Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... Newton’s second law applies. – For example, a “stationary” reference frame or one that moves with constant velocity. – This is sort of a circular argument but it is still useful. ...
... Newton’s second law applies. – For example, a “stationary” reference frame or one that moves with constant velocity. – This is sort of a circular argument but it is still useful. ...
Force and Motion {PowerPoint}
... Answer: False Newton’s First Law of Motion states: Objects in motion stay in motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... Answer: False Newton’s First Law of Motion states: Objects in motion stay in motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
Concept Summary
... o Acceleration of a freely falling body called acceleration due to gravity Magnitude at Earth’s surface = g = 9.80 m/s2 = 32.3 ft/s2 Always directed downward toward center of the Earth o In absence of air resistance, book and feather fall with same acceleration and land at same time o Any object ...
... o Acceleration of a freely falling body called acceleration due to gravity Magnitude at Earth’s surface = g = 9.80 m/s2 = 32.3 ft/s2 Always directed downward toward center of the Earth o In absence of air resistance, book and feather fall with same acceleration and land at same time o Any object ...
ce-phy ii
... (2000-CE-PHY II - 2) 2. It is said that Galileo Galilei (1564-1642), an Italian scientist, dropped a small iron ball and a large cannon ball from the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. He found that the two balls reached the ground at almost the same time. Which of the following is/are correct deduct ...
... (2000-CE-PHY II - 2) 2. It is said that Galileo Galilei (1564-1642), an Italian scientist, dropped a small iron ball and a large cannon ball from the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. He found that the two balls reached the ground at almost the same time. Which of the following is/are correct deduct ...
MATH10222, Chapter 2: Newtonian Dynamics 1 Newton`s Laws 2
... Having considered motion confined to a line in the previous section, we now go on to consider motion confined to a plane. At any given instant in time the particle’s position relative to the origin of a coordinate system is denoted by r(t). At this same instant the particle is moving in the directio ...
... Having considered motion confined to a line in the previous section, we now go on to consider motion confined to a plane. At any given instant in time the particle’s position relative to the origin of a coordinate system is denoted by r(t). At this same instant the particle is moving in the directio ...
Lecture19
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
Newton`s 1st Law of Motion
... boy sits on it. The coefficient of friction for the snow and metal sled is 0.012. What force is necessary to pull the sled at constant speed? (Hint: the applied force is equal, but opposite direction to the force of friction.) ...
... boy sits on it. The coefficient of friction for the snow and metal sled is 0.012. What force is necessary to pull the sled at constant speed? (Hint: the applied force is equal, but opposite direction to the force of friction.) ...
ƒ A S ƒ ƒ B
... Using Newton’s first law: When a body is in equilibrium in an inertial frame of reference—that is, either at rest or moving with constant velocity—the vector sum of forces acting on it must be zero (Newton’s first law). Free-body diagrams are essential in identifying the forces that act on the body ...
... Using Newton’s first law: When a body is in equilibrium in an inertial frame of reference—that is, either at rest or moving with constant velocity—the vector sum of forces acting on it must be zero (Newton’s first law). Free-body diagrams are essential in identifying the forces that act on the body ...
Bumper Cars Observations about Bumper Cars
... Moving cars tend to stay moving Changing a car’s motion takes time Impacts alter velocities and angular velocities Cars often appear to exchange their motions The fullest cars are the hardest to redirect The least-full cars get slammed during collisions ...
... Moving cars tend to stay moving Changing a car’s motion takes time Impacts alter velocities and angular velocities Cars often appear to exchange their motions The fullest cars are the hardest to redirect The least-full cars get slammed during collisions ...
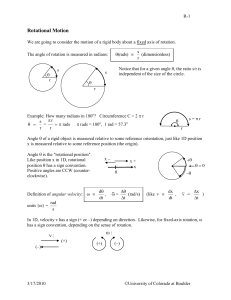
Rotational Motion - University of Colorado Boulder
... r = "lever arm" = distance from axis to point of application of force F = component of force perpendicular to lever arm Example: Wheel on a fixed axis: Notice that only the perpendicular component of the force F will rotate the wheel. The component of the force parallel to the lever arm (F||) has n ...
... r = "lever arm" = distance from axis to point of application of force F = component of force perpendicular to lever arm Example: Wheel on a fixed axis: Notice that only the perpendicular component of the force F will rotate the wheel. The component of the force parallel to the lever arm (F||) has n ...
The Answer
... 49. What is the net force (in Newtons) causing the system of masses to accelerate? (0.238 kg ─0.235 kg)x 9.8 m/s2 = 0.0294 N a) slowly b) with a sudden jerk (inertia!) 47. (From the inertia activity stations) When a cork is tied to a string in a flask of water and the flask is quickly accelerated to ...
... 49. What is the net force (in Newtons) causing the system of masses to accelerate? (0.238 kg ─0.235 kg)x 9.8 m/s2 = 0.0294 N a) slowly b) with a sudden jerk (inertia!) 47. (From the inertia activity stations) When a cork is tied to a string in a flask of water and the flask is quickly accelerated to ...
lec12 - UConn Physics
... This is an example of turning one form of energy into another (thermal energy). ...
... This is an example of turning one form of energy into another (thermal energy). ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... (This question is from Regular Conceptual Physics) 54. The force of air resistance acting on an elephant, compared to the force of air resistance acting on a feather is . . a) greater for the elephant The effect of the air resistance is greater on the feather because it is lighter in weight, but the ...
... (This question is from Regular Conceptual Physics) 54. The force of air resistance acting on an elephant, compared to the force of air resistance acting on a feather is . . a) greater for the elephant The effect of the air resistance is greater on the feather because it is lighter in weight, but the ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... Do they find that acceleration is proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass? Numerically, are their results consistent with the equation F = ma? You may wish to point out that the experiment can only show proportionality. In other words, we can only conclude that F = kma, where k is ...
... Do they find that acceleration is proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass? Numerically, are their results consistent with the equation F = ma? You may wish to point out that the experiment can only show proportionality. In other words, we can only conclude that F = kma, where k is ...