SEISMIC ACTIVITY (mainly shallow earthquakes)
... along the Mid-Ocean-Ridges is one of the most central elements of Plate-Tectonics. The Mid-Ocean-Ridges have a length of ca 60 000 km; they are a formidable system with major importance for the driving force of the plates and in the enery-budget of the plate-tectonics. ...
... along the Mid-Ocean-Ridges is one of the most central elements of Plate-Tectonics. The Mid-Ocean-Ridges have a length of ca 60 000 km; they are a formidable system with major importance for the driving force of the plates and in the enery-budget of the plate-tectonics. ...
NGC 2014 POSTER Tectonic setting of basaltic dykes from the
... Basaltic dykes of Peninsular Malaysia are confined to the Eastern Belt (Indochina/East Malaya block) as compared with the Western Belt (Sibumasu Block). The dyke intruded through a crustal fracture formed by stress developed from the evolution of two offshore basins (Malay and Penyu basins) east off ...
... Basaltic dykes of Peninsular Malaysia are confined to the Eastern Belt (Indochina/East Malaya block) as compared with the Western Belt (Sibumasu Block). The dyke intruded through a crustal fracture formed by stress developed from the evolution of two offshore basins (Malay and Penyu basins) east off ...
Physical Properties of Earth`s Layers
... The physical layers of Earth are the lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core, and inner core. The lithosphere is the outer layer of solid rock that is found at Earth’s surface. It includes both the crust and the solid, uppermost part of the mantle. The lithosphere is relatively less dense ...
... The physical layers of Earth are the lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core, and inner core. The lithosphere is the outer layer of solid rock that is found at Earth’s surface. It includes both the crust and the solid, uppermost part of the mantle. The lithosphere is relatively less dense ...
Convection Currents Lab
... Convection currents in the mantle form and transfer heat as rock slowly rises toward the top of the mantle. The rock is still hard, but it flows very slowly like a fluid. As the rock rises, it cools and sinks back down into the mantle. As with all convection currents, convection in Earth’s mantle is ...
... Convection currents in the mantle form and transfer heat as rock slowly rises toward the top of the mantle. The rock is still hard, but it flows very slowly like a fluid. As the rock rises, it cools and sinks back down into the mantle. As with all convection currents, convection in Earth’s mantle is ...
Earthquake Definitions - Red Hook Central Schools
... As the Earth’s plates move past one another, friction causes the plates to get “stuck”. · Stress and pressure builds up and causes the plate to become deformed (bend) as it continues to try and move (the plates are elastic-they can change shape). · Eventually, the pressure is great enough to over ...
... As the Earth’s plates move past one another, friction causes the plates to get “stuck”. · Stress and pressure builds up and causes the plate to become deformed (bend) as it continues to try and move (the plates are elastic-they can change shape). · Eventually, the pressure is great enough to over ...
101_MT2_V2_S08
... 19) (3 pts) Explain and draw a simple picture of marine magnetic anomalies around a mid-ocean ridge. ...
... 19) (3 pts) Explain and draw a simple picture of marine magnetic anomalies around a mid-ocean ridge. ...
Temperatures and tectonic history of the North American continent
... Background: There are many open questions about the internal structure of the continental plates that we live on, and what this structure tells us about how continents are formed. For example, why are old continental cores impervious to the type of recycling that happens to oceanic lithosphere? Is t ...
... Background: There are many open questions about the internal structure of the continental plates that we live on, and what this structure tells us about how continents are formed. For example, why are old continental cores impervious to the type of recycling that happens to oceanic lithosphere? Is t ...
GeologyOfTheUS
... post-shield, and rejuvenated stages. During their younger phases, most Hawaiian volcanoes rise above sea level, forming islands. As the islands age, they erode and subside, becoming atolls and seamounts. ...
... post-shield, and rejuvenated stages. During their younger phases, most Hawaiian volcanoes rise above sea level, forming islands. As the islands age, they erode and subside, becoming atolls and seamounts. ...
C1.7 Changes in Earth and atmosphere
... Describe how the crust and upper mantle are divided into tectonic plates Explain why the tectonic plates move at a few centimetres per year Describe some of the effects of tectonic plate movements, particularly at plate boundaries Describe how Wegener’s theory explained the formation of mountains de ...
... Describe how the crust and upper mantle are divided into tectonic plates Explain why the tectonic plates move at a few centimetres per year Describe some of the effects of tectonic plate movements, particularly at plate boundaries Describe how Wegener’s theory explained the formation of mountains de ...
Powerpoint
... around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its selfgravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has s ...
... around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its selfgravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. (2) A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has s ...
V: 0
... In your INB, answer the following: One piece of evidence that supports the Theory of Plate Tectonics is the discovery of what in both South America and Africa? A. Insects on both continents have similar feeding habits B. The rates of sedimentary rock formation are similar C. The ancient atmosphere i ...
... In your INB, answer the following: One piece of evidence that supports the Theory of Plate Tectonics is the discovery of what in both South America and Africa? A. Insects on both continents have similar feeding habits B. The rates of sedimentary rock formation are similar C. The ancient atmosphere i ...
