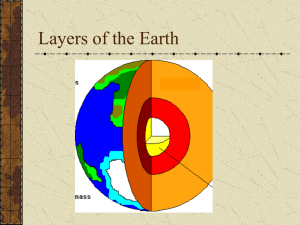
Scale Model of Earth`s Layers
... is a layer that is kind of like tar on a hot day. It flows, but very, very slowly. ...
... is a layer that is kind of like tar on a hot day. It flows, but very, very slowly. ...
Geological map interpretation
... Geological map interpretation – Listing the sequence of geological events happening in an area Look at the 1:20 000 Geological map of Sai Kung (Map 2) and answer the following questions. 1. a) Identify the major rock types and superficial deposits shown on the map. Describe their distribution. b) At ...
... Geological map interpretation – Listing the sequence of geological events happening in an area Look at the 1:20 000 Geological map of Sai Kung (Map 2) and answer the following questions. 1. a) Identify the major rock types and superficial deposits shown on the map. Describe their distribution. b) At ...
Rock ID handout
... • Sandstones (grains ∼0.5-2mm) are named by the dominant grain composition and whether there is a muddy matrix. Arenite for no matrix. Graywacke for 15% clay or above. Sand grains divided into quartz, feldspar, and lithic (e.g. other). So: quartz arenite, lithic wacke, etc. • If you can’t see the in ...
... • Sandstones (grains ∼0.5-2mm) are named by the dominant grain composition and whether there is a muddy matrix. Arenite for no matrix. Graywacke for 15% clay or above. Sand grains divided into quartz, feldspar, and lithic (e.g. other). So: quartz arenite, lithic wacke, etc. • If you can’t see the in ...
Contributions to the geology of Algarve (Portugal)
... makes separation of the Meso-Cenozoic terrain from the south border of Carboniferous rocks. The observed structures are characterized: 1) by the presence of clasts of Triasic sandstones in the volcanic breccias of pipes; 2) by the pipes cutting the Lower Liassic dolostones at Moinho de Arrife or cu ...
... makes separation of the Meso-Cenozoic terrain from the south border of Carboniferous rocks. The observed structures are characterized: 1) by the presence of clasts of Triasic sandstones in the volcanic breccias of pipes; 2) by the pipes cutting the Lower Liassic dolostones at Moinho de Arrife or cu ...
CANADA`S LANDFORM REGIONS:
... It is the geologic core of the country. The shield (shaped like a shield) used to be a mountain range that was 12 000 metres tall that was eroded by glaciers millions of years ago. • The eroded rock became the flat plains that surrounds the rounded bump (all that is left of the original mountain) ...
... It is the geologic core of the country. The shield (shaped like a shield) used to be a mountain range that was 12 000 metres tall that was eroded by glaciers millions of years ago. • The eroded rock became the flat plains that surrounds the rounded bump (all that is left of the original mountain) ...
Take a walk Back InTo our volcanIc pasT
... the magma is blasted out as fragments, rather than flowing out as lava Pyroclastic flow The hottest, most violent type of pyroclastic eruption Caldera A large depression (about 15km long and 10km wide) created during a pyroclastic flow eruption Sill Magma that doesn’t reach the surface, but cools do ...
... the magma is blasted out as fragments, rather than flowing out as lava Pyroclastic flow The hottest, most violent type of pyroclastic eruption Caldera A large depression (about 15km long and 10km wide) created during a pyroclastic flow eruption Sill Magma that doesn’t reach the surface, but cools do ...
Classifying rocks
... 20 minerals make up most of the rocks of Earth’s crust, these minerals are known as rockforming minerals ...
... 20 minerals make up most of the rocks of Earth’s crust, these minerals are known as rockforming minerals ...
Planforms of self-consistently generated plates in 3D spherical
... viscosity, strong enough to form a rigid lid in the absence of yielding. The vast majority of such research to date has been in either two-dimensional, or three-dimensional cartesian geometry. In the present study, mantle convection calculations are performed to investigate the planform of self-cons ...
... viscosity, strong enough to form a rigid lid in the absence of yielding. The vast majority of such research to date has been in either two-dimensional, or three-dimensional cartesian geometry. In the present study, mantle convection calculations are performed to investigate the planform of self-cons ...
A Tectonic explanation of the May 12, 2008, Sichuan Earthquake
... toward the east, in a process called “extrusion tectonics” or “tectonic escape”. ...
... toward the east, in a process called “extrusion tectonics” or “tectonic escape”. ...
Constraints on shallow mantle viscosity from morphology and
... spreading center. Braun et al. [2000] also concluded that the sub‐ridge viscosity must be low based on thermo‐mechanical models for mid‐ocean ridges with melting effects considered. They suggested that a viscosity as low as 1018 Pa·s is required for the buoyancy driven upwelling of mantle and that t ...
... spreading center. Braun et al. [2000] also concluded that the sub‐ridge viscosity must be low based on thermo‐mechanical models for mid‐ocean ridges with melting effects considered. They suggested that a viscosity as low as 1018 Pa·s is required for the buoyancy driven upwelling of mantle and that t ...
HST_CRF_04_02_03.qxd
... Directed Reading B Section: Volcanic Eruptions Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. ...
... Directed Reading B Section: Volcanic Eruptions Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. ...
