* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download presentation source
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Milankovitch cycles wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
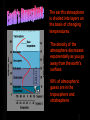
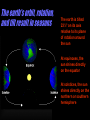
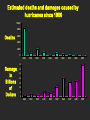
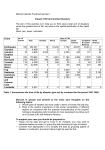
The earth's atmosphere is divided into layers on the basis of changing temperatures. The density of the atmosphere decreases exponentially as you go away from the earth's surface. 99% of atmospheric gases are in the troposphere and stratosphere. Two factors add complexity to these patterns: • The coriolis effect produced by the earth's rotation on its axis • The earth's topography The earth's orbit, rotation, and tilt result in seasons The earth is tilted 23½° on its axis relative to its plane of rotation around the sun At equinoxes, the sun shines directly on the equator At solstices, the sun shines directly on the northern or southern hemisphere Natural hazards are generally rare, but normal, natural events. Natural hazards only become disasters if people are present. Earthquakes Earthquakes are shock waves that result when large masses of rock in the earth's crust move relative to each other Volcanoes Volcanoes are found at places in the earth's crust where hot, molten rock (magma) wells up to the surface; found at tectonic plate boundaries and hot spots Land Instability Occurs in many places; includes: landslides, rockfalls, slumps Barrier Island coast Impacts of a jetty on beach sand deposition and erosion Tropical cyclones, hurricanes and typhoons are intense storms that develop over warm tropical areas. Tornadoes are a rapidly rotating vortice of air that forms a funnel. When they touch the ground, they can be one of the most deadly natural hazards. Floods can be nothing more than a normal but not frequent natural occurrence but seem disastrous from a human perspective. Cumulatively, floods are among the most destructive of natural hazards. Wildfire Coastal storm surges Drought (1988 drought – est. cost of 39 Billion $) Hail Estimated deaths and damages caused by hurricanes since 1900 10000 8000 Deaths 6000 4000 2000 0 Damage in Billions of Dollars 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Estimated deaths from natural hazards during 1965 to 1995 (tropical storm) (earthquake) (flood) (slides) (volcano) Example slides of various natural disasters such as: Earthquakes, Tornadoes, Volcanoes and Wildfires are not included on the website.