Gluep-Honors
... Introduction: The interior of the Earth is complex. While it is made of 3 major layers, some of these layers can be subdivided or grouped into regions. The mantle of the Earth, and more specifically the asthenosphere, is a unique substance. Its composition is different from that of any other layer o ...
... Introduction: The interior of the Earth is complex. While it is made of 3 major layers, some of these layers can be subdivided or grouped into regions. The mantle of the Earth, and more specifically the asthenosphere, is a unique substance. Its composition is different from that of any other layer o ...
Dynamic Earth - Ms. Tasneem`s Class
... 3. What do earthquakes tell us about the interior of the Earth? 1. Types of volcanoes, their origins, and differences in their eruptions (difference in types of lava/magma) 2. Major volcanoes/eruptions around the world 3. Any local major volcanoes? If so, list the type, origin, status of each. 1. Su ...
... 3. What do earthquakes tell us about the interior of the Earth? 1. Types of volcanoes, their origins, and differences in their eruptions (difference in types of lava/magma) 2. Major volcanoes/eruptions around the world 3. Any local major volcanoes? If so, list the type, origin, status of each. 1. Su ...
Microsoft Word - Plate Tectonics Lab
... 2. What directions do the plates move relative to one another in a divergent plate boundary? ...
... 2. What directions do the plates move relative to one another in a divergent plate boundary? ...
Introduction to Atmospheric Science, PHSC 3223
... • By studying the processes that shape Earth’s surface both from without and from within, we gain the following: – We learn about the nature of these processes themselves and their origins – By so doing, we can look for similar results on other planets and infer past geologic history for that world ...
... • By studying the processes that shape Earth’s surface both from without and from within, we gain the following: – We learn about the nature of these processes themselves and their origins – By so doing, we can look for similar results on other planets and infer past geologic history for that world ...
Abstract - gemoc - Macquarie University
... Figure 1 shows a series of tomographic slices through the African continent from 100-175 km, 175-250km, 250-325km and 325 – 400km using a high-resolution global tomography model derived from SH body wave travel times based on the approach of Grand (2002) and fully described by Begg et al. (2009) and ...
... Figure 1 shows a series of tomographic slices through the African continent from 100-175 km, 175-250km, 250-325km and 325 – 400km using a high-resolution global tomography model derived from SH body wave travel times based on the approach of Grand (2002) and fully described by Begg et al. (2009) and ...
theory of plate tectonics text
... movements are so slow and gradual that you can’t see or feel them—the movement is measured in centimeters per year. The Global Positioning System Scientists use a system of satellites called the global positioning system(GPS), shown in Figure 2, to measure the rate of tectonic plate movement. Radio ...
... movements are so slow and gradual that you can’t see or feel them—the movement is measured in centimeters per year. The Global Positioning System Scientists use a system of satellites called the global positioning system(GPS), shown in Figure 2, to measure the rate of tectonic plate movement. Radio ...
EPS050 – Review for Midterm 1 (Fall 2009)
... composition of the whole Earth and crust? What processes have given rise to these differences? ...
... composition of the whole Earth and crust? What processes have given rise to these differences? ...
Chapter 15
... towards each other. One is subducted back into the mantle on a falling convection current. ...
... towards each other. One is subducted back into the mantle on a falling convection current. ...
6.1_Notes_powerpoint
... crust where molten material, or magma comes to the surface. • Volcanic Activity is a constructive force that adds new rock to existing land or forms new islands. ...
... crust where molten material, or magma comes to the surface. • Volcanic Activity is a constructive force that adds new rock to existing land or forms new islands. ...
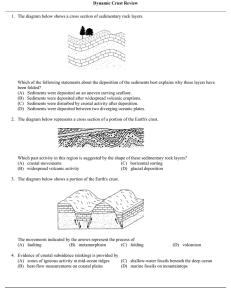
Dynamic Crust Review
... (C) New oceanic crust will form. (B) Earths circumference will increase. (D) Earths magnetic field will reverse direction. 37. Which inference is supported by a study of the Earth's magnetic rock record? (A) The Earth's magnetic poles appear to have changed location over time. (B) The Earth's magnet ...
... (C) New oceanic crust will form. (B) Earths circumference will increase. (D) Earths magnetic field will reverse direction. 37. Which inference is supported by a study of the Earth's magnetic rock record? (A) The Earth's magnetic poles appear to have changed location over time. (B) The Earth's magnet ...
Expedition Worksheet, if you do not have course workbook
... 6. Earthquakes Below the Atlantic Ocean The boundary in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean separates the North American and Eurasian plates and lies along an underwater volcanic mountain range called the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This boundary is composed of north-south oriented divergent boundary segments ...
... 6. Earthquakes Below the Atlantic Ocean The boundary in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean separates the North American and Eurasian plates and lies along an underwater volcanic mountain range called the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This boundary is composed of north-south oriented divergent boundary segments ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.