Newton`s Laws
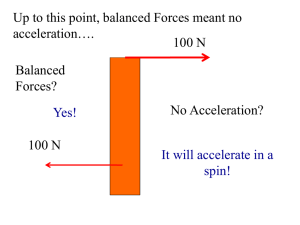
... The net force is NOT zero. Forces on different objects cannot be added to make zero ...
... The net force is NOT zero. Forces on different objects cannot be added to make zero ...
Newton"s 1st
... ____________________. (motion, change in motion, increase in motion, or decrease in motion) The force exerted by air is a ____________ force. (small, balanced, or negative) The equation F= _____ is a mathematical model of Newton’s 2nd Law. ...
... ____________________. (motion, change in motion, increase in motion, or decrease in motion) The force exerted by air is a ____________ force. (small, balanced, or negative) The equation F= _____ is a mathematical model of Newton’s 2nd Law. ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
... A net torque would produce an angular acceleration. An object spinning at a constant rate will accelerate if the mass is redistributed farther or closer to the axis of rotation. Rotational Inertia is the resistance of a rotating object to changes in its rotational velocity-- it depends on mass, dist ...
1.9 Simple Harmonic Motion
... Not only the mass oscillates when it is released, but also the spring itself. The period of oscillation is affected by the mass of the spring. ...
... Not only the mass oscillates when it is released, but also the spring itself. The period of oscillation is affected by the mass of the spring. ...
Potential Energy
... 2. Depends upon object mass and object height. 3. The energy an object possesses due to its motion. 4. The amount is expressed using the unit joule (abbreviated J). 5. The energy stored in an object due to its position (or height). 6. The amount depends upon the arbitrarily assigned zero level. 7. D ...
... 2. Depends upon object mass and object height. 3. The energy an object possesses due to its motion. 4. The amount is expressed using the unit joule (abbreviated J). 5. The energy stored in an object due to its position (or height). 6. The amount depends upon the arbitrarily assigned zero level. 7. D ...
File
... The elephant and the feather each have the same force of gravity. The elelphant has more mass, yet both elephant and feather experience the same force of gravity. The elephant experiences a greater force of gravity, yet both the elephant and the feather have the same mass. On earth, all objects (whe ...
... The elephant and the feather each have the same force of gravity. The elelphant has more mass, yet both elephant and feather experience the same force of gravity. The elephant experiences a greater force of gravity, yet both the elephant and the feather have the same mass. On earth, all objects (whe ...
Recitation 1
... Plugging our A and ω into our x(t) yields the equation of motion we set out to find. (b) To find the maximum speed, we could either take the derivative of x(t) (like we did in 12.2), or realize that the derivative will have another factor of ω in it’s amplitude and jump to the answer vmax = Aω = 6π ...
... Plugging our A and ω into our x(t) yields the equation of motion we set out to find. (b) To find the maximum speed, we could either take the derivative of x(t) (like we did in 12.2), or realize that the derivative will have another factor of ω in it’s amplitude and jump to the answer vmax = Aω = 6π ...
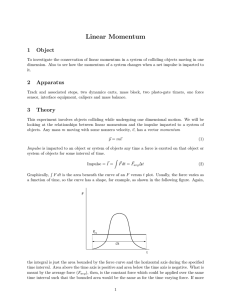
Linear Momentum - Gonzaga Physics Department
... zero. However, Newton’s 3rd law does not imply that each object will do the same amount of ...
... zero. However, Newton’s 3rd law does not imply that each object will do the same amount of ...
A 2.0-kg object moving at 5.0 m/s encounters a 30
... An impulse occurs when a _____ is acting upon an object for a given amount of _____ in order to cause a change in ____. Enter the letters of the three answers in their respective order. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. ...
... An impulse occurs when a _____ is acting upon an object for a given amount of _____ in order to cause a change in ____. Enter the letters of the three answers in their respective order. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. ...
Measurement and Force
... A. As mass decreases, the net force will increase if the acceleration remains constant. B. As mass and acceleration increase together, so will the net force. C. As mass increases so will the acceleration, but force will remain constant. D. As acceleration increases and the mass remains constant, the ...
