131KB - NZQA
... basalt so is denser than Australian Plate. It is dragged down under the Australian Plate by gravity. Above this zone is region of Hawke’s Bay. Hawke’s Bay is on the Australian Plate but west of Hikurangi Trough, which is where subduction occurs. This subduction is not smooth, friction between the pl ...
... basalt so is denser than Australian Plate. It is dragged down under the Australian Plate by gravity. Above this zone is region of Hawke’s Bay. Hawke’s Bay is on the Australian Plate but west of Hikurangi Trough, which is where subduction occurs. This subduction is not smooth, friction between the pl ...
TEKS Based Lesson Plan
... 4. Have each student tear the cup into about 12 pieces to represent the major tectonic plates underlying the earth’s surface, and float them on the water, in turns. They have just modeled the lithosphere—the place deep below the surface of the earth where the tectonic plates are located. In the real ...
... 4. Have each student tear the cup into about 12 pieces to represent the major tectonic plates underlying the earth’s surface, and float them on the water, in turns. They have just modeled the lithosphere—the place deep below the surface of the earth where the tectonic plates are located. In the real ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Minerals
... How We Go Places: Plate Tectonics • The crust is cracked into large slabs called tectonic plates and float on magma • Convection currents move plates around • Collisions between plates cause EQ! ...
... How We Go Places: Plate Tectonics • The crust is cracked into large slabs called tectonic plates and float on magma • Convection currents move plates around • Collisions between plates cause EQ! ...
Layers of the Earth
... • Earth’s made up of two parts, a shell called the outer core and a sphere called the inner core. • The outer core temperature ranges from 2,200 to 5000 degrees C. which is the temperature of the inner core. • Both cores are made up of iron and nickel. • However, while the iron and nickel in the out ...
... • Earth’s made up of two parts, a shell called the outer core and a sphere called the inner core. • The outer core temperature ranges from 2,200 to 5000 degrees C. which is the temperature of the inner core. • Both cores are made up of iron and nickel. • However, while the iron and nickel in the out ...
Inside Earth Notes
... mantle has three parts. • The top layer of the mantle, along with the crust, is the lithosphere. The top layer of the mantle is hard rock. • The middle layer of the mantle is the asthenosphere. The middle layer is soft rock, like hot road tar. • The bottom layer of the mantle is called the lower man ...
... mantle has three parts. • The top layer of the mantle, along with the crust, is the lithosphere. The top layer of the mantle is hard rock. • The middle layer of the mantle is the asthenosphere. The middle layer is soft rock, like hot road tar. • The bottom layer of the mantle is called the lower man ...
Mountain Types Outline 1) Describe the 2 mountain belts and where
... remain flat instead of faulting and folding Located near mountain ranges Plateaus can form when layers of molten rock harden and pile up on Earth’s surface or when large areas of rock are eroded b) Grabens Same type of faulting as fault- block mountains Develop when steep faults break the cr ...
... remain flat instead of faulting and folding Located near mountain ranges Plateaus can form when layers of molten rock harden and pile up on Earth’s surface or when large areas of rock are eroded b) Grabens Same type of faulting as fault- block mountains Develop when steep faults break the cr ...
Alaska 1964 animation text
... destroyed entire communities….. This earthquake also rocked the scientific community by confirming a major principle of plate tectonics with the observation that the oceanic Pacific Plate dives beneath the continental North American Plate at the Aleutian trench. Alaska has over 24,000 measured earth ...
... destroyed entire communities….. This earthquake also rocked the scientific community by confirming a major principle of plate tectonics with the observation that the oceanic Pacific Plate dives beneath the continental North American Plate at the Aleutian trench. Alaska has over 24,000 measured earth ...
Archaean Crustal Evolution Protocontinents to Microcontinents
... time was formed by volcanic activity, either from hot spots or subduction zones. Continents, even small ones, are still a distance in the future. ...
... time was formed by volcanic activity, either from hot spots or subduction zones. Continents, even small ones, are still a distance in the future. ...
The Origin of Alkaline Lavas
... lkaline lavas—mantle-derived magmas rich in alkali metals such as potassium and sodium—are commonly found in the interiors of tectonic plates, both on continents and on islands in ocean basins. Melting of metasomatic materials in the mantle lithosphere has long been conjectured to be the main source ...
