
“Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Study Guide”
... states that magma travels to the earth’s surface. The magma forms cracks in the ocean floor. The magma pushes out of the cracks. Magma piles up and forms mid-ocean ridges. As the magma hardens it pushes the layers of the ocean floor away from the mid-ocean ridge. The process then repeats it self. Pr ...
... states that magma travels to the earth’s surface. The magma forms cracks in the ocean floor. The magma pushes out of the cracks. Magma piles up and forms mid-ocean ridges. As the magma hardens it pushes the layers of the ocean floor away from the mid-ocean ridge. The process then repeats it self. Pr ...
Notes_-_Earths_Layers
... Chemical composition: rocks rich in iron and magnesium silicates Common rock types: basalt, obsidian, gabbro Rocks are more dense, darker in color than continental crust Mantle Lies underneath the crust 2900 Km thick The lithosphere is a zone made of the upper mantle and entire crust. It ...
... Chemical composition: rocks rich in iron and magnesium silicates Common rock types: basalt, obsidian, gabbro Rocks are more dense, darker in color than continental crust Mantle Lies underneath the crust 2900 Km thick The lithosphere is a zone made of the upper mantle and entire crust. It ...
oceans
... – thin outer layer • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...
... – thin outer layer • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...
paleogeography (plate tectonics)
... 1. rock is neither created nor destroyed; there are earthquakes, but no volcanoes 2. transform faults form perpendicular to divergent spreading centers due to stress from seafloor spreading; thus, they are common near mid-ocean ridges; they occur to accommodate a change in shape of the plate 3. frac ...
... 1. rock is neither created nor destroyed; there are earthquakes, but no volcanoes 2. transform faults form perpendicular to divergent spreading centers due to stress from seafloor spreading; thus, they are common near mid-ocean ridges; they occur to accommodate a change in shape of the plate 3. frac ...
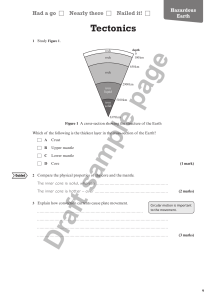
the earth`s interior
... fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid ...
... fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid ...
Activity #8 slide presentation pdf
... our planet in earlier times, and that the truth of the matter can only be reached by combing all this evidence. . . It is only by combing the information furnished by all the earth sciences that we can hope to determine 'truth' here, that is to say, to find the picture that sets out all the known fa ...
... our planet in earlier times, and that the truth of the matter can only be reached by combing all this evidence. . . It is only by combing the information furnished by all the earth sciences that we can hope to determine 'truth' here, that is to say, to find the picture that sets out all the known fa ...
Plate_tectonics[1]
... • A continental plate colliding with another continental plate • Continental plates are less dense than the mantle so the plates will not sink and form a subduction zone • NO SUBDUCTION • Mountain building takes place • Example: Himalayas ...
... • A continental plate colliding with another continental plate • Continental plates are less dense than the mantle so the plates will not sink and form a subduction zone • NO SUBDUCTION • Mountain building takes place • Example: Himalayas ...
File - South Sevier High School
... three different types. They are: a. ______________________________ boundary, marked by ____________________________ b. ______________________________ boundary, marked by ____________________________ c. ______________________________ boundary, marked by ____________________________ 30. The collision ...
... three different types. They are: a. ______________________________ boundary, marked by ____________________________ b. ______________________________ boundary, marked by ____________________________ c. ______________________________ boundary, marked by ____________________________ 30. The collision ...
Earth Structure - Cal State LA
... Plate Tectonics The theory --the surface of the Earth is broken into large plates. The size and position of these plates change over time. The edges of these plates, where they move against each other, are sites of intense geologic activity, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building. ...
... Plate Tectonics The theory --the surface of the Earth is broken into large plates. The size and position of these plates change over time. The edges of these plates, where they move against each other, are sites of intense geologic activity, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building. ...
Chapter 4: Plate - Frankfort School District 157c
... dense material below the Earth’s crust rises towards the surface at the mid-ocean ridges It then flows sideways, carrying the seafloor away in both directions As the seafloor spreads apart, magma moves upward and flows from the cracks This magma becomes solid as it cools and forms ...
... dense material below the Earth’s crust rises towards the surface at the mid-ocean ridges It then flows sideways, carrying the seafloor away in both directions As the seafloor spreads apart, magma moves upward and flows from the cracks This magma becomes solid as it cools and forms ...
Pangea Location of different fossils, location of different types of
... Sonar is sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor. These sound waves show features on the ocean floor. The midocean ridge and trenches The plates moving apart along the midocean ridge have different ages of rocks. The newest rocks are along the midocean ridge where lava comes out. The o ...
... Sonar is sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor. These sound waves show features on the ocean floor. The midocean ridge and trenches The plates moving apart along the midocean ridge have different ages of rocks. The newest rocks are along the midocean ridge where lava comes out. The o ...
Handout 2-1.b, c, and d Name: Period
... the solid, plastic layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it ...
