CHAPTER 18
... Answer: If the physiological adaptation hypothesis had been correct, mutations should have occurred after the cells were plated on the media containing T1 bacteriophages. Because the same numbers of bacteria were streaked on each plate, we would have expected to see roughly the same number of resist ...
... Answer: If the physiological adaptation hypothesis had been correct, mutations should have occurred after the cells were plated on the media containing T1 bacteriophages. Because the same numbers of bacteria were streaked on each plate, we would have expected to see roughly the same number of resist ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 1
... 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generation to generation ...
... 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generation to generation ...
Bacteria cells reproduce differently from other single celled
... phase of the Human Genome Project. What have they accomplished through this project? a. They used a single cell from one organism to create an identical organism. b. They created a single pedigree for every genetic disorder. c. They created DNA synthetically in a laboratory. d. They identified the s ...
... phase of the Human Genome Project. What have they accomplished through this project? a. They used a single cell from one organism to create an identical organism. b. They created a single pedigree for every genetic disorder. c. They created DNA synthetically in a laboratory. d. They identified the s ...
What determines who we are?
... autosome pairs and one pair of sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes control gender • Females have 2 X chromosomes and males have an X and a Y chromosome • Autosomes determine other traits ...
... autosome pairs and one pair of sex chromosomes • Sex chromosomes control gender • Females have 2 X chromosomes and males have an X and a Y chromosome • Autosomes determine other traits ...
Name Unit 6 DNA Test (Chapters 8) Study Guide
... that the a. genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on different chromosomes. b. type of genes present in the fruit fly is dependent upon environmental temperature. c. environment affects the expression of the genes for this trait. d. higher temperature produces a gene mutation. ...
... that the a. genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on different chromosomes. b. type of genes present in the fruit fly is dependent upon environmental temperature. c. environment affects the expression of the genes for this trait. d. higher temperature produces a gene mutation. ...
Practice Quizzes for Honors Biology Unit 3
... Chapter 26: Control of Gene Expression and Cancer 1. How do cells become specialized when they all contain the exact same DNA? 2. For the operon; name the participant that: a. transcribes the DNA into ...
... Chapter 26: Control of Gene Expression and Cancer 1. How do cells become specialized when they all contain the exact same DNA? 2. For the operon; name the participant that: a. transcribes the DNA into ...
DNA Test Review
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
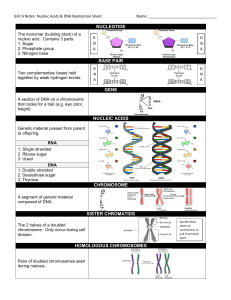
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
Section 8.7 Mutations
... Two Categories of Mutations: 1.Single Gene – affects one gene – usually caused by an error in DNA replication 2. Chromosomal – affects chromosomes – usually error in meiosis . Usually more harmful since many genes are affected. ...
... Two Categories of Mutations: 1.Single Gene – affects one gene – usually caused by an error in DNA replication 2. Chromosomal – affects chromosomes – usually error in meiosis . Usually more harmful since many genes are affected. ...
Name_____________________ Date__________ Class
... substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation. occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic mat ...
... substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation. occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic mat ...
Variation exists within individuals, within populations, and among
... Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygote, allele, reciprocal cross, dominance A syndrome in humans is manifest by follicle death, so that n ...
... Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygote, allele, reciprocal cross, dominance A syndrome in humans is manifest by follicle death, so that n ...
Recitation 17 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... mutations in genes leads to cancer. Less than 10% of cancers are inherited, however. This is because most mutations leading to cancer occur in somatic cells. Benign tumors are clumps of cells that may be growing but are not invading other tissues. Metastatic tumors are tumors that have had specific ...
... mutations in genes leads to cancer. Less than 10% of cancers are inherited, however. This is because most mutations leading to cancer occur in somatic cells. Benign tumors are clumps of cells that may be growing but are not invading other tissues. Metastatic tumors are tumors that have had specific ...
Use of curcumin and Andrographolide combination with
... ABSTRACT Cancer remains a mayor cause of death globally. An estimated 7.6 million people died of cancer in 2005 and 84 million people will die within the next 10 years if no preventive action is taken (WHO, 2006). But until now has not found an anticancer drug that selectively kills cancer cells wit ...
