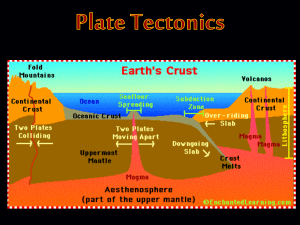
Plate Tectonics.common.assessment.studyguide
... 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago 9. the continents were once joined together in a single landmass 10. evidence from landforms, fossils, and climate 11 ...
... 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago 9. the continents were once joined together in a single landmass 10. evidence from landforms, fossils, and climate 11 ...
Earth*s Layers - Madison County Schools
... The continents of Earth look as if they could fit together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. A German scientist named Alfred Wegener came up with the Continental Drift Theory. This theory says that all the continents used to be together, but drifted apart over millions of years. ...
... The continents of Earth look as if they could fit together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. A German scientist named Alfred Wegener came up with the Continental Drift Theory. This theory says that all the continents used to be together, but drifted apart over millions of years. ...
A fault is a CRACK in the Earth. 1. A tsunami is a giant wave formed
... 8. The SIERRA NEVADA Mountains are FAULT BLOCK mountains that form when PLATES RUB TOGETHER. 9. MAGMA RISING can cause the sea floor to spread apart. 10. You often see snow on mountain tops because th ...
... 8. The SIERRA NEVADA Mountains are FAULT BLOCK mountains that form when PLATES RUB TOGETHER. 9. MAGMA RISING can cause the sea floor to spread apart. 10. You often see snow on mountain tops because th ...
iscience earth science unit 1 chapter 2 study guide
... 1. How do Scientists know about the center of the earth? What is the deepest mine/well we have ever dug? Have we even been able to dig our way to the Mantle? Why not? ...
... 1. How do Scientists know about the center of the earth? What is the deepest mine/well we have ever dug? Have we even been able to dig our way to the Mantle? Why not? ...
The Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics (PowerPoint)
... Outflowing heat can cause convective motions – in churning soup, and in the Earth. ...
... Outflowing heat can cause convective motions – in churning soup, and in the Earth. ...
Theme 8 – The Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics
... http://smp.uq.edu.au/content/pitch-drop-experiment ...
... http://smp.uq.edu.au/content/pitch-drop-experiment ...
Lab2
... Earth condensed together from the original nebula that formed the Solar System. The Capture Theory: The Moon was formed somewhere else, and was later captured by the gravitational field of the Earth. The Colliding Planetesimals Theory: The interaction of earth-orbiting and Sun-orbiting planetesimals ...
... Earth condensed together from the original nebula that formed the Solar System. The Capture Theory: The Moon was formed somewhere else, and was later captured by the gravitational field of the Earth. The Colliding Planetesimals Theory: The interaction of earth-orbiting and Sun-orbiting planetesimals ...
Plate Techtonics
... earth along faults Seismograph – measures the intensity of earthquakes Focus – the point in the earth where an earthquake begins Epicenter – the point on the surface above the focus of an earthquake ...
... earth along faults Seismograph – measures the intensity of earthquakes Focus – the point in the earth where an earthquake begins Epicenter – the point on the surface above the focus of an earthquake ...
File
... 14) Conservation- The practice of using less of a resource so that it will not be used up. 15) Continental Drift- The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. 16) Contrast- To examine two or more objects and note unlikeness or differences. 17) Controlled Experiment- An expe ...
... 14) Conservation- The practice of using less of a resource so that it will not be used up. 15) Continental Drift- The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. 16) Contrast- To examine two or more objects and note unlikeness or differences. 17) Controlled Experiment- An expe ...
Gravitational and electric fields
... 2. Draw diagrams showing the gravitational field of the earth when viewed from: (a) a large distance away (b) close to the earth's surface (c) over an area of high density rock 3. The gravitational field of the Earth is 10 Nkg-1. What would the field strength be at a distance above the Earth's surfa ...
... 2. Draw diagrams showing the gravitational field of the earth when viewed from: (a) a large distance away (b) close to the earth's surface (c) over an area of high density rock 3. The gravitational field of the Earth is 10 Nkg-1. What would the field strength be at a distance above the Earth's surfa ...
Drawing the Earth
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
... Directions: You will be creating a representation of the Earth, its layers (structural and compositional) and spheres. You have three (3) options: 1. Work with a group (3-4) and make a large poster 2. Work individually or with a partner and create a smaller drawing (8.5 x 11) 3. Create a layered “bo ...
PRESENTSS
... Deriving its name from the Greek word asthenos (without strength) and contained entirely in the upper mantle is the asthenosphere. This zone is known as a plastic zone because of the sometimes semi-solid nature of its materials. The asthenospheres lack of rigidity is because the temperature is so cl ...
... Deriving its name from the Greek word asthenos (without strength) and contained entirely in the upper mantle is the asthenosphere. This zone is known as a plastic zone because of the sometimes semi-solid nature of its materials. The asthenospheres lack of rigidity is because the temperature is so cl ...
Mountain Building - Hicksville Public Schools
... Isostasy – Isostasy (Greek ísos "equal", stásis "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. – Parts of ...
... Isostasy – Isostasy (Greek ísos "equal", stásis "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. – Parts of ...
Earth`s Interior
... Earth’s surface is 0° C (32° F) Heat flows from the core to the surface ...
... Earth’s surface is 0° C (32° F) Heat flows from the core to the surface ...
final_examgq - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 8. [True or False] The Hawaiian Islands are a textbook example of a volcanic island arc formed from subduction. 9. [True or False] High pressure systems are generally associated with the development of large weather systems like warm fronts and cold fronts. 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t ...
... 8. [True or False] The Hawaiian Islands are a textbook example of a volcanic island arc formed from subduction. 9. [True or False] High pressure systems are generally associated with the development of large weather systems like warm fronts and cold fronts. 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t ...
Name ____________ Date ______________ Period ________
... Mid-Ocean Ridge - An undersea mountain range that forms where two parts of the Earth’s crust are pushing apart. (a diverging plate boundary) Subduction - The process, in which one lithospheric plate slides under another, occurs at converging plate boundaries. ...
... Mid-Ocean Ridge - An undersea mountain range that forms where two parts of the Earth’s crust are pushing apart. (a diverging plate boundary) Subduction - The process, in which one lithospheric plate slides under another, occurs at converging plate boundaries. ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.