density of water
... mass in column 1 = mass in column 2 = mass in column 3 density mantle > density oceanic crust > density continental crust if more mantle in column -- column will be thinner if more continental crust in column -- column will be thicker implication is that mountains have “roots” -- crust is thicker be ...
... mass in column 1 = mass in column 2 = mass in column 3 density mantle > density oceanic crust > density continental crust if more mantle in column -- column will be thinner if more continental crust in column -- column will be thicker implication is that mountains have “roots” -- crust is thicker be ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... 7. Which of the following energy sources is thought to drive the lateral motions of Earth's lithospheric plates? A) gravitational attractive forces of the Sun and Moon B) electrical and magnetic fields localized in the inner core C) export of heat from deep in the mantle to the top of the asthenosph ...
... 7. Which of the following energy sources is thought to drive the lateral motions of Earth's lithospheric plates? A) gravitational attractive forces of the Sun and Moon B) electrical and magnetic fields localized in the inner core C) export of heat from deep in the mantle to the top of the asthenosph ...
Impact on Landscape and Population
... Earthquakes are mainly found along the boundaries of tectonic plates as shown on the map above. There are bands of earthquakes found all around the Pacific Ocean e.g. Japan which is known as the Pacific ring of fire. The West coasts of North and South America are in earthquake zones as is the midAtl ...
... Earthquakes are mainly found along the boundaries of tectonic plates as shown on the map above. There are bands of earthquakes found all around the Pacific Ocean e.g. Japan which is known as the Pacific ring of fire. The West coasts of North and South America are in earthquake zones as is the midAtl ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... 7. Which of the following energy sources is thought to drive the lateral motions of Earth's lithospheric plates? A) gravitational attractive forces of the Sun and Moon B) electrical and magnetic fields localized in the inner core C) export of heat from deep in the mantle to the top of the asthenosph ...
... 7. Which of the following energy sources is thought to drive the lateral motions of Earth's lithospheric plates? A) gravitational attractive forces of the Sun and Moon B) electrical and magnetic fields localized in the inner core C) export of heat from deep in the mantle to the top of the asthenosph ...
Assembly and Breakup of Supercontinents
... records, on a map of the world, at the end of the exercise we may be surprised to find that the earth's surface has been divided into smaller segments of 'stable areas' (virtually free of earthquakes and volcanoes) bounded by narrow strips of unstable zones (Figure 2). The stable areas are called 'p ...
... records, on a map of the world, at the end of the exercise we may be surprised to find that the earth's surface has been divided into smaller segments of 'stable areas' (virtually free of earthquakes and volcanoes) bounded by narrow strips of unstable zones (Figure 2). The stable areas are called 'p ...
Name - seattlescience
... Questions: Use the globe and what you learned in this lab to answer the following questions. 1. Where on earth do you see evidence that plates collided in the past? 2. Where on the globe do you think plates are separating? Find evidence of this both within continents and under the ocean? 3. Find Jap ...
... Questions: Use the globe and what you learned in this lab to answer the following questions. 1. Where on earth do you see evidence that plates collided in the past? 2. Where on the globe do you think plates are separating? Find evidence of this both within continents and under the ocean? 3. Find Jap ...
Layers of the Earth Investigation 2
... Layers of the Earth Our Earth is much more complex than just a large mass of soil and rock. The Earth definitely includes soil and rock, but beneath the Earth’s solid surface, it’s quite different. Research shows that Earth is made of several materials arranged in different layers. The deeper you tr ...
... Layers of the Earth Our Earth is much more complex than just a large mass of soil and rock. The Earth definitely includes soil and rock, but beneath the Earth’s solid surface, it’s quite different. Research shows that Earth is made of several materials arranged in different layers. The deeper you tr ...
Geology Unit Jeopardy Part 2
... What type of plate boundaries created each of the following landforms? a. Aleutian Islands b. Mid-Atlantic Ridge c. Andes Mountains ...