... ABSTRACT Cancer remains a mayor cause of death globally. An estimated 7.6 million people died of cancer in 2005 and 84 million people will die within the next 10 years if no preventive action is taken (WHO, 2006). But until now has not found an anticancer drug that selectively kills cancer cells wit ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...
Genetic Variation Mutations
... is based on the accumulation of many mutations. Gene flow is any movement of genes from one population to another and is an important source of genetic variation. Sex can introduce new gene combinations into a population. This genetic shuffling is another important source of genetic variation. ...
... is based on the accumulation of many mutations. Gene flow is any movement of genes from one population to another and is an important source of genetic variation. Sex can introduce new gene combinations into a population. This genetic shuffling is another important source of genetic variation. ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet Genetics and Biotechnology Vocabulary
... - Do you know how to use the codon chart? - Why is the sequence of amino acids important to the shape and function of a protein? *You do NOT need to know the names of the enzymes involved in this process. Mutations - What is a mutation? - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide i ...
... - Do you know how to use the codon chart? - Why is the sequence of amino acids important to the shape and function of a protein? *You do NOT need to know the names of the enzymes involved in this process. Mutations - What is a mutation? - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide i ...
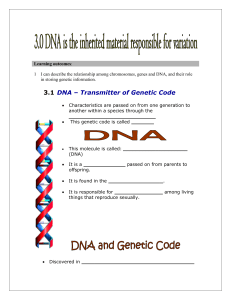
What is DNA?
... An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced. What is a clone? ...
... An organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced. What is a clone? ...
Things to Cover for Exam 1
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
... If the chromosome number of a diploid cell is 102, what is its haploid chromosome number? What is a zygote and when is it formed? Meiosis involves a single duplication of DNA followed by two successive cell divisions. When during meiosis do homologous chromosomes cross over? Ch. 10 “Foundation ...
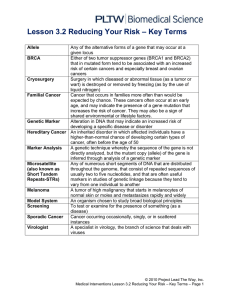
L3.2ReducingYourRisk - jj-sct
... given locus BRCA Either of two tumor suppressor genes (BRCA1 and BRCA2) that in mutated form tend to be associated with an increased risk of certain cancers and especially breast and ovarian cancers Cryosurgery Surgery in which diseased or abnormal tissue (as a tumor or wart) is destroyed or removed ...
... given locus BRCA Either of two tumor suppressor genes (BRCA1 and BRCA2) that in mutated form tend to be associated with an increased risk of certain cancers and especially breast and ovarian cancers Cryosurgery Surgery in which diseased or abnormal tissue (as a tumor or wart) is destroyed or removed ...
Intro to DNA
... Intro to DNA • NOTE: • “matching pairs” of chromosomes • = “homologous pairs”. • In every human somatic cell, there are 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
... Intro to DNA • NOTE: • “matching pairs” of chromosomes • = “homologous pairs”. • In every human somatic cell, there are 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
Cancer is generally understood as a genetic or cellular disease
... Professor of Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology in Oncology, Department of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Rome “La Sapienza” Cancer is generally understood as a genetic or cellular disease, which results either from the overexpression or lack of expression of certain genes and r ...
... Professor of Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology in Oncology, Department of Experimental Medicine and Pathology, University of Rome “La Sapienza” Cancer is generally understood as a genetic or cellular disease, which results either from the overexpression or lack of expression of certain genes and r ...
Ch 16-17 Practice Quiz
... a. semi conservative b. dispersive c. conservative 4. Put these events in the correct chronological order: • Chargaff–base pairing (A-T, C-G) • Meselson-Stahl –DNA Replication details • Watson and Crick (discovered the chemical structure of DNA) • Thomas Hunt Morgan (fruit flies, linked genes) • Ave ...
... a. semi conservative b. dispersive c. conservative 4. Put these events in the correct chronological order: • Chargaff–base pairing (A-T, C-G) • Meselson-Stahl –DNA Replication details • Watson and Crick (discovered the chemical structure of DNA) • Thomas Hunt Morgan (fruit flies, linked genes) • Ave ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.