Plate Tectonics - Physiographic Chart of the Sea Floor
... Write a short essay that explains the relationship between Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. What causes E.Q’s? Where do they occur? Why? Is the depth of the E.Q. related to the type of plate boundary? Why? ...
... Write a short essay that explains the relationship between Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. What causes E.Q’s? Where do they occur? Why? Is the depth of the E.Q. related to the type of plate boundary? Why? ...
subduction zone
... The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. The word, tectonic, refers to ...
... The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. The word, tectonic, refers to ...
File
... ___T_________ 10. In a strike-slip fault, the rocks on either side of the fault slip past each other ...
... ___T_________ 10. In a strike-slip fault, the rocks on either side of the fault slip past each other ...
Earth`s Landforms
... extreme heat from core causes mantle to create pressure on crust forcing crust to rise pushing large blocks of rock upward mountains, plateaus ...
... extreme heat from core causes mantle to create pressure on crust forcing crust to rise pushing large blocks of rock upward mountains, plateaus ...
Print › Explaining plate collisions | Quizlet
... Explain how volcanoes form over hot-spot (4 marks) ...
... Explain how volcanoes form over hot-spot (4 marks) ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Igneous rocks are mixtures of minerals • Melting occurs over a range of temperatures • Produces a magma with a higher silica content than the original rock ...
... • Igneous rocks are mixtures of minerals • Melting occurs over a range of temperatures • Produces a magma with a higher silica content than the original rock ...
ES11_Ch09_Lecture
... • Igneous rocks are mixtures of minerals • Melting occurs over a range of temperatures • Produces a magma with a higher silica content than the original rock ...
... • Igneous rocks are mixtures of minerals • Melting occurs over a range of temperatures • Produces a magma with a higher silica content than the original rock ...
Exam #2: study guide
... Seismology: Seismogram; P and S wave arrival times; The types of waves and how they move Locating an earthquake Measuring earthquakes The Japan earthquake: tectonic setting, magnitude, hazards Tsunami : causes; how tsunami travel on shore and through open ocean; relationship between depth ...
... Seismology: Seismogram; P and S wave arrival times; The types of waves and how they move Locating an earthquake Measuring earthquakes The Japan earthquake: tectonic setting, magnitude, hazards Tsunami : causes; how tsunami travel on shore and through open ocean; relationship between depth ...
Volcano formation dbq
... beneath the other plate. The subducted plate is melted and the molten rock rises to the surface forming a volcano. The ring of fire, the area around the Pacific Ocean that has a high level of volcanic activity, is an excellent example of plate boundary volcanoes. ...
... beneath the other plate. The subducted plate is melted and the molten rock rises to the surface forming a volcano. The ring of fire, the area around the Pacific Ocean that has a high level of volcanic activity, is an excellent example of plate boundary volcanoes. ...
CompositionoftheEarth
... Earthquakes occur at transform plate boundaries. They can happen elsewhere, but that is fairly rare. The spot where an earthquake starts is called the epicenter. Earthquakes form when jagged rocks get caught on one another causing pressure/stress to build until the rocks break and move sudde ...
... Earthquakes occur at transform plate boundaries. They can happen elsewhere, but that is fairly rare. The spot where an earthquake starts is called the epicenter. Earthquakes form when jagged rocks get caught on one another causing pressure/stress to build until the rocks break and move sudde ...
Shapes of igneous bodies
... Pyroclastic volcano (cinder or scoria cones, 2 km across and < 0.3 km high) volcanic complex Dome lava flow ash-flow tuff (ignimbrite) flood basalt caldera Extrusive bodies – Fissure Landforms Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic ...
... Pyroclastic volcano (cinder or scoria cones, 2 km across and < 0.3 km high) volcanic complex Dome lava flow ash-flow tuff (ignimbrite) flood basalt caldera Extrusive bodies – Fissure Landforms Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic ...
presentation source
... Tropical cyclones, hurricanes and typhoons are intense storms that develop over warm tropical areas. Tornadoes are a rapidly rotating vortice of air that forms a funnel. When they touch the ground, they can be one of the most deadly natural hazards. Floods can be nothing more than a normal but not ...
... Tropical cyclones, hurricanes and typhoons are intense storms that develop over warm tropical areas. Tornadoes are a rapidly rotating vortice of air that forms a funnel. When they touch the ground, they can be one of the most deadly natural hazards. Floods can be nothing more than a normal but not ...