... lkaline lavas—mantle-derived magmas rich in alkali metals such as potassium and sodium—are commonly found in the interiors of tectonic plates, both on continents and on islands in ocean basins. Melting of metasomatic materials in the mantle lithosphere has long been conjectured to be the main source ...
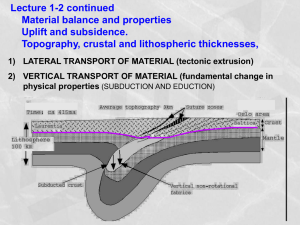
In this lecture we will discuss the Lithosphere, the solid part of the
... Diatoms are made of calcium carbonite. Over geological time they form sediments that then when uplifted can form mountain ranges like the Dolomites in Italy or the Cliffs of Dover in England ...
... Diatoms are made of calcium carbonite. Over geological time they form sediments that then when uplifted can form mountain ranges like the Dolomites in Italy or the Cliffs of Dover in England ...
V: 0
... Students will be able to explain that convection currents in the mantle is what causes Earth's tectonic plates to move ...
... Students will be able to explain that convection currents in the mantle is what causes Earth's tectonic plates to move ...
Chapteer 1 study guide rev
... Chapter 1 you review the concept � Know the name and location of the world’s oceans � Be able to explain the difference between an ocean and a sea � Be able to describe how the ocean has been explored, by which cultures, and for what reasons � Be able to describe the 4 cultures � Be able to ex ...
... Chapter 1 you review the concept � Know the name and location of the world’s oceans � Be able to explain the difference between an ocean and a sea � Be able to describe how the ocean has been explored, by which cultures, and for what reasons � Be able to describe the 4 cultures � Be able to ex ...
05c_U7E_PlanetEarth_p396-410
... A diverging boundary is one where two of Earth’s plates are moving apart. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge on the floor of the Atlantic Ocean is an example of a diverging plate boundary. At this type of boundary, lava flows from the ridge to form new oceanic crust. Sometimes, volcanoes grow high enough that t ...
... A diverging boundary is one where two of Earth’s plates are moving apart. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge on the floor of the Atlantic Ocean is an example of a diverging plate boundary. At this type of boundary, lava flows from the ridge to form new oceanic crust. Sometimes, volcanoes grow high enough that t ...
Name: Date: Title: Candy Bar Tectonics Introduction: In this lab, you
... gently push one side away from you while pulling the other side towards you so that the pieces move along the crack. You have created a transform boundary. Write or draw 2 observations: ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
... gently push one side away from you while pulling the other side towards you so that the pieces move along the crack. You have created a transform boundary. Write or draw 2 observations: ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ...
Plate Tectonics Lab
... There are 3 types of plate boundaries and a fourth called a “plate boundary zone” in which the type of plate boundary is not clearly defined. Go to the website: ...
... There are 3 types of plate boundaries and a fourth called a “plate boundary zone” in which the type of plate boundary is not clearly defined. Go to the website: ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Plate Tectonics Cylinder
... To demonstrate to the class how plates rubbing together can cause an earthquake, conduct the following activity. Ask the students to press their two palms tightly together. As they press their palms together, instruct them to try to rub one palm over the other. Their palms will suddenly slip past ea ...
... To demonstrate to the class how plates rubbing together can cause an earthquake, conduct the following activity. Ask the students to press their two palms tightly together. As they press their palms together, instruct them to try to rub one palm over the other. Their palms will suddenly slip past ea ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Plate Tectonics Cylinder
... To demonstrate to the class how plates rubbing together can cause an earthquake, conduct the following activity. Ask the students to press their two palms tightly together. As they press their palms together, instruct them to try to rub one palm over the other. Their palms will suddenly slip past ea ...
... To demonstrate to the class how plates rubbing together can cause an earthquake, conduct the following activity. Ask the students to press their two palms tightly together. As they press their palms together, instruct them to try to rub one palm over the other. Their palms will suddenly slip past ea ...
9-26 Review SFS and CD.notebook
... is too mild today for continental glaciers to form. Wegener concluded that when Pangaea existed, South Africa was much closer to the South Pole. ...
... is too mild today for continental glaciers to form. Wegener concluded that when Pangaea existed, South Africa was much closer to the South Pole. ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.