WAVE MECHANICS AND QUANTUM NUMBERS
... 5. space orbital- highly probable location where an electron can be found 6. electron cloud- the size and shape of an atom as defined by the electron paths B. Quantum Theory- describes the wave properties of electrons in a mathematical fashion; it utilizes quantum numbers that describe the unique en ...
... 5. space orbital- highly probable location where an electron can be found 6. electron cloud- the size and shape of an atom as defined by the electron paths B. Quantum Theory- describes the wave properties of electrons in a mathematical fashion; it utilizes quantum numbers that describe the unique en ...
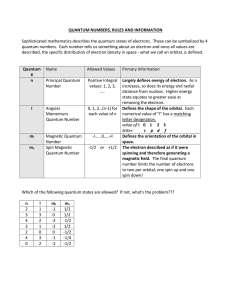
Quantum Number Table
... Largely defines energy of electron. As n increases, so does its energy and radial distance from nucleus. Higher energy state equates to greater ease at removing the electron. Defines the shape of the orbital. Each numerical value of "l" has a matching letter designation. value of l: 0 1 2 3 letter: ...
... Largely defines energy of electron. As n increases, so does its energy and radial distance from nucleus. Higher energy state equates to greater ease at removing the electron. Defines the shape of the orbital. Each numerical value of "l" has a matching letter designation. value of l: 0 1 2 3 letter: ...
A1979HZ36600001
... mechanics’ description of the state of a system is very different from those of classical theories, which give positions, veloci-ties, etc. of the constituents. Quantum mechanics describes the state of the system by a vector in an abstract space, called complex Hilbert space, a space of infinite dim ...
... mechanics’ description of the state of a system is very different from those of classical theories, which give positions, veloci-ties, etc. of the constituents. Quantum mechanics describes the state of the system by a vector in an abstract space, called complex Hilbert space, a space of infinite dim ...
Materials Computation Center R.M. Martin and J.P. Leburton
... semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) for applications in quantum information processing. Approach: We concentrate on material and design parameters that influence the exchange interaction between conduction electrons in realistic double QDs. For this purpose, we use a combined approach based on density ...
... semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) for applications in quantum information processing. Approach: We concentrate on material and design parameters that influence the exchange interaction between conduction electrons in realistic double QDs. For this purpose, we use a combined approach based on density ...
PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #3
... (1) We discussed in class the first order energy shifts ∆K from “relativistic kinetic energy.” ...
... (1) We discussed in class the first order energy shifts ∆K from “relativistic kinetic energy.” ...
Quantum phase transition - Condensed Matter Theory and Quantum
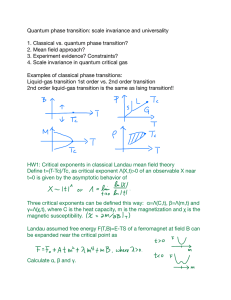
... Quantum phase transition: scale invariance and universality ...
... Quantum phase transition: scale invariance and universality ...
What is Entanglement? Entangled Fields Looking at Entangled
... cannot really be considered as separate objects, but are intrinsically connected or “entangled” with each other. For example, performing a measurement on one, such as measuring the particles spin as in the diagram above, instantaneously affects the result of measuring the other. This phenomena occur ...
... cannot really be considered as separate objects, but are intrinsically connected or “entangled” with each other. For example, performing a measurement on one, such as measuring the particles spin as in the diagram above, instantaneously affects the result of measuring the other. This phenomena occur ...