Chapter 6 - Lemon Bay High School
... Results in loss of information. Terminal deletion is the loss of the end of a chromosome. Intercalary deletion is the loss within the interior of the chromosome. ...
... Results in loss of information. Terminal deletion is the loss of the end of a chromosome. Intercalary deletion is the loss within the interior of the chromosome. ...
Genit 3
... (acetic acid with methanol ) 6. Drop them into a slide and stain and study them under the microscope *72 hours if it’s a lymphocyte and about 40 if it epithilal cell (the dr said this note and I write it exactly as he said it ) Now how can we them under the microscope ? If we examined them immediate ...
... (acetic acid with methanol ) 6. Drop them into a slide and stain and study them under the microscope *72 hours if it’s a lymphocyte and about 40 if it epithilal cell (the dr said this note and I write it exactly as he said it ) Now how can we them under the microscope ? If we examined them immediate ...
SPRI_buffers_v2_2
... Fragmentase® kit (NEB #M0348S) for 20 minutes, according to the manufacturer's instructions, and purify the reaction product with 2 volumes of previously validated beads, then elute in TE+Tween. This produces a flat smear (50 to 2000 bp) that is easy to see on an agarose gel or an Agilent Bioanalyze ...
... Fragmentase® kit (NEB #M0348S) for 20 minutes, according to the manufacturer's instructions, and purify the reaction product with 2 volumes of previously validated beads, then elute in TE+Tween. This produces a flat smear (50 to 2000 bp) that is easy to see on an agarose gel or an Agilent Bioanalyze ...
Fish-on-a-chip: a sensitive detection microfluidic system for
... Recently, Ivan and colleagues reported that human brain diseases such as AD, which are present in the human brain and are associated with chromosomal disorders [40-42]. In this research, chromosome 21 aneuploidy in lymphocytes and fibroblasts cells of AD patients was observed using FISH techniques [ ...
... Recently, Ivan and colleagues reported that human brain diseases such as AD, which are present in the human brain and are associated with chromosomal disorders [40-42]. In this research, chromosome 21 aneuploidy in lymphocytes and fibroblasts cells of AD patients was observed using FISH techniques [ ...
Down Syndrome Research and Practice Volume 5 Issue 3 Pages
... disturbance of the oxidant-antioxidant system could be the direct cause of this chromosomal nondisjunction. These data as well as the predominant maternal origin of the extra chromosome and the age-dependent incidence was the basis for the mtDNA sequencing in a donor of extra chromosome 21. Three ne ...
... disturbance of the oxidant-antioxidant system could be the direct cause of this chromosomal nondisjunction. These data as well as the predominant maternal origin of the extra chromosome and the age-dependent incidence was the basis for the mtDNA sequencing in a donor of extra chromosome 21. Three ne ...
Identification of the target DNA sequence and characterization of
... HlyU Vc binds to an imperfect palindrome about 164 bp upstream of hlyA transcription start site As Williams and Manning showed a 710-bp DNA sequence upstream of hlyA gene in conjunction with HlyU Vc increases HlyA production (16), we scanned the region upstream of the hlyA gene for the precise delin ...
... HlyU Vc binds to an imperfect palindrome about 164 bp upstream of hlyA transcription start site As Williams and Manning showed a 710-bp DNA sequence upstream of hlyA gene in conjunction with HlyU Vc increases HlyA production (16), we scanned the region upstream of the hlyA gene for the precise delin ...
The Functional Organization of the Vestigial Locus in Drosophila
... WILLIAMS, ATKIN, AND BELL, MOLECULAR AND GENERAL GENETICS 221 (1990) ...
... WILLIAMS, ATKIN, AND BELL, MOLECULAR AND GENERAL GENETICS 221 (1990) ...
Part III: Laboratory – Electrophoresis
... 1. Grind tissue in a microfuge with plastic pestle for 1 minute. Note: It is important to use tissue from young plants. The quantity is also important. Best results come from using the opposite end of a 1000 µl micropipette to “punch” a whole in the leaf. The resulting leaf disk is the ideal size. 2 ...