... What type of plate boundaries created each of the following landforms? a. Aleutian Islands b. Mid-Atlantic Ridge c. Andes Mountains ...
CHAPTER 1 - INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY
... the discipline – plate tectonics and the geological time scale. The discussion then turns to examine the range of work modern geoscientists may find themselves doing and how this differs from the ‘traditional’ image of the geologist working in the bush. The exciting challenges that lie ahead in the ...
... the discipline – plate tectonics and the geological time scale. The discussion then turns to examine the range of work modern geoscientists may find themselves doing and how this differs from the ‘traditional’ image of the geologist working in the bush. The exciting challenges that lie ahead in the ...
chapter 3 – answers to questions in text
... 6. Plate tectonic theory is based on the simple model in which rigid lithosphere, of both oceanic and continental crust as well as the underlying upper mantle, is broken into seven major and numerous smaller plates. Most geologists accept plate tectonic theory because the evidence overwhelming suppo ...
... 6. Plate tectonic theory is based on the simple model in which rigid lithosphere, of both oceanic and continental crust as well as the underlying upper mantle, is broken into seven major and numerous smaller plates. Most geologists accept plate tectonic theory because the evidence overwhelming suppo ...
31. From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics
... drift. While at this point we could simply rehearse the modern version of this theory, there are at least two good reasons for delaying that part of the story. First, while the observations in favor of continental drift were not accumulated all at once, they turn out to make a rather impressive and ...
... drift. While at this point we could simply rehearse the modern version of this theory, there are at least two good reasons for delaying that part of the story. First, while the observations in favor of continental drift were not accumulated all at once, they turn out to make a rather impressive and ...
lecture * 2011 japanese tsunami and wave properties
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes occur along or near the boundaries of the plates. As the plates continue moving, rocks are locked together at the boundaries until stresses accumulate past the breaking point. Earthquakes occur when the rocks suddenly crack and slip along lines called faults (often at or ne ...
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes occur along or near the boundaries of the plates. As the plates continue moving, rocks are locked together at the boundaries until stresses accumulate past the breaking point. Earthquakes occur when the rocks suddenly crack and slip along lines called faults (often at or ne ...
Ocean - abyss of time planet earth
... What Earth processes affect the formation and evolution of continental margins, and what benefits and threats do continental margins offer to mankind? The relatively steep slopes of the continental margins, which extend vertically over several kilometres, can affect the directions of ocean currents ...
... What Earth processes affect the formation and evolution of continental margins, and what benefits and threats do continental margins offer to mankind? The relatively steep slopes of the continental margins, which extend vertically over several kilometres, can affect the directions of ocean currents ...
Plate Tectonics
... *Note that plate tectonics is a theory. It is not something that we can directly sample or touch, or for that matter prove. That is why we will refer to it as a theory. *In 1915, a Bavarian scientist named Alfred Wegener (later referred to as the "Father of Plate Tectonics") noticed, while working n ...
... *Note that plate tectonics is a theory. It is not something that we can directly sample or touch, or for that matter prove. That is why we will refer to it as a theory. *In 1915, a Bavarian scientist named Alfred Wegener (later referred to as the "Father of Plate Tectonics") noticed, while working n ...
Convection - Animated Science
... The Earth’s lithosphere (the crust) is cracked into a number of large pieces (tectonic plates) which are constantly moving. This is as a result of convection currents within the Earth’s mantle driven by heat released by natural radioactive processes. ...
... The Earth’s lithosphere (the crust) is cracked into a number of large pieces (tectonic plates) which are constantly moving. This is as a result of convection currents within the Earth’s mantle driven by heat released by natural radioactive processes. ...
Waves and Plate tectonics
... • The German meteorologist Alfred Wegener advocated "continental drift" in 1924. But people didn’t believe this idea. People started to think differently in the 1960’s due to evidence such as ; • Fossil records are similar between South America and Africa. • Some types of rocks match between South A ...
