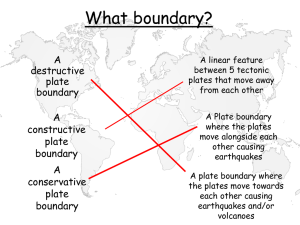
Earth Communication
... This packet is your weeklong guide for reviewing our unit on plate tectonics. You are to complete each section in its entirety the day it is given to you. You will complete one section each day. Each section will include three parts: vocabulary definitions, inquiry based questions based on your own ...
... This packet is your weeklong guide for reviewing our unit on plate tectonics. You are to complete each section in its entirety the day it is given to you. You will complete one section each day. Each section will include three parts: vocabulary definitions, inquiry based questions based on your own ...
Open file
... mantle and crust allow scientist to determine how the Earth’s interior is structured? (1) The earth is made up of 4 aligned layers: The inner and outer core, mantle and crust. The crust is the solid surface layer that is made up of tectonic plates. These plates can move and when this occurs pressure ...
... mantle and crust allow scientist to determine how the Earth’s interior is structured? (1) The earth is made up of 4 aligned layers: The inner and outer core, mantle and crust. The crust is the solid surface layer that is made up of tectonic plates. These plates can move and when this occurs pressure ...
Convection in the Mantle (5-2)
... are on two different continents, separated by an ocean. Also, mountain ranges are usually located along or parallel to the edges of continents. Coals beds in Europe and South and North America also lined up when Pangaea was together. 3. Fossil evidence - Fossils of organisms have been found on two c ...
... are on two different continents, separated by an ocean. Also, mountain ranges are usually located along or parallel to the edges of continents. Coals beds in Europe and South and North America also lined up when Pangaea was together. 3. Fossil evidence - Fossils of organisms have been found on two c ...
rocks and minerals!
... rocks like granite. Some magna cools above the earth to form light rocks like basalt. ...
... rocks like granite. Some magna cools above the earth to form light rocks like basalt. ...
Isostatic Adjustments
... in the rocks along a break it is called fracture. • When rocks do move at a break it is called a fault. ...
... in the rocks along a break it is called fracture. • When rocks do move at a break it is called a fault. ...
geology - South Dakota Space Grant Consortium
... This interpretive site is located near a significant geologic boundary. ...
... This interpretive site is located near a significant geologic boundary. ...
"postorogenie" magmatism
... postdate deformed orogenie granites, some formed later, by as much as 40 m.y. This time lag between magmatic pulses does not necessarily imply any lag between the end of deformation and the first appearance of nondeformed granites. Features such as miarolitic cavities, granophyric intergrowths, and ...
... postdate deformed orogenie granites, some formed later, by as much as 40 m.y. This time lag between magmatic pulses does not necessarily imply any lag between the end of deformation and the first appearance of nondeformed granites. Features such as miarolitic cavities, granophyric intergrowths, and ...
earthquakes - WordPress.com
... There was slippage along a conservative plate boundary that runs through Haiti. ...
... There was slippage along a conservative plate boundary that runs through Haiti. ...
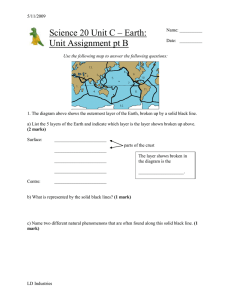
Unit C UA pt B - LD Industries
... ________ - relating to waves that travel through Earth as a result of explosions or earthquakes ________ - a large concentration of petroleum confined between layers of impermeable shale ________ - an instrument that records seismic waves ________ - a submerged ridge of rock, sand, or coral that ris ...
... ________ - relating to waves that travel through Earth as a result of explosions or earthquakes ________ - a large concentration of petroleum confined between layers of impermeable shale ________ - an instrument that records seismic waves ________ - a submerged ridge of rock, sand, or coral that ris ...
ttu_gs0001_000441.
... River Plains of Idaho are among the finest examples of this type of volcanism. The Columbia River Plateau has an area of 100,000 square miles, and the total volume of basaltic lava approximates 35,000 cubic miles. Individual lava flows can be traced for distances of more than 100 miles. Such lavas m ...
... River Plains of Idaho are among the finest examples of this type of volcanism. The Columbia River Plateau has an area of 100,000 square miles, and the total volume of basaltic lava approximates 35,000 cubic miles. Individual lava flows can be traced for distances of more than 100 miles. Such lavas m ...
11 Earth and Atmos
... In 1962, scientists produced the theory of plate tectonics.The theory of plate tectonics supported Wegener’s theory that continents move. Describe and explain what causes tectonic plates to move. ...
... In 1962, scientists produced the theory of plate tectonics.The theory of plate tectonics supported Wegener’s theory that continents move. Describe and explain what causes tectonic plates to move. ...
Lab- Magnetics and Seafloor Spreading
... Figure 1 shows the three basic types of plate boundaries. Warm mantle material upwells at spreading centers, also known as midocean ridges, and then cools. Because the strength of rock decreases with temperature the cooling material forms strong plates of new oceanic lithosphere. The cooling oceanic ...
... Figure 1 shows the three basic types of plate boundaries. Warm mantle material upwells at spreading centers, also known as midocean ridges, and then cools. Because the strength of rock decreases with temperature the cooling material forms strong plates of new oceanic lithosphere. The cooling oceanic ...
