Physical Science Energy Chapter 9 Extra Credit
... _____ 17. Which of the following can measure the energy from the sun? a. radiometer b. energy meter c. thermometer d. thermal meter _____ 18. When is the potential energy the greatest in a roller coaster? a. at the bottom of the first hill b. at the top of the first hill c. at the top of the second ...
... _____ 17. Which of the following can measure the energy from the sun? a. radiometer b. energy meter c. thermometer d. thermal meter _____ 18. When is the potential energy the greatest in a roller coaster? a. at the bottom of the first hill b. at the top of the first hill c. at the top of the second ...
’ Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s
... and F2 = +3000 N acting on an object, the plus signs indicating that the forces act along the +x axis. A third force F3 also acts on the object but is not shown in the figure. The object is moving with a constant velocity of +750 m/s along the x axis. Find the magnitude and direction of F3. ...
... and F2 = +3000 N acting on an object, the plus signs indicating that the forces act along the +x axis. A third force F3 also acts on the object but is not shown in the figure. The object is moving with a constant velocity of +750 m/s along the x axis. Find the magnitude and direction of F3. ...
Conservation of Energy
... in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape or form. Example: An object being held up has potential energy because of its position (gravitational potential energy). Example: A compressed spring has potential energy (elastic potential energy to spring open). ...
... in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape or form. Example: An object being held up has potential energy because of its position (gravitational potential energy). Example: A compressed spring has potential energy (elastic potential energy to spring open). ...
work, power and energy
... The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position or state is called potential energy. Expression for Potential Energy: Consider a body of mass ‘m’ initially at rest on the surface of the earth. The force acting on the body is its weight mg, vertically downwards. Force required to lift the bo ...
... The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position or state is called potential energy. Expression for Potential Energy: Consider a body of mass ‘m’ initially at rest on the surface of the earth. The force acting on the body is its weight mg, vertically downwards. Force required to lift the bo ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 5. Universal Laws of Motion
... • Any object which is being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be in a state of free fall. There are two important motion characteristics which are true of free-falling objects: – Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance. – All free-falling objects (on Earth) accelerate d ...
... • Any object which is being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be in a state of free fall. There are two important motion characteristics which are true of free-falling objects: – Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance. – All free-falling objects (on Earth) accelerate d ...
Chapter 5
... present, then the full Work-Energy Theorem must be used instead of the equation for Conservation of Energy Often techniques from previous chapters will need to be employed ...
... present, then the full Work-Energy Theorem must be used instead of the equation for Conservation of Energy Often techniques from previous chapters will need to be employed ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 1. Misconception - A force is needed to continue the objects motion An object can fly through space with a constant velocity as long as no external forces act on it (unbalanced force). 2. Misconception – There are no forces in spaces A spaceship can be accelerated if acted upon an external force (ex ...
... 1. Misconception - A force is needed to continue the objects motion An object can fly through space with a constant velocity as long as no external forces act on it (unbalanced force). 2. Misconception – There are no forces in spaces A spaceship can be accelerated if acted upon an external force (ex ...
Walker3_Lecture_Ch08 - Tennessee State University
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
mass and weight - Project PHYSNET
... This problem is really the same as in [S-1] and [S-2] with a few new twists. The only new point is that you must recognize that while the third law says the ratio of the acceleration of the two cars is always the same, the connection between velocity and acceleration means the velocities always have ...
... This problem is really the same as in [S-1] and [S-2] with a few new twists. The only new point is that you must recognize that while the third law says the ratio of the acceleration of the two cars is always the same, the connection between velocity and acceleration means the velocities always have ...
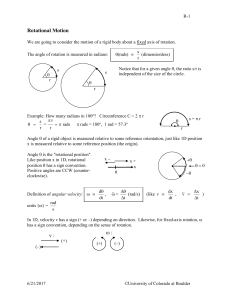
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... r = "lever arm" = distance from axis to point of application of force F = component of force perpendicular to lever arm Example: Wheel on a fixed axis: Notice that only the perpendicular component of the force F will rotate the wheel. The component of the force parallel to the lever arm (F||) has n ...
... r = "lever arm" = distance from axis to point of application of force F = component of force perpendicular to lever arm Example: Wheel on a fixed axis: Notice that only the perpendicular component of the force F will rotate the wheel. The component of the force parallel to the lever arm (F||) has n ...
The Nature of Force
... Newton’s first law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object that is moving at constant velocity will continue moving at constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s first law of motion is also called the law of inertia. Inertia explains ...
... Newton’s first law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object that is moving at constant velocity will continue moving at constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s first law of motion is also called the law of inertia. Inertia explains ...
Energy - Images
... This is the definition of work. The magnitude of the force vector times the magnitude of the displacement vector times the cosine of the angle between the vectors. ...
... This is the definition of work. The magnitude of the force vector times the magnitude of the displacement vector times the cosine of the angle between the vectors. ...