... A. As mass decreases, the net force will increase if the acceleration remains constant. B. As mass and acceleration increase together, so will the net force. C. As mass increases so will the acceleration, but force will remain constant. D. As acceleration increases and the mass remains constant, the ...
Physics 20
... 2. define, operationally, and compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. 3. explain, qualitatively and quantitatively, uniform and uniformly accelerated motion when provided with written descriptions and numerical and graphical data. 4. interpret, quantitatively, the motion of one object rel ...
... 2. define, operationally, and compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. 3. explain, qualitatively and quantitatively, uniform and uniformly accelerated motion when provided with written descriptions and numerical and graphical data. 4. interpret, quantitatively, the motion of one object rel ...
Chapter 4 Conservation laws for systems of particles
... 1. The linear impulse of a force 2. The angular impulse of a force 3. The power transmitted by a force 4. The work done by a force 5. The potential energy of a force. 6. The linear momentum of a particle (or system of particles) 7. The angular momentum of a particle, or system of particles. 8. The k ...
... 1. The linear impulse of a force 2. The angular impulse of a force 3. The power transmitted by a force 4. The work done by a force 5. The potential energy of a force. 6. The linear momentum of a particle (or system of particles) 7. The angular momentum of a particle, or system of particles. 8. The k ...
TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS
... where: C = 2.00 and vc and fc are both measured in lbf/in2. What numerical value should be used for C if vc and fc are both measured in MPa? a. 6.02 b. 0.166 c. 2.00 d. 0.500 e. 1.00 17. If the mass of an object is 13.2 lbm on earth, what is the weight on the moon where the acceleration of gravity i ...
... where: C = 2.00 and vc and fc are both measured in lbf/in2. What numerical value should be used for C if vc and fc are both measured in MPa? a. 6.02 b. 0.166 c. 2.00 d. 0.500 e. 1.00 17. If the mass of an object is 13.2 lbm on earth, what is the weight on the moon where the acceleration of gravity i ...
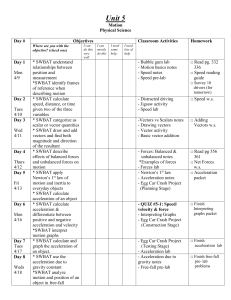
Unit 5 plan motion
... *SWBAT identify frames of reference when describing motion * SWBAT calculate speed, distance, or time given two of the three variables * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of bal ...
... *SWBAT identify frames of reference when describing motion * SWBAT calculate speed, distance, or time given two of the three variables * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of bal ...
Chapter 11
... A non-zero torque produces a change in the angular momentum The result of the change in angular momentum is a precession about the z axis The direction of the angular momentum is changing The precessional motion is the motion of the symmetry axis about the vertical The precession is usually slow rel ...
... A non-zero torque produces a change in the angular momentum The result of the change in angular momentum is a precession about the z axis The direction of the angular momentum is changing The precessional motion is the motion of the symmetry axis about the vertical The precession is usually slow rel ...
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY
... when θ = 0°. Neglect the mass of the pistons. Find: The angular velocity of rod AB at θ = 0° if the rod is released from rest when θ = 30°. Plan: Use the energy conservation equation since all forces are conservative and distance is a parameter (represented here by θ). The potential energy and kinet ...
... when θ = 0°. Neglect the mass of the pistons. Find: The angular velocity of rod AB at θ = 0° if the rod is released from rest when θ = 30°. Plan: Use the energy conservation equation since all forces are conservative and distance is a parameter (represented here by θ). The potential energy and kinet ...
Monday, Oct. 7, 2002
... A small ball of mass 2.00g is released from rest in a large vessel filled with oil, where it experiences a resistive force proportional to its speed. The ball reaches a terminal speed of 5.00 cm/s. Determine the time constant t and the time it takes the ball to reach 90% of its terminal speed. ...
... A small ball of mass 2.00g is released from rest in a large vessel filled with oil, where it experiences a resistive force proportional to its speed. The ball reaches a terminal speed of 5.00 cm/s. Determine the time constant t and the time it takes the ball to reach 90% of its terminal speed. ...
Force and Motion {PowerPoint}
... Answer: False Newton’s First Law of Motion states: Objects in motion stay in motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... Answer: False Newton’s First Law of Motion states: Objects in motion stay in motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an outside force. ...