Reasons for the Seasons Notes
... to revolve around Earth one time Year – the amount of time it takes for the Earth to revolve around the Sun one time ...
... to revolve around Earth one time Year – the amount of time it takes for the Earth to revolve around the Sun one time ...
Turtle
... File for the TURTLE/Earth Science of the 5 pointed star* *Activities/Ideas like Stars-Ancestors-Descendants in the Tree/MilkyWay/River of Sky & Earth ...
... File for the TURTLE/Earth Science of the 5 pointed star* *Activities/Ideas like Stars-Ancestors-Descendants in the Tree/MilkyWay/River of Sky & Earth ...
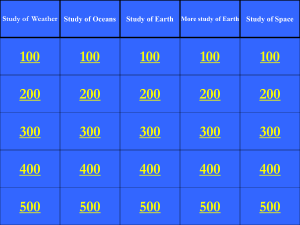
C1 Topic 7 the earth revision Earth`s Structure (and rocks) 1. List the
... 10. Why don’t governments always act upon to scientist’s predictions of earthquakes? ...
... 10. Why don’t governments always act upon to scientist’s predictions of earthquakes? ...
ESU-LT1-4
... Gravity: the force of attraction that exists between all matter in the universe Isaac Newton was first to explain Law of Gravitation: the force of attraction between any two objects depends on the masses of the objects and distance between the objects. ...
... Gravity: the force of attraction that exists between all matter in the universe Isaac Newton was first to explain Law of Gravitation: the force of attraction between any two objects depends on the masses of the objects and distance between the objects. ...
Science Vocabulary Constructive and Destructive Forces Lava
... Lava: Molten rock that flows from a volcano onto the earth’s surface. Sand Dune: A hill of sand made and shaped by the wind. Topography: Surface landforms of an area. Erosion: The process of moving sediment by wind, moving water, or ice. Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river formed from ...
... Lava: Molten rock that flows from a volcano onto the earth’s surface. Sand Dune: A hill of sand made and shaped by the wind. Topography: Surface landforms of an area. Erosion: The process of moving sediment by wind, moving water, or ice. Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river formed from ...
D. Tectonics
... Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from the motion of plates. Sea floor spreading, revealed in mapping of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, and subduction zones are evidence for the theory of plate tectonics. ...
... Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from the motion of plates. Sea floor spreading, revealed in mapping of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, and subduction zones are evidence for the theory of plate tectonics. ...
Dynamic Earth Review Sheet Plate Tectonics Be able to use the
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
Name
... d. The density of ice cannot be measured 3. An iceberg floats in water. In terms of balanced and unbalanced forces, which of the following best explains why this occurs? a. An iceberg floats because its weight is balanced by the buoyant force b. An iceberg floats because its smaller than a glacier c ...
... d. The density of ice cannot be measured 3. An iceberg floats in water. In terms of balanced and unbalanced forces, which of the following best explains why this occurs? a. An iceberg floats because its weight is balanced by the buoyant force b. An iceberg floats because its smaller than a glacier c ...
Chap. 1 Unit C Study Guide
... Directions: Fill out the questions, and then use this to study for your test on Friday. ...
... Directions: Fill out the questions, and then use this to study for your test on Friday. ...
Name
... Although the atmosphere extends more than 100km up, 90% is within 16km of the surface. The ____________________ includes all life on Earth. The biosphere is concentrated in a zone that extends from the ocean floor upward several kilometers in the atmosphere. The geosphere consists of the ___________ ...
... Although the atmosphere extends more than 100km up, 90% is within 16km of the surface. The ____________________ includes all life on Earth. The biosphere is concentrated in a zone that extends from the ocean floor upward several kilometers in the atmosphere. The geosphere consists of the ___________ ...
Earth
... closest to Moon has slightly stronger pull to Moon => bulges towards it. Other side has weaker pull => bulges away compared to rest of Earth. The Earth spins once a day while the bulge always points towards and away from the Moon => high and low tides. ...
... closest to Moon has slightly stronger pull to Moon => bulges towards it. Other side has weaker pull => bulges away compared to rest of Earth. The Earth spins once a day while the bulge always points towards and away from the Moon => high and low tides. ...
Chapter 1, Changes to Earth`s Surface
... Mass movement – downhill movement of rock and soil because of gravity Lesson 2 Crust – other layer of Earth, made of rock Mantle – layer of rock beneath Earth’s crust Core – center layer of Earth Plates – rigid blocks of crust and upper mantle rock Magma – molten rock from Earth’s mantle Volcano – m ...
... Mass movement – downhill movement of rock and soil because of gravity Lesson 2 Crust – other layer of Earth, made of rock Mantle – layer of rock beneath Earth’s crust Core – center layer of Earth Plates – rigid blocks of crust and upper mantle rock Magma – molten rock from Earth’s mantle Volcano – m ...
Gravity - My CCSD
... 1. The sun (1.98892 x 1030 kg) is the most massive object in our solar system and exerts a huge gravitational force. This is why all the planets stay in orbit around the sun. 2. The Earth (5.9742 x 1024 kg) is so massive that its gravitational force keeps us from falling off the planet. ...
... 1. The sun (1.98892 x 1030 kg) is the most massive object in our solar system and exerts a huge gravitational force. This is why all the planets stay in orbit around the sun. 2. The Earth (5.9742 x 1024 kg) is so massive that its gravitational force keeps us from falling off the planet. ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.