... the solid, plastic layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it ...
Discovering Plate Tectonics PDF Name
... ____3. Who came up with the theory of sea floor spreading? a. Alfred Wegener b. Harry Hess c. ancient Greeks ____4. Where does sea floor spreading happen? a. at the rift valley along the mid-ocean ridges b. at deep sea trenches c. at the Ring of Fire ____5. What material forms new ocean floor? a. se ...
... ____3. Who came up with the theory of sea floor spreading? a. Alfred Wegener b. Harry Hess c. ancient Greeks ____4. Where does sea floor spreading happen? a. at the rift valley along the mid-ocean ridges b. at deep sea trenches c. at the Ring of Fire ____5. What material forms new ocean floor? a. se ...
Test Review: Geosphere Part 1: Lithosphere, Earthquakes
... 10. The asthenosphere is _the layer below the lithosphere (helps it move) liquid-solid_____. 11. There are three ways that the lithosphere crust moves on the mantle. A. __Convection current______________ - Hot less dense material rises up to the crust, cools, and the denser colder material sinks bac ...
... 10. The asthenosphere is _the layer below the lithosphere (helps it move) liquid-solid_____. 11. There are three ways that the lithosphere crust moves on the mantle. A. __Convection current______________ - Hot less dense material rises up to the crust, cools, and the denser colder material sinks bac ...
Name: Date: Period: ______
... Earth’s surface. Plate tectonics is the theory that describes how tectonic plates move and shape Earth’s surface. They move in different directions and at different rates relative to one another, and they interact with one another at their boundaries. Types of Plate Boundaries Divergent Boundary: tw ...
... Earth’s surface. Plate tectonics is the theory that describes how tectonic plates move and shape Earth’s surface. They move in different directions and at different rates relative to one another, and they interact with one another at their boundaries. Types of Plate Boundaries Divergent Boundary: tw ...
10-2
... _____ 50. What happens to newer, warmer rock at a mid-ocean ridge as it cools? a. It is elevated above nearby rock. b. It slopes downward away from the ridge. c. It slides down the slope between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. d. It exerts force on the plate. 51. The force on the rest of the ...
... _____ 50. What happens to newer, warmer rock at a mid-ocean ridge as it cools? a. It is elevated above nearby rock. b. It slopes downward away from the ridge. c. It slides down the slope between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. d. It exerts force on the plate. 51. The force on the rest of the ...
File
... 14. Which of these statements about Earth's crust is true? A) It is a layer of solid rock that remains the same throughout time. B) It includes the continents, but not the ocean floor. C) It is a changing, moving surface with the same thickness everywhere. D) It is a system of large masses called pl ...
... 14. Which of these statements about Earth's crust is true? A) It is a layer of solid rock that remains the same throughout time. B) It includes the continents, but not the ocean floor. C) It is a changing, moving surface with the same thickness everywhere. D) It is a system of large masses called pl ...
Earth`s Structure
... coastlines of Africa and South America looked like they might fit together. He also discovered evidence that the same __________________________________ were found along the coasts of these continents, although they were now separated by vast oceans. In addition, he noticed that ____________________ ...
... coastlines of Africa and South America looked like they might fit together. He also discovered evidence that the same __________________________________ were found along the coasts of these continents, although they were now separated by vast oceans. In addition, he noticed that ____________________ ...
Tour of Plate Boundaries
... As you have learned, where there is upwelling of the asthenosphere, the crust above spreads apart, and new material from below bulges up into ridges. Where there is subsidence of the asthenosphere, the crust is being pulled down along with it to form depressions, or trenches. This can be visualized ...
... As you have learned, where there is upwelling of the asthenosphere, the crust above spreads apart, and new material from below bulges up into ridges. Where there is subsidence of the asthenosphere, the crust is being pulled down along with it to form depressions, or trenches. This can be visualized ...
draw a diagram of earth`s interior and label each
... DRAW A DIAGRAM DESCRIBING HOW THIS PROCESS WORKS CONVECTION OCCURS IN THE MANTLE WHEN COOL DENSE MATERIAL SINKS TO THE BOTTOM OF THE MANTLE NEAR THE CORE AND WARM LESS DENSE MATERIAL RISES TO THE TOP OF THE MANTLE TO HEAT EARTH’S SURFACE ...
... DRAW A DIAGRAM DESCRIBING HOW THIS PROCESS WORKS CONVECTION OCCURS IN THE MANTLE WHEN COOL DENSE MATERIAL SINKS TO THE BOTTOM OF THE MANTLE NEAR THE CORE AND WARM LESS DENSE MATERIAL RISES TO THE TOP OF THE MANTLE TO HEAT EARTH’S SURFACE ...
Earth Science Text Assignments
... Geologists believe that plates can be moved due the convection currents within the mantle. ...
... Geologists believe that plates can be moved due the convection currents within the mantle. ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.







![Plate_tectonics[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002008574_1-75611a1f04cab56ed6d6f0dd254e9b31-300x300.png)