INTRUSIVE IGNEOUS ROCKS, PART 2
... tin, tungsten, uranium, zirconium, and the rare earth elements. The presence of some of these minerals may make the pegmatite an ore. Pegmatites commonly form at the margins of batholiths and represent the last, most hydrous portions of the magma to crystallize. Although generally of granitic compos ...
... tin, tungsten, uranium, zirconium, and the rare earth elements. The presence of some of these minerals may make the pegmatite an ore. Pegmatites commonly form at the margins of batholiths and represent the last, most hydrous portions of the magma to crystallize. Although generally of granitic compos ...
The Earth in cross-section: what`s down there and how we know it
... Seismic waves involve stress, strain, and density Two important types of stresses and strains: Pressure, P and volume change per unit volume, DV/V Shear stress and shear strain ...
... Seismic waves involve stress, strain, and density Two important types of stresses and strains: Pressure, P and volume change per unit volume, DV/V Shear stress and shear strain ...
The Earth`s Layers
... This volcano has been erupting continuously since January 1983. Lava is pouring down the edge of the island and into the ocean, becoming solid rock. ...
... This volcano has been erupting continuously since January 1983. Lava is pouring down the edge of the island and into the ocean, becoming solid rock. ...
Lab #2 – Interpreting Tectonic and Bathymetric Maps
... Pacific Plate is moving? The Pacific Plate is moving northwest as new oceanic crust is formed by the mid-ocean ridge in the SE and crust is subducted in the trenches along the western boundaries of the plate. 4) Locate the Hawaiian-Emperor Seamount Chain. Notice the bend in the chain. How might this ...
... Pacific Plate is moving? The Pacific Plate is moving northwest as new oceanic crust is formed by the mid-ocean ridge in the SE and crust is subducted in the trenches along the western boundaries of the plate. 4) Locate the Hawaiian-Emperor Seamount Chain. Notice the bend in the chain. How might this ...
The Layers of Earth
... portion of the mantle is made of solid rock like the crust. Some of the upper mantle is semimolten. It is able to flow. It is like thick, gooey syrup. This allows the rigid, crustal plates resting on the upper mantle to float. Even though we can't feel it, the plates are slowly moving all of the tim ...
... portion of the mantle is made of solid rock like the crust. Some of the upper mantle is semimolten. It is able to flow. It is like thick, gooey syrup. This allows the rigid, crustal plates resting on the upper mantle to float. Even though we can't feel it, the plates are slowly moving all of the tim ...
Antipodal hotspots and bipolar catastrophes: Were oceanic large
... difference) or overlap. Monte Carlo simulations indicate that the antipodal primary hotspots’ locations and ages are not due to chance at the N 99% confidence level ( p b 0.01). All hotspot pairs include at least one oceanic hotspot, and these are consistently opposite those hotspots related to larg ...
... difference) or overlap. Monte Carlo simulations indicate that the antipodal primary hotspots’ locations and ages are not due to chance at the N 99% confidence level ( p b 0.01). All hotspot pairs include at least one oceanic hotspot, and these are consistently opposite those hotspots related to larg ...
Why Volcanoes Form
... Lava that flows at divergent boundaries forms from melted mantle rock. As a result, this lava is rich in the elements iron and magnesium and relatively poor in silica. Because of its composition, lava from mantle rock cools to form dark-colored rock. The term mafic describes magma, lava, and rocks—s ...
... Lava that flows at divergent boundaries forms from melted mantle rock. As a result, this lava is rich in the elements iron and magnesium and relatively poor in silica. Because of its composition, lava from mantle rock cools to form dark-colored rock. The term mafic describes magma, lava, and rocks—s ...
Rundić, Lj. Centenary anniversary of the Theory of continental drift by
... ted by earthquakes. Recently, historians of science have uncovered nascent hints of continental drift in the works of Francis Bacon, and Comte de Buffon. But it was the genius of Wegener that assembled widely divergent lines of evidence into the first coherent model of continental motion. He promote ...
... ted by earthquakes. Recently, historians of science have uncovered nascent hints of continental drift in the works of Francis Bacon, and Comte de Buffon. But it was the genius of Wegener that assembled widely divergent lines of evidence into the first coherent model of continental motion. He promote ...
QAD-Answers
... A Sea floor spreading occurs when new material is added to the Earth’s crust when the older crust is pulled apart at a mid ocean ridge. D Occurs at mid-ocean ridges Older material is pulled away New material added to ocean floor ...
... A Sea floor spreading occurs when new material is added to the Earth’s crust when the older crust is pulled apart at a mid ocean ridge. D Occurs at mid-ocean ridges Older material is pulled away New material added to ocean floor ...
3.8 Rocks and Processes of the Rock Cycle
... The rock beneath the Earth’s surface is sometimes heated to high enough temperatures that it melts to create magma. Different magmas have different composition and contain whatever elements were in the rock or rocks that melted. Magmas also contain gases. The main elements are the same as the elemen ...
... The rock beneath the Earth’s surface is sometimes heated to high enough temperatures that it melts to create magma. Different magmas have different composition and contain whatever elements were in the rock or rocks that melted. Magmas also contain gases. The main elements are the same as the elemen ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.