Year 8 Activity Pack sample - UNIT 8HB
... Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma cools down underground. They are named because the magma has ‘intruded’ into rocks that were already present. Most intrusive igneous rocks have large crystals, but not always! The diagram shows three different ways in which magma can be intruded. Large v ...
... Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma cools down underground. They are named because the magma has ‘intruded’ into rocks that were already present. Most intrusive igneous rocks have large crystals, but not always! The diagram shows three different ways in which magma can be intruded. Large v ...
1 Evolution of continental crust through two Wilson
... the rift where it cannot be restored by conventional methods. Along-strike variations in rift expression between lower-plate and upper-plate configurations of basement faults are partitioned by transform faults, some of which offset the trace of the rift. Facies and thickness of synrift and passive- ...
... the rift where it cannot be restored by conventional methods. Along-strike variations in rift expression between lower-plate and upper-plate configurations of basement faults are partitioned by transform faults, some of which offset the trace of the rift. Facies and thickness of synrift and passive- ...
Mantle discontinuities beneath the Deccan volcanic
... of the continental lithosphere over a thermal anomaly caused due to a mantle plume and subsequent outpouring of basalts by decompressional melting of hot asthenospheric mantle. Alternatively, in the starting plume model [8], basalts are formed, again, by decompression melting at shallow depths withi ...
... of the continental lithosphere over a thermal anomaly caused due to a mantle plume and subsequent outpouring of basalts by decompressional melting of hot asthenospheric mantle. Alternatively, in the starting plume model [8], basalts are formed, again, by decompression melting at shallow depths withi ...
Introduction to Plate Tectonics via Google Earth
... 5. If the earth’s lowest spots aren’t in the middle of the ocean, where are they? Focus on the west coast of South America, and in the space below complete the topographic profile of the Pacific Ocean floor from South America westward about 600 miles (1000 km). ...
... 5. If the earth’s lowest spots aren’t in the middle of the ocean, where are they? Focus on the west coast of South America, and in the space below complete the topographic profile of the Pacific Ocean floor from South America westward about 600 miles (1000 km). ...
rockcycle&classification1&2
... grain size from the largest phenocrysts to the average sized grain in the groundmass. Sideromelane - basaltic glass; characteristic of palagonite tuff. Spherulite - a spheroidal mass of acicular crystals (orthoclase and quartz), radially arranged. Spherulites are frequently encountered in glassy roc ...
... grain size from the largest phenocrysts to the average sized grain in the groundmass. Sideromelane - basaltic glass; characteristic of palagonite tuff. Spherulite - a spheroidal mass of acicular crystals (orthoclase and quartz), radially arranged. Spherulites are frequently encountered in glassy roc ...
Title Special issue `Geofluid processes in subduction zones and
... Shiina et al. (2014) show that hydrated mineralogy alone cannot sufficiently explain the low velocities observed in the subducting crust beneath Hokkaido, suggesting that fluids may coexist with hydrated rocks down to 80-km depth. Nakajima (2014) provides evidence of the presence of high-attenuation ...
... Shiina et al. (2014) show that hydrated mineralogy alone cannot sufficiently explain the low velocities observed in the subducting crust beneath Hokkaido, suggesting that fluids may coexist with hydrated rocks down to 80-km depth. Nakajima (2014) provides evidence of the presence of high-attenuation ...
Chapter 3: Rocks Study Guide
... 19-22. By observing a rock’s color, texture and mineral composition, geologists can determine the rock’s ________________________, which is how the rock formed. Then geologists can classify the rocks into one of 3 major rock groups: _______________________, ______________________ & _________________ ...
... 19-22. By observing a rock’s color, texture and mineral composition, geologists can determine the rock’s ________________________, which is how the rock formed. Then geologists can classify the rocks into one of 3 major rock groups: _______________________, ______________________ & _________________ ...
Chp 18.3 Notes TYPES OF VOLCANOES & WHERE THEY …
... the peak of another volcano. Lava domes can act like a cork and can eventually result in explosive pyroclastic flows. Magma type: Very viscous (thick & resistant to Flow) ...
... the peak of another volcano. Lava domes can act like a cork and can eventually result in explosive pyroclastic flows. Magma type: Very viscous (thick & resistant to Flow) ...
Sedimentary Rock Identification
... metamorphic based on origin. Igneous rocks form when magma rises from the mantle, cools, and hardens either below the Earth’s surface or on the surface. Sedimentary rocks are layered accumulations of mineral particles derived from weathering and erosion of preexisting rocks, chemical deposition, or ...
... metamorphic based on origin. Igneous rocks form when magma rises from the mantle, cools, and hardens either below the Earth’s surface or on the surface. Sedimentary rocks are layered accumulations of mineral particles derived from weathering and erosion of preexisting rocks, chemical deposition, or ...
Essay: “Where Is (and Was) Pennsylvania?”
... enough, though, to cause the consolidated cosmic materials to eventually transform into rocks. The oldest rocks on Earth have been dated at 3.9 billion years of age, so this initial rock formation process took some 600 million to a billion years to occur (Windley 1995, Taylor 2004). The pressure ...
... enough, though, to cause the consolidated cosmic materials to eventually transform into rocks. The oldest rocks on Earth have been dated at 3.9 billion years of age, so this initial rock formation process took some 600 million to a billion years to occur (Windley 1995, Taylor 2004). The pressure ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.























