The Language of Medicine - Respiratory Therapy Files
... atria just before contraction; • QRS wave = spread of excitation wave over the ventricles as the ventricles contract; • T wave = electrical recovery and relaxation of ventricles. • A heart attack (myocardial infarction or MI) can be recognized by an elevation in the S-T segment of the ECG. ...
... atria just before contraction; • QRS wave = spread of excitation wave over the ventricles as the ventricles contract; • T wave = electrical recovery and relaxation of ventricles. • A heart attack (myocardial infarction or MI) can be recognized by an elevation in the S-T segment of the ECG. ...
WS-Heart
... 7. ventricular relaxation 8. ventricular ejection A. 3, 5, 6, 4, 2, 1, 8, 7 B. 4, 5, 1, 2, 7, 8, 3, 6 C. 3, 2, 6, 4, 5, 8, 7, 1 D. 3, 2, 6, 1, 4, 5, 8, 7 E. 3, 5, 6, 1, 8, 4, 2, 7 ...
... 7. ventricular relaxation 8. ventricular ejection A. 3, 5, 6, 4, 2, 1, 8, 7 B. 4, 5, 1, 2, 7, 8, 3, 6 C. 3, 2, 6, 4, 5, 8, 7, 1 D. 3, 2, 6, 1, 4, 5, 8, 7 E. 3, 5, 6, 1, 8, 4, 2, 7 ...
4.4.1.P UnblockVesselsF
... Project 4.4.1: Unblocking the Vessels Introduction Heart disease is a broad term used to refer to the range of diseases that can affect the heart. This may include diseases of the blood vessels, heart rhythm problems, heart infections, and problems in the heart a person is born with, called congenit ...
... Project 4.4.1: Unblocking the Vessels Introduction Heart disease is a broad term used to refer to the range of diseases that can affect the heart. This may include diseases of the blood vessels, heart rhythm problems, heart infections, and problems in the heart a person is born with, called congenit ...
Arteries - LPS.org
... • Right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary trunk • Left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta ...
... • Right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary trunk • Left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta ...
Algorithm for therapeutic management of acute heart failure
... Cardiology and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine further classified acute heart failure patients in six categories [4]: (1) Hypertensive acute HF: signs and symptoms of HF are accompanied by high blood pressure and relatively preserved left ventricular function with a chest radiograph ...
... Cardiology and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine further classified acute heart failure patients in six categories [4]: (1) Hypertensive acute HF: signs and symptoms of HF are accompanied by high blood pressure and relatively preserved left ventricular function with a chest radiograph ...
powerpoint - WordPress.com
... blood into the plumonary artery. The right ventricle has a triangular shape, and extends from the right atrium to the apex of the heart. The left ventricle is one of four chambers within the human heart. The left atrium gives the left ventricle blood which is pumped to the aorta valve. ...
... blood into the plumonary artery. The right ventricle has a triangular shape, and extends from the right atrium to the apex of the heart. The left ventricle is one of four chambers within the human heart. The left atrium gives the left ventricle blood which is pumped to the aorta valve. ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... It can occur as a result of age, AVN or SVN problems, metabolic disturbances, as a result of taking certain medications, drug abuse, or as a result of a pre-existing heart disease. Trained athletes tend to have slow resting heart rates, and resting bradycardia in athletes is not abnormal if no sympt ...
... It can occur as a result of age, AVN or SVN problems, metabolic disturbances, as a result of taking certain medications, drug abuse, or as a result of a pre-existing heart disease. Trained athletes tend to have slow resting heart rates, and resting bradycardia in athletes is not abnormal if no sympt ...
Guidelines for Postoperative Care of Tetralogy of Fallot Hala Agha, MD
... wires are usually required to improve cardiac output . ...
... wires are usually required to improve cardiac output . ...
Teacher Guidance
... disease, and how many die from it each year? Respectively, 5 million have heart failure and 600,000 die each year in the U.S. 2. What is ischemia? It is reduced blood flow to the heart. 3. When the body senses ischemia, the heart attempts to compensate using either, or both, of two processes. What a ...
... disease, and how many die from it each year? Respectively, 5 million have heart failure and 600,000 die each year in the U.S. 2. What is ischemia? It is reduced blood flow to the heart. 3. When the body senses ischemia, the heart attempts to compensate using either, or both, of two processes. What a ...
Surgical Ventricular Reconstruction for Heart Failure
... Congestive heart failure is one of the leading causes of death and complications in the developed world, and coronary artery disease is the major cause of heart failure. Efforts to improve ventricular function, symptoms, and clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure have included neurohormona ...
... Congestive heart failure is one of the leading causes of death and complications in the developed world, and coronary artery disease is the major cause of heart failure. Efforts to improve ventricular function, symptoms, and clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure have included neurohormona ...
Steps of rheumatic fever
... rheumatic heart disease. A heart valve acts like a one-way door. It makes sure that blood pumped by the heart flows in one direction only. When the heart valve is damaged it can leak and may: • make it hard to breathe • make your child feel tired all the time. ...
... rheumatic heart disease. A heart valve acts like a one-way door. It makes sure that blood pumped by the heart flows in one direction only. When the heart valve is damaged it can leak and may: • make it hard to breathe • make your child feel tired all the time. ...
Heart sounds and murmurs
... papillary muscles is because during ventricular contraction the ventricle size decreases and the papillary muscle must contract to shorten the chordea tendinei to prevent the leakage of valves ...