... 1. Grind tissue in a microfuge with plastic pestle for 1 minute. Note: It is important to use tissue from young plants. The quantity is also important. Best results come from using the opposite end of a 1000 µl micropipette to “punch” a whole in the leaf. The resulting leaf disk is the ideal size. 2 ...
simultaneous detection of four food borne bacterial pathogens by
... their specificities. The sensitivity of the detection depends on the condition of the PCR reaction such as, primer annealing temperature, primer concentration, Mg2+ concentration, extension time and characteristics of DNA polymerase used. In this study, PerfectShotTM Ex Taq (from Takara) master-mix ...
... their specificities. The sensitivity of the detection depends on the condition of the PCR reaction such as, primer annealing temperature, primer concentration, Mg2+ concentration, extension time and characteristics of DNA polymerase used. In this study, PerfectShotTM Ex Taq (from Takara) master-mix ...
Document
... due to crossing over in a single generation. In a human being, on average, one cM equates to one million base pairs. Central dogma. The theory of DNA v RNA v protein flow of genetic information. Centromere. The region of a chromosome that separates the two arms; centromeres are the sites of attachme ...
... due to crossing over in a single generation. In a human being, on average, one cM equates to one million base pairs. Central dogma. The theory of DNA v RNA v protein flow of genetic information. Centromere. The region of a chromosome that separates the two arms; centromeres are the sites of attachme ...
Chapter 13 Genetics and Biotechnology
... primers are bound, DNA poly–merase incorporates the correct nucleotides between the two primers as in DNA replication. This process of heating, cooling, and nucleotide incorporation is repeated 20 to 40 times, resulting in millions of copies of the original fragment. Because the separation of DNA st ...
... primers are bound, DNA poly–merase incorporates the correct nucleotides between the two primers as in DNA replication. This process of heating, cooling, and nucleotide incorporation is repeated 20 to 40 times, resulting in millions of copies of the original fragment. Because the separation of DNA st ...
Transduction of DNA information through water and electromagnetic
... In the previous Section we have reported the experimental observation that EMS can be emitted by diluted aqueous solutions of bacterial and viral DNA under proper conditions. Moreover, it has been observed that duplication of the emitting DNA segment can be obtained by using pure water exposed to th ...
... In the previous Section we have reported the experimental observation that EMS can be emitted by diluted aqueous solutions of bacterial and viral DNA under proper conditions. Moreover, it has been observed that duplication of the emitting DNA segment can be obtained by using pure water exposed to th ...
The polymerase chain reaction
... • Multiplex-PCR: consists of multiple primer sets within a single PCR mixture to produce amplicons of varying sizes that are specific to different DNA sequences. By targeting multiple genes at once, additional information may be gained from a single test-run that otherwise would require several time ...
... • Multiplex-PCR: consists of multiple primer sets within a single PCR mixture to produce amplicons of varying sizes that are specific to different DNA sequences. By targeting multiple genes at once, additional information may be gained from a single test-run that otherwise would require several time ...
The effect of human serum DNAases on the ability to detect
... was taken as the total bacterial count and set at 100%. The percentage of bacteria that had released DNA was calculated as the difference between the total bacterial count and the number of bacteria which remained visible in the ¯uorescence mode. In addition, ¯ow cytometry was used to assess the rel ...
... was taken as the total bacterial count and set at 100%. The percentage of bacteria that had released DNA was calculated as the difference between the total bacterial count and the number of bacteria which remained visible in the ¯uorescence mode. In addition, ¯ow cytometry was used to assess the rel ...
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) The polymerase chain reaction
... generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence. Developed in 1983 by Kary Mullis, PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical and biological research labs for a variety of applications. These include DNA cloning for sequencing, DNA-based phylogeny, ...
... generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence. Developed in 1983 by Kary Mullis, PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical and biological research labs for a variety of applications. These include DNA cloning for sequencing, DNA-based phylogeny, ...
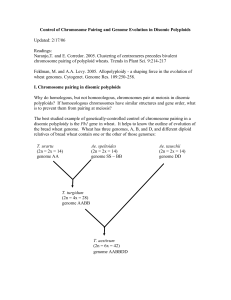
Control of Chromosome Pairing and Genome Evolution in Disomic
... telomere) are derived from 1Am. RSL104 has a CS centromere and both telomeres are from CS, but has two interstitial segments derive from 1Am. See Figure 1 from Luo et al. (1996). Each of these lines was crossed to CS with Ph1 to form a mapping population (in which case only recombination within the ...
