Oceanic Crust
... Eruptions usually have fluid lava which flows from it. *Lava flows not only from the top but also from the cracks in the ground. *Slow to erupt so usually animals and people have enough time to escape. *Some of the largest volcanoes in the world ...
... Eruptions usually have fluid lava which flows from it. *Lava flows not only from the top but also from the cracks in the ground. *Slow to erupt so usually animals and people have enough time to escape. *Some of the largest volcanoes in the world ...
Surface Features of Venus
... – about 1000 of them from 2 to 280 km diameter – cf. Earth has 150; Moon has many more – very few are under 10 km (Why?) – nearly all are “pristine” – entire surface ~15% of Lunar maria density – entire surface is about 500 million years old ...
... – about 1000 of them from 2 to 280 km diameter – cf. Earth has 150; Moon has many more – very few are under 10 km (Why?) – nearly all are “pristine” – entire surface ~15% of Lunar maria density – entire surface is about 500 million years old ...
FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES
... of shield volcanoes including Kilauea and Mauna Loa on the island of Hawaii ,which are two of the world’s most active volcanoes. As you go northeast from the island of Hawaii, the volcanoes become inactive, and the islands grow older and older. The Hawaiian Lava flow from Hawaii. Islands are one of ...
... of shield volcanoes including Kilauea and Mauna Loa on the island of Hawaii ,which are two of the world’s most active volcanoes. As you go northeast from the island of Hawaii, the volcanoes become inactive, and the islands grow older and older. The Hawaiian Lava flow from Hawaii. Islands are one of ...
Geological Changes - Woodside Australian Science Project
... Although most of the original heat from formation has since been radiated out into space radioactive decay still provides enough heat to warm the rocks of our planet from within. In some places, such as the asthenosphere, a band of sticky melted rock which lies between the crust and mantle, hot molt ...
... Although most of the original heat from formation has since been radiated out into space radioactive decay still provides enough heat to warm the rocks of our planet from within. In some places, such as the asthenosphere, a band of sticky melted rock which lies between the crust and mantle, hot molt ...
Evidence of Plate Tectonics
... shoreline, youngest nearest the ridge ◦ Therefore: The ridge is producing new oceanic crust while older crust is being pushed toward the shoreline ...
... shoreline, youngest nearest the ridge ◦ Therefore: The ridge is producing new oceanic crust while older crust is being pushed toward the shoreline ...
Earth`s Surface:
... subsurface rocks. Gases (including water vapor) mixed with the molten rock, rise through cracks in the crust, driven by the intense pressure of the heated gases. Magma may be released at the surface explosively (e.g., Mount St Helens) or as flowing rock (e.g., Kilauea Volcano in Hawaii). New crust i ...
... subsurface rocks. Gases (including water vapor) mixed with the molten rock, rise through cracks in the crust, driven by the intense pressure of the heated gases. Magma may be released at the surface explosively (e.g., Mount St Helens) or as flowing rock (e.g., Kilauea Volcano in Hawaii). New crust i ...
Glossary
... is formed when molten rock from a volcano cools and hardens. Planning that looks beyond the immediate costs and benefits by exploring impacts in the future. the uppermost layer of the Earth. It is cool and brittle. It includes the crust and the solid top layer of the mantle. the invisible magnetic f ...
... is formed when molten rock from a volcano cools and hardens. Planning that looks beyond the immediate costs and benefits by exploring impacts in the future. the uppermost layer of the Earth. It is cool and brittle. It includes the crust and the solid top layer of the mantle. the invisible magnetic f ...
Volcano - Warren County Schools
... Amount of water vapor & other gases in the magma. The chemical make-up of the magma. ...
... Amount of water vapor & other gases in the magma. The chemical make-up of the magma. ...
File
... • Measuring Slope and Temperature As magma moves upward prior to an eruption, it can cause the Earth’s surface to swell. Also, infrared satellite images record changes in the surface temperature. If the site is getting hotter, the magma below is probably rising. End of Slide Copyright © by Holt, Rin ...
... • Measuring Slope and Temperature As magma moves upward prior to an eruption, it can cause the Earth’s surface to swell. Also, infrared satellite images record changes in the surface temperature. If the site is getting hotter, the magma below is probably rising. End of Slide Copyright © by Holt, Rin ...
forces of change
... Process that breaks down rocks on the earth’s surface into smaller pieces. Form of weathering that occurs when large masses of rock are broken down into smaller pieces. Give an example of this process: ...
... Process that breaks down rocks on the earth’s surface into smaller pieces. Form of weathering that occurs when large masses of rock are broken down into smaller pieces. Give an example of this process: ...
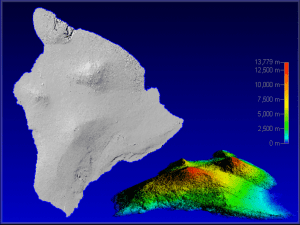
Hawai`i (Big Island)
... The island of Hawai'i, known as the Big Island, is the largest in the Hawaiian Chain. Greater than twice the area of the remaining main eight Hawaiian Islands combined, Hawai'i encompasses 10,432 sq km (4028 sq mi). The island was formed from five major volcanoes. The volcano of Mauna Kea is the ta ...
... The island of Hawai'i, known as the Big Island, is the largest in the Hawaiian Chain. Greater than twice the area of the remaining main eight Hawaiian Islands combined, Hawai'i encompasses 10,432 sq km (4028 sq mi). The island was formed from five major volcanoes. The volcano of Mauna Kea is the ta ...
Volcanic hazards of rift environments
... time scales of advection and cooling (crust formation), as well as the strength of internal convection ...
... time scales of advection and cooling (crust formation), as well as the strength of internal convection ...
Mars Tectonics & Volcanology
... Valles Marineris • Nearly ¼ or the planets circumference • Nine times longer than the grand canyon ...
... Valles Marineris • Nearly ¼ or the planets circumference • Nine times longer than the grand canyon ...
Orogenesis: Folding, Faulting, and Volcanism
... – “Composite”: layers of pyroclastics and lava (mostly felsic) – Explosive and dangerous; found in subduction zones ...
... – “Composite”: layers of pyroclastics and lava (mostly felsic) – Explosive and dangerous; found in subduction zones ...
Fundamental Concepts and Skills
... 2. The lithosphere is the solid outer shell of Earth. It is divided into plates that are in motion with respect to one another. 3. There are two different types of crust (oceanic and continental) that have very different characteristics. ...
... 2. The lithosphere is the solid outer shell of Earth. It is divided into plates that are in motion with respect to one another. 3. There are two different types of crust (oceanic and continental) that have very different characteristics. ...
The Earth`s Layers
... when tsunamis and volcanoes will occur • Tsunami – a huge wave caused by an earthquake under the ocean • Seismographs watch for underwater earthquakes to predict when one will occur ...
... when tsunamis and volcanoes will occur • Tsunami – a huge wave caused by an earthquake under the ocean • Seismographs watch for underwater earthquakes to predict when one will occur ...
Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Islands . . . Oh My!
... Crash Course on Plate Tectonics • The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which move in various directions. • This motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. – This movement in turn causes earthquakes, volcanoes and builds mountains – The movement is caused b ...
... Crash Course on Plate Tectonics • The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which move in various directions. • This motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. – This movement in turn causes earthquakes, volcanoes and builds mountains – The movement is caused b ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.