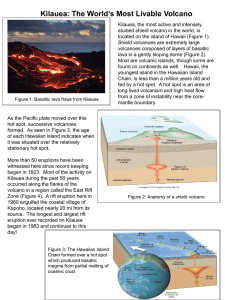
Kilauea: The World`s Most Livable Volcano
... tubes carrying lava from the volcanic vent to the flow’s leading edge. These openings develop when the interior or a flow remains hot long after the surface hardens. In these circumstances, still-molten lava within the tubes continues its forward motion leaving behind cave-like voids. Lava tubes all ...
... tubes carrying lava from the volcanic vent to the flow’s leading edge. These openings develop when the interior or a flow remains hot long after the surface hardens. In these circumstances, still-molten lava within the tubes continues its forward motion leaving behind cave-like voids. Lava tubes all ...
Chapter 3 Kūkulu-o-ka-honua Pillars of Earth Volcanism Among the
... gases. These hybrid words describe two common problems associated with Hawai„i‟s ongoing eruptions. Vog forms around craters and vents when sulfur dioxide (SO2) gases mix with the atmosphere producing an aerosol of tiny, suspended droplets of sulfuric acid. As this drifts and accumulates downwind, a ...
... gases. These hybrid words describe two common problems associated with Hawai„i‟s ongoing eruptions. Vog forms around craters and vents when sulfur dioxide (SO2) gases mix with the atmosphere producing an aerosol of tiny, suspended droplets of sulfuric acid. As this drifts and accumulates downwind, a ...
notes for geologofe - sciencepowerpoint.com
... Hexagonal. (Four axes, three are equal in length and lie at an angle of 120° from each other). Triclinic: (3 axis, all unequal and none at 90° angles). Orthorhombic: (All axis unequal in length, and 90° degrees from each other). Monoclinic:All axis unequal in length. Two of them are at right ...
... Hexagonal. (Four axes, three are equal in length and lie at an angle of 120° from each other). Triclinic: (3 axis, all unequal and none at 90° angles). Orthorhombic: (All axis unequal in length, and 90° degrees from each other). Monoclinic:All axis unequal in length. Two of them are at right ...
power point notes
... are moving apart and new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. ...
... are moving apart and new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. ...
1 REVIEW Exam #2. GG101 Below are some example questions to
... 9) Draw and describe the types of faults (normal, thrust, strike-slip). 10) What are the kinds of directed stress? 11) Define geologic ‘strain’. 12) What is the difference between a fracture and a fault? ...
... 9) Draw and describe the types of faults (normal, thrust, strike-slip). 10) What are the kinds of directed stress? 11) Define geologic ‘strain’. 12) What is the difference between a fracture and a fault? ...
msword - rgs.org
... conduit to a magma source. The volcano is almost 3800 m high, consisting of a wide, flat caldera and the summit cone inside it. Scientists go to Erebus to study the volcano itself, but also its ice caves and the extremophile bacteria that survive in the warm volcanic soils. The work of the Erebus vo ...
... conduit to a magma source. The volcano is almost 3800 m high, consisting of a wide, flat caldera and the summit cone inside it. Scientists go to Erebus to study the volcano itself, but also its ice caves and the extremophile bacteria that survive in the warm volcanic soils. The work of the Erebus vo ...
Chapter 29 Notes
... rock. The minerals horneblende, quartz, mica, and feldspar are found in this rock. Faulted rock systems (areas where rocks are exposed) would be the best place to start prospecting for precious minerals like gold and silver . Graphite and diamonds are two different minerals that are made of pure ...
... rock. The minerals horneblende, quartz, mica, and feldspar are found in this rock. Faulted rock systems (areas where rocks are exposed) would be the best place to start prospecting for precious minerals like gold and silver . Graphite and diamonds are two different minerals that are made of pure ...
Chapter 18 Volcanic Activity
... • Violent eruptions that send out a wave of gas, ash, and tephra that can travel up to 400 mph. ...