... telomere) are derived from 1Am. RSL104 has a CS centromere and both telomeres are from CS, but has two interstitial segments derive from 1Am. See Figure 1 from Luo et al. (1996). Each of these lines was crossed to CS with Ph1 to form a mapping population (in which case only recombination within the ...
Reversing Chromatin Accessibility Differences that Distinguish
... Previous studies have used chromatin modifying reagents to study chromosome biology and investigate the large scale folding of the chromatin fiber. This has been performed, for instance, using chemical inhibitors which disrupt canonical chromatin-associating proteins [5–9] or enzymes which map chrom ...
... Previous studies have used chromatin modifying reagents to study chromosome biology and investigate the large scale folding of the chromatin fiber. This has been performed, for instance, using chemical inhibitors which disrupt canonical chromatin-associating proteins [5–9] or enzymes which map chrom ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... Eukaryotic proteins can be made in bacteria by inserting a cDNA fragment into an expression vector . Large amounts of a desired protein can be purified from the transformed cells. In some cases, the proteins can be used to treat patients with genetic disorders. ...
... Eukaryotic proteins can be made in bacteria by inserting a cDNA fragment into an expression vector . Large amounts of a desired protein can be purified from the transformed cells. In some cases, the proteins can be used to treat patients with genetic disorders. ...
Inheritance of Organelle DNA Sequences in a Citrus–Poncirus
... polymorphisms, and seven probes were selected for use in inheritance analysis. Plastid DNA appeared to exhibit strict maternal inheritance in the intergeneric hybrids. The petA probe detected the maternal 13 kb BamHI fragment in all the 26 F1 progeny, and no P. trifoliata (10 kb) fragments were obse ...
... polymorphisms, and seven probes were selected for use in inheritance analysis. Plastid DNA appeared to exhibit strict maternal inheritance in the intergeneric hybrids. The petA probe detected the maternal 13 kb BamHI fragment in all the 26 F1 progeny, and no P. trifoliata (10 kb) fragments were obse ...
Chromosome Analysis Suite 3.1 (ChAS 3.1)
... ChAS 3.1 includes a table with the following calls made for each mutation: “high confidence,”, “lower confidence,” and “undetected.” The thresholds for the “high-confidence” calls were established based on separations between the normal reference and mutant calls that resulted in 95% sensitivity and ...
... ChAS 3.1 includes a table with the following calls made for each mutation: “high confidence,”, “lower confidence,” and “undetected.” The thresholds for the “high-confidence” calls were established based on separations between the normal reference and mutant calls that resulted in 95% sensitivity and ...
Comparative genomic hybridization

Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resoIution of 5-10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.This is achieved through the use of competitive fluorescence in situ hybridization. In short, this involves the isolation of DNA from the two sources to be compared, most commonly a test and reference source, independent labelling of each DNA sample with a different fluorophores (fluorescent molecules) of different colours (usually red and green), denaturation of the DNA so that it is single stranded, and the hybridization of the two resultant samples in a 1:1 ratio to a normal metaphase spread of chromosomes, to which the labelled DNA samples will bind at their locus of origin. Using a fluorescence microscope and computer software, the differentially coloured fluorescent signals are then compared along the length of each chromosome for identification of chromosomal differences between the two sources. A higher intensity of the test sample colour in a specific region of a chromosome indicates the gain of material of that region in the corresponding source sample, while a higher intensity of the reference sample colour indicates the loss of material in the test sample in that specific region. A neutral colour (yellow when the fluorophore labels are red and green) indicates no difference between the two samples in that location.CGH is only able to detect unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities. This is because balanced chromosomal abnormalities such as reciprocal translocations, inversions or ring chromosomes do not affect copy number, which is what is detected by CGH technologies. CGH does, however, allow for the exploration of all 46 human chromosomes in single test and the discovery of deletions and duplications, even on the microscopic scale which may lead to the identification of candidate genes to be further explored by other cytological techniques.Through the use of DNA microarrays in conjunction with CGH techniques, the more specific form of array CGH (aCGH) has been developed, allowing for a locus-by-locus measure of CNV with increased resolution as low as 100 kilobases. This improved technique allows for the aetiology of known and unknown conditions to be discovered.