... papillary muscles is because during ventricular contraction the ventricle size decreases and the papillary muscle must contract to shorten the chordea tendinei to prevent the leakage of valves ...
Effects of Exercise Training
... • Peak HR is slightly lower than normal (~150 beats/min) • Heart rate may remain near its peak value for several minutes during recovery. • Return to resting levels is delayed ...
... • Peak HR is slightly lower than normal (~150 beats/min) • Heart rate may remain near its peak value for several minutes during recovery. • Return to resting levels is delayed ...
Module 34 / Valves of the Heart
... back against the valves during ventricular contraction, the valves may not remain closed. If many of these connections are ruptured or if the thicker ones are affected, the valves can open in the reverse direction, and blood can backflow into the atria. This results in increased pressure in the atri ...
... back against the valves during ventricular contraction, the valves may not remain closed. If many of these connections are ruptured or if the thicker ones are affected, the valves can open in the reverse direction, and blood can backflow into the atria. This results in increased pressure in the atri ...
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND SCIENCE OF THE RUSSIAN
... PC-1(The ability and readiness for the early diagnosis of disease, identify the causes and conditions of their emergence and development). PC-2 (the ability and willingness to conduct preventive medical examinations (fluoroscopy), clinical examination and implementation of follow-up. PC-5 (Readiness ...
... PC-1(The ability and readiness for the early diagnosis of disease, identify the causes and conditions of their emergence and development). PC-2 (the ability and willingness to conduct preventive medical examinations (fluoroscopy), clinical examination and implementation of follow-up. PC-5 (Readiness ...
Heart Failure - the Helderberg Cardiac Support Group
... • The most common causes of heart failure are coronary heart disease, hypertension, alcohol abuse, and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy • Other causes are valvular and pericardial disease; or anaemia, thyrotoxicosis, septicaemia, Paget's disease of bone, and arteriovenous fistulae. ...
... • The most common causes of heart failure are coronary heart disease, hypertension, alcohol abuse, and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy • Other causes are valvular and pericardial disease; or anaemia, thyrotoxicosis, septicaemia, Paget's disease of bone, and arteriovenous fistulae. ...
Understanding the Heart.
... coronary arteries is the main cause of a group of disorders known as ischaemic heart disease. ...
... coronary arteries is the main cause of a group of disorders known as ischaemic heart disease. ...
An usual cardiac manifestation of a very common
... A 69 year old lady presents to the primary percutaneous ...
... A 69 year old lady presents to the primary percutaneous ...
What is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
... and may be recommended in advanced stages of heart failure. For children with heart rhythm problems, anti-arrhythmic medications (amiodarone, digoxin, disopyramide, procaineamide, verapamil) may be used to keep the heart beating at a regular rate. In some cases, an anti-coagulant (aspirin, dipyridam ...
... and may be recommended in advanced stages of heart failure. For children with heart rhythm problems, anti-arrhythmic medications (amiodarone, digoxin, disopyramide, procaineamide, verapamil) may be used to keep the heart beating at a regular rate. In some cases, an anti-coagulant (aspirin, dipyridam ...
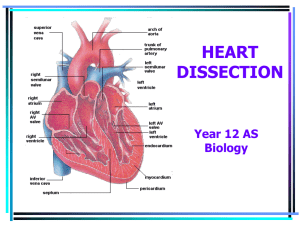
heart dissection
... The first incision… … is along the right ventricle. The right ventricle can be identified by squeezing the heart, since the myocardium on the right side is much less rigid than that of the left ventricle. This allows us to see the tricuspid valve and the right ventricular outflow tract which includ ...
... The first incision… … is along the right ventricle. The right ventricle can be identified by squeezing the heart, since the myocardium on the right side is much less rigid than that of the left ventricle. This allows us to see the tricuspid valve and the right ventricular outflow tract which includ ...
Regulation of the Heart`s Functions
... distention in intact animals during the transition from the standing to the recumbent position.1 2 However, other forms of cardiovascular adjustments appear to be initiated primarily by increased discharge of sympathetic nerves to the heart and peripheral vasculature. In a dog that is familiar with ...
... distention in intact animals during the transition from the standing to the recumbent position.1 2 However, other forms of cardiovascular adjustments appear to be initiated primarily by increased discharge of sympathetic nerves to the heart and peripheral vasculature. In a dog that is familiar with ...
Clinical - Bart.indd - The Minnesota Heart Failure Consortium
... diverse interventions such as withholding diuretics and replacing fluids, increasing the intensity of diuretic therapy, adding vasodilators or inotropes, and using ultrafiltration. The CARRESS HF study will compare ultrafiltration with a stepped-care algorithm emphasizing the use of diuretic agents. ...
... diverse interventions such as withholding diuretics and replacing fluids, increasing the intensity of diuretic therapy, adding vasodilators or inotropes, and using ultrafiltration. The CARRESS HF study will compare ultrafiltration with a stepped-care algorithm emphasizing the use of diuretic agents. ...
Cardiovascular System - Downey Unified School District
... http://www.sharecare.com/health/blood-basics/howblood-travel-human-body http://learn.fi.edu/learn/heart/vessels/capillaries.html http://www.cliffsnotes.com/sciences/anatomy-andphysiology/the-cardiovascular-system/blood-vessels ...
... http://www.sharecare.com/health/blood-basics/howblood-travel-human-body http://learn.fi.edu/learn/heart/vessels/capillaries.html http://www.cliffsnotes.com/sciences/anatomy-andphysiology/the-cardiovascular-system/blood-vessels ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.