... • Violent eruptions that send out a wave of gas, ash, and tephra that can travel up to 400 mph. ...
Use of Remote Sensing and GIS in Volcanic Eruption
... magma or fluid was moving towards the surface. Based on the history of the volcano and the analysis of the monitoring data, the scientists were able to determine what types of materials could be moving towards the surface. The possible magma and fluid compositions helped figure out what types of haz ...
... magma or fluid was moving towards the surface. Based on the history of the volcano and the analysis of the monitoring data, the scientists were able to determine what types of materials could be moving towards the surface. The possible magma and fluid compositions helped figure out what types of haz ...
Earth science
... Plate Tectonics Seven large plates, several smaller ones Constant motion (a few cm per year) driven ...
... Plate Tectonics Seven large plates, several smaller ones Constant motion (a few cm per year) driven ...
volcanoes - Math/Science Nucleus
... Volcanoes form when molten rock, created inside the crust or upper mantle of the Earth, moves upward and erupts on the Earth’s surface. Molten rock is less dense than the surrounding rock, so it is buoyant and rises, just like hot air. Each eruption can produce layers of lava that will later become ...
... Volcanoes form when molten rock, created inside the crust or upper mantle of the Earth, moves upward and erupts on the Earth’s surface. Molten rock is less dense than the surrounding rock, so it is buoyant and rises, just like hot air. Each eruption can produce layers of lava that will later become ...
Volcanoes and Plate Boundaries
... Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth’s plates because… • At plate boundaries, huge pieces of the crust diverge (pull apart) or converge (push together) • These movements cause fractures in the crust that allows magma to reach the surface • Most volcanoes form along diverging plate boun ...
... Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth’s plates because… • At plate boundaries, huge pieces of the crust diverge (pull apart) or converge (push together) • These movements cause fractures in the crust that allows magma to reach the surface • Most volcanoes form along diverging plate boun ...
File
... Know the three types of heat transfer and how the move heat from one object to another. What is a convection current? Where inside the Earth do convection currents occur? What is the Theory of Continental Drift? Who hypothesized this theory? Why did most other scientists of his day not believe ...
... Know the three types of heat transfer and how the move heat from one object to another. What is a convection current? Where inside the Earth do convection currents occur? What is the Theory of Continental Drift? Who hypothesized this theory? Why did most other scientists of his day not believe ...
Extinction of Dinosaurs
... Extinction caused by Mantle Plumes? Mantle plume: volcanic eruption that starts within the mantle Heat causes eruption on earth Up to 1,000 km in diameter Eruptions can last between 12 million years ...
... Extinction caused by Mantle Plumes? Mantle plume: volcanic eruption that starts within the mantle Heat causes eruption on earth Up to 1,000 km in diameter Eruptions can last between 12 million years ...
Unit 3 study Guide
... 43.) Explain what the weather should be for a landslide to occur. years of drought followed by an abundant rain 44.) What could happen on a hillside when logging has occurred? It is vulnerable to mass movements by gravity ...
... 43.) Explain what the weather should be for a landslide to occur. years of drought followed by an abundant rain 44.) What could happen on a hillside when logging has occurred? It is vulnerable to mass movements by gravity ...
Plate Margin
... Tectonic Activity and Plate Margins– in the right hand column add EXTRA case studies in the empty spaces (with thanks to D McGuinness) Plate Margin NAME Constructive (Spreading or Divergent margins) ...
... Tectonic Activity and Plate Margins– in the right hand column add EXTRA case studies in the empty spaces (with thanks to D McGuinness) Plate Margin NAME Constructive (Spreading or Divergent margins) ...
Section 1 - Pelham City Schools
... • Mountains built from ______________ (molten rock) • Magma rises to surface from interior • Most common at convergent or divergent plate boundaries • Can occur on land or in oceans ...
... • Mountains built from ______________ (molten rock) • Magma rises to surface from interior • Most common at convergent or divergent plate boundaries • Can occur on land or in oceans ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.