activity, more supply of clastic sediment. ...
... magma viscosity and gas content. – More silicic magmas in more evolved arcs - therefore greater explosive activity, more supply of clastic sediment. ...
File
... thick. The interior of the Earth became soft. The heaviest elements sank to the middle and the lightest elements floated on top. This caused the formation of distinct layers in the Earth, called differentiation. ...
... thick. The interior of the Earth became soft. The heaviest elements sank to the middle and the lightest elements floated on top. This caused the formation of distinct layers in the Earth, called differentiation. ...
Correlation and Time`s Arrow
... sedimentary types. • Islands emerge somewhere along here, but leave little trace. • So both primitive and transitional rocks are considered universal. • Continued lowering of water levels leads to floetz deposits: many fossils, some of these deposits are local only, as land masses grew in extent. Fi ...
... sedimentary types. • Islands emerge somewhere along here, but leave little trace. • So both primitive and transitional rocks are considered universal. • Continued lowering of water levels leads to floetz deposits: many fossils, some of these deposits are local only, as land masses grew in extent. Fi ...
New Zealand`s Plates - Royal Society of New Zealand
... The collision zone (plate boundary) can be seen on the poster set map as a dark line running from Tonga, down past East Cape, curving towards the South Island south of Wellington, running along the alpine spine of the South Island and back out to sea south of Milford Sound. The edges of the Pacific ...
... The collision zone (plate boundary) can be seen on the poster set map as a dark line running from Tonga, down past East Cape, curving towards the South Island south of Wellington, running along the alpine spine of the South Island and back out to sea south of Milford Sound. The edges of the Pacific ...
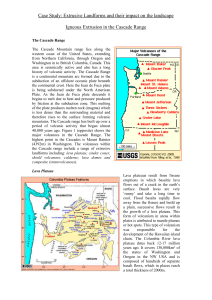
Case Study: Extrusive Landforms and their impact on the
... Lava Plateau Lava plateaus result from fissure eruptions in which basaltic lava flows out of a crack in the earth’s surface. Basalt lavas are very ‘runny’ and take a long time to cool. Flood basalts rapidly flow away from the fissure and build up a plain, successive flows result in the growth of a l ...
... Lava Plateau Lava plateaus result from fissure eruptions in which basaltic lava flows out of a crack in the earth’s surface. Basalt lavas are very ‘runny’ and take a long time to cool. Flood basalts rapidly flow away from the fissure and build up a plain, successive flows result in the growth of a l ...
metamorphism and metamorphic rocks
... Metamorphism is the process by which conditions within the Earth alter the mineral content and structure of solid rock without melting it. Metamorphic rocks generally form under temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions that exist beneath the zone of diagenesis but above the 50-250 km deep “zon ...
... Metamorphism is the process by which conditions within the Earth alter the mineral content and structure of solid rock without melting it. Metamorphic rocks generally form under temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions that exist beneath the zone of diagenesis but above the 50-250 km deep “zon ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.