Earth and the Moon - Nutley Public Schools
... Moisture from _______ and ______ react chemically with exposed _________ Over time, ________ develops Wind, waves, and birds scatter ________, ______________ and _________ ________ and _________ appear and break down rock Ocean currents bring _________ ...
... Moisture from _______ and ______ react chemically with exposed _________ Over time, ________ develops Wind, waves, and birds scatter ________, ______________ and _________ ________ and _________ appear and break down rock Ocean currents bring _________ ...
Describing Matter & Energy
... Magma forces its way upward through cracks in the crust, but overlying rock layers keep the magma from reaching the surface. The magma forces the rock layers to bend upward into a dome shape. When the rock layers wear away, the dome is exposed. ...
... Magma forces its way upward through cracks in the crust, but overlying rock layers keep the magma from reaching the surface. The magma forces the rock layers to bend upward into a dome shape. When the rock layers wear away, the dome is exposed. ...
TOPIC WORD DEFINITION Volcanoes aftershock An earthquake
... A steep, cone-‐shaped hill or small mountain made of volcanic ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around a volcano’s opening. A tall, cone-‐shaped mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers ...
... A steep, cone-‐shaped hill or small mountain made of volcanic ash, cinders, and bombs piled up around a volcano’s opening. A tall, cone-‐shaped mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers ...
Volcanoes - SPS186.org
... last ten thousand years. Every year, about thirtyfive or forty volcanoes erupt at various places around the world. Sometimes observers are only able to see a small amount of smoke or steam emerging from an erupting volcano. Some volcanoes are always erupting, but they do it very slowly. Others, like ...
... last ten thousand years. Every year, about thirtyfive or forty volcanoes erupt at various places around the world. Sometimes observers are only able to see a small amount of smoke or steam emerging from an erupting volcano. Some volcanoes are always erupting, but they do it very slowly. Others, like ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Igneous rocks are mixtures of minerals • Melting occurs over a range of temperatures • Produces a magma with a higher silica content than the original rock ...
... • Igneous rocks are mixtures of minerals • Melting occurs over a range of temperatures • Produces a magma with a higher silica content than the original rock ...
DYNAMIC EARTH NOTES
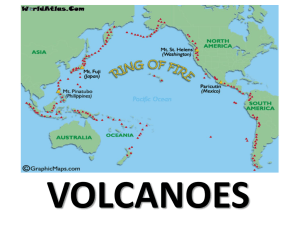
... range before the continents separated. (EX: Appalachian Mts correlate with Mt’s in Africa and Europe) II. PLATE TECTONICS: MANY SCIENTISTS - 1960’s - EXPLAINED PLATE MOTION a. Earthquake patterns: earthquakes tend to occur in areas along plate boundaries (Ex: The Ring of Fire) b. Paleomagnetism: whe ...
... range before the continents separated. (EX: Appalachian Mts correlate with Mt’s in Africa and Europe) II. PLATE TECTONICS: MANY SCIENTISTS - 1960’s - EXPLAINED PLATE MOTION a. Earthquake patterns: earthquakes tend to occur in areas along plate boundaries (Ex: The Ring of Fire) b. Paleomagnetism: whe ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawaiian Islands ...
... tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawaiian Islands ...
The Rock cycle: Initially proposed by James Hutton
... AA lava: Blocky, sharp and rough lava Columnar Joints: 5- to 7-sided columns of basalt. Produced by slow cooling. Pillow Lava: Surface like pile of pillows. Erupted under water Pyroclastics: (Tephra) Lava Fragments. Bomb: Large pieces. More than 64 mm in diameter. Cinders: (Lapilli) Up to 64mm Ash: ...
... AA lava: Blocky, sharp and rough lava Columnar Joints: 5- to 7-sided columns of basalt. Produced by slow cooling. Pillow Lava: Surface like pile of pillows. Erupted under water Pyroclastics: (Tephra) Lava Fragments. Bomb: Large pieces. More than 64 mm in diameter. Cinders: (Lapilli) Up to 64mm Ash: ...
6th Grade Honors Final Exam Review 2013
... of Fire – major volcanic belt in the Pacific Ocean Island arc – string of islands which can form from the collision of two oceanic plates Quiet Eruption – low silica content in magma Explosive Eruption – high silica content in magma ...
... of Fire – major volcanic belt in the Pacific Ocean Island arc – string of islands which can form from the collision of two oceanic plates Quiet Eruption – low silica content in magma Explosive Eruption – high silica content in magma ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.