Physics 106P: Lecture 15 Notes
... It is equal to the force used to throw it up but in opposite direction It is equal to the weight of the rock Its direction changes from up to down Its magnitude is equal to the sum of the force used to throw it up and its weight ...
... It is equal to the force used to throw it up but in opposite direction It is equal to the weight of the rock Its direction changes from up to down Its magnitude is equal to the sum of the force used to throw it up and its weight ...
Physics 104 - How Things Work
... o 10 miles east of my house could both be same location! Position is an example of a vector quantity. Both magnitude and direction If a ball is moving, then its position is changing. Velocity o How quickly the position is changing o Speed the ball is moving & direction it is heading. ...
... o 10 miles east of my house could both be same location! Position is an example of a vector quantity. Both magnitude and direction If a ball is moving, then its position is changing. Velocity o How quickly the position is changing o Speed the ball is moving & direction it is heading. ...
3. Newton`s laws
... of the very small, the very fast, or the very large, that Newton's laws fail. Quantum mechanics ( 1920), special relativity ( 1905), and general relativity ( 1915) are needed to describe the physics in these three domains. We will brie y talk about these three theories at the end of the semester. ...
... of the very small, the very fast, or the very large, that Newton's laws fail. Quantum mechanics ( 1920), special relativity ( 1905), and general relativity ( 1915) are needed to describe the physics in these three domains. We will brie y talk about these three theories at the end of the semester. ...
Concept Questions
... A steel washer is mounted on a cylindrical rotor . The inner radius of the washer is R. A massless string, with an object of mass m attached to the other end, is wrapped around the side of the rotor and passes over a massless pulley. Assume that there is a constant frictional torque about the axis o ...
... A steel washer is mounted on a cylindrical rotor . The inner radius of the washer is R. A massless string, with an object of mass m attached to the other end, is wrapped around the side of the rotor and passes over a massless pulley. Assume that there is a constant frictional torque about the axis o ...
Nonconservative Forces
... is a good example of a nonconservative force. As illustrated in Figure 1, work done against friction depends on the length of the path between the starting and ending points. Because of this dependence on path, there is no potential energy associated with nonconservative forces. An important charact ...
... is a good example of a nonconservative force. As illustrated in Figure 1, work done against friction depends on the length of the path between the starting and ending points. Because of this dependence on path, there is no potential energy associated with nonconservative forces. An important charact ...
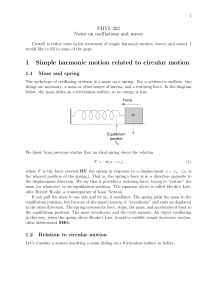
1 Simple harmonic motion related to circular motion
... We know that the potential energy function for a spring is (1/2)kx2 , which we found by taking the area under the curve of the force function F = kx (recall, this is force on the spring, so there is no negative sign.) Another way to describe conditions for SHO is that the potential energy function i ...
... We know that the potential energy function for a spring is (1/2)kx2 , which we found by taking the area under the curve of the force function F = kx (recall, this is force on the spring, so there is no negative sign.) Another way to describe conditions for SHO is that the potential energy function i ...
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... because of a force called friction. Isaac Newton built on Galileo's thoughts about motion. Newton's first law of motion declares that a force is not needed to keep an object in motion. Slide a book across a table and watch it slide to a stop. The book in motion on the table top does not come to rest ...
... because of a force called friction. Isaac Newton built on Galileo's thoughts about motion. Newton's first law of motion declares that a force is not needed to keep an object in motion. Slide a book across a table and watch it slide to a stop. The book in motion on the table top does not come to rest ...
Chapter 11
... In general, the motion of a pendulum is not simple harmonic However, for small angles, it becomes simple harmonic › In general, angles < 15° are small enough › sin θ = θ › Ft = - m g θ This force obeys Hooke’s Law ...
... In general, the motion of a pendulum is not simple harmonic However, for small angles, it becomes simple harmonic › In general, angles < 15° are small enough › sin θ = θ › Ft = - m g θ This force obeys Hooke’s Law ...
Lesson #8: The Link Between Force and Motion
... unbalanced force acting upon it. The presence of an unbalanced force will accelerate an object changing either its speed, its direction, or both its speed and direction. Newton’s Second Law Newton's second law of motion predicts the behavior of objects when all existing forces are not balanced. ...
... unbalanced force acting upon it. The presence of an unbalanced force will accelerate an object changing either its speed, its direction, or both its speed and direction. Newton’s Second Law Newton's second law of motion predicts the behavior of objects when all existing forces are not balanced. ...