... • The German meteorologist Alfred Wegener advocated "continental drift" in 1924. But people didn’t believe this idea. People started to think differently in the 1960’s due to evidence such as ; • Fossil records are similar between South America and Africa. • Some types of rocks match between South A ...
tectonics
... The theory of continental drift formulated by Alfred Wegener in the early 20th century is the forerunner to the modern theory of plate tectonics. It was based on the observation that many continents "fit together like a jigsaw puzzle" (e.g. S. America and Africa) and, if joined back together, many s ...
... The theory of continental drift formulated by Alfred Wegener in the early 20th century is the forerunner to the modern theory of plate tectonics. It was based on the observation that many continents "fit together like a jigsaw puzzle" (e.g. S. America and Africa) and, if joined back together, many s ...
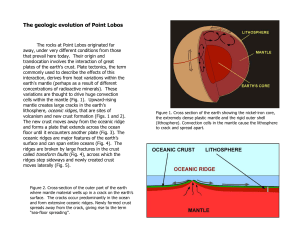
The geologic evolution of Point Lobos
... Figure 5. “Transform faults” are giant fractures in the earth’s crust, across which an oceanic ridge is displaced. Offset of the ridge is not necessarily ongoing, but the crust on opposite sides of the fracture may be moving in opposite directions or in the same direction, but at different rates an ...
... Figure 5. “Transform faults” are giant fractures in the earth’s crust, across which an oceanic ridge is displaced. Offset of the ridge is not necessarily ongoing, but the crust on opposite sides of the fracture may be moving in opposite directions or in the same direction, but at different rates an ...
The Thermal Evolution of an Earth with Strong Subduction Zones
... It is commonly supposed that plate tectonic rates are controlled by the temperature-dependent viscosity of Earth's deep interior. If this were so, a small decrease in mantle temperature would lead to a large decreasein global heat transport. This negative feedback mechanism would prevent mantle temp ...
... It is commonly supposed that plate tectonic rates are controlled by the temperature-dependent viscosity of Earth's deep interior. If this were so, a small decrease in mantle temperature would lead to a large decreasein global heat transport. This negative feedback mechanism would prevent mantle temp ...
Ocean Basins - University of Washington
... continental and oceanic plates move in same direction at same speed examples – margins around Atlantic Ocean contain: coastal plain (was continental shelf during higher sea level) broad continental shelf continental slope and rise Collision margins continental and oceanic plates move toward each oth ...
... continental and oceanic plates move in same direction at same speed examples – margins around Atlantic Ocean contain: coastal plain (was continental shelf during higher sea level) broad continental shelf continental slope and rise Collision margins continental and oceanic plates move toward each oth ...
Document
... A present-day mantle upwelling beneath Iceland dynamically supports the bathymetry of the North Atlantic Ocean. Varying dynamic support has controlled uplift and subsidence at Earth's surface throughout Neogene times. Intersection of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge with the Iceland plume provides us with a w ...
... A present-day mantle upwelling beneath Iceland dynamically supports the bathymetry of the North Atlantic Ocean. Varying dynamic support has controlled uplift and subsidence at Earth's surface throughout Neogene times. Intersection of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge with the Iceland plume provides us with a w ...
UNIT 5 – Earth`s Internal Structure
... • between 5 and 10 km under the oceans (oceanic crust) • between 30 and 65 km under the continents (continental crust) ...
... • between 5 and 10 km under the oceans (oceanic crust) • between 30 and 65 km under the continents (continental crust) ...
Year 7 Georgraphy - Finborough School
... To understand the events at the transform boundaries of plates sliding past each other and build-up of pressure due to friction results in a sudden jolt. To learn the key terms: ...
... To understand the events at the transform boundaries of plates sliding past each other and build-up of pressure due to friction results in a sudden jolt. To learn the key terms: ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.