Arginine Vasopressin Antagonist Tolvaptan in the treatment of heart
... elevation in plasma osmolality and decreases in arterial pressure in patients with HF and left ventricular systolic dysfunction.4 ...
... elevation in plasma osmolality and decreases in arterial pressure in patients with HF and left ventricular systolic dysfunction.4 ...
heart failure
... TYPES OF HEART FAILURE 2. Right sided heart failure • It occurs in chronic lung disease, pulmonary valve stenosis. There is reduction of RV output and back pressure on right atrium ( Increased JVP, Liver enlargement, peripheral edema ). 3. Biventricular failure • It affects both ventricle and occurs ...
... TYPES OF HEART FAILURE 2. Right sided heart failure • It occurs in chronic lung disease, pulmonary valve stenosis. There is reduction of RV output and back pressure on right atrium ( Increased JVP, Liver enlargement, peripheral edema ). 3. Biventricular failure • It affects both ventricle and occurs ...
Cardio Bulletin Nov 2014 - East Dorset NHS Library
... Uncertainties about medical treatment of acute heart failure Jonathan R Dalzell and Jane A Cannon Concerns about latest NICE guidelines on acute heart failure Angiotensin receptor blocker in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction with preserved left ventricular systolic function: p ...
... Uncertainties about medical treatment of acute heart failure Jonathan R Dalzell and Jane A Cannon Concerns about latest NICE guidelines on acute heart failure Angiotensin receptor blocker in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction with preserved left ventricular systolic function: p ...
glossary of terms
... greater saphenous veins – Veins in the leg often used as a source for a bypass graft to be placed during open heart surgery. heart-lung machine – Functions as the patient’s heart and lungs during the conventional bypass surgery; also called cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). hemodynamic – The study of th ...
... greater saphenous veins – Veins in the leg often used as a source for a bypass graft to be placed during open heart surgery. heart-lung machine – Functions as the patient’s heart and lungs during the conventional bypass surgery; also called cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). hemodynamic – The study of th ...
Aerobics 11th Grade Study Guide Terms • Aerobic – means with
... When working above the target heart rate zone muscles will begin to build up lactic acid and the person will not be able to continue the activity for the full 25 minutes or more. Lactic acid build up is what prevents a person from sprinting as fast as they can for 2 miles, the body simply cannot mai ...
... When working above the target heart rate zone muscles will begin to build up lactic acid and the person will not be able to continue the activity for the full 25 minutes or more. Lactic acid build up is what prevents a person from sprinting as fast as they can for 2 miles, the body simply cannot mai ...
Principles of cardiovascular measurement I and II
... – Brachial/femoral artery aorta, left, ventricle, left atrium ...
... – Brachial/femoral artery aorta, left, ventricle, left atrium ...
The Cardiovascular System - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... the heart is provided by the coronary arteries which stem from base of the aorta and encircle the heart. • These arteries fill when the heart is relaxed, and are compressed when the heart is contracting. ...
... the heart is provided by the coronary arteries which stem from base of the aorta and encircle the heart. • These arteries fill when the heart is relaxed, and are compressed when the heart is contracting. ...
Your Heart And How It Works
... At rest, the heart beats approximately 60 to 100 times a minute. In children the heart rate is higher than in adults. Over an average lifetime, the heart will beat more than a million times. When you are physically active, excited or ill, your heart rate can rise significantly. This is a natural res ...
... At rest, the heart beats approximately 60 to 100 times a minute. In children the heart rate is higher than in adults. Over an average lifetime, the heart will beat more than a million times. When you are physically active, excited or ill, your heart rate can rise significantly. This is a natural res ...
acute heart failure syndrome - Rajiv Gandhi University of Health
... than 1 million patients present to hospitals with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) every year. Approximately one-third of the ADHF patients develop AKI as defined by an increase in serum creatinine of ≥0.3 mg/dl. In patients with cardiogenic shock, the incidence of AKI can exceed 70%. Furthe ...
... than 1 million patients present to hospitals with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) every year. Approximately one-third of the ADHF patients develop AKI as defined by an increase in serum creatinine of ≥0.3 mg/dl. In patients with cardiogenic shock, the incidence of AKI can exceed 70%. Furthe ...
Update on Feline Cardiomyopathy: Diagnosis, Treatment and
... similar to the canine form. It is uncommon in cats but can be associated with taurine (an essential feline amino acid) deficiency. Although most commercial cat foods today are well supplemented, special diets or owner-created diets may be deficient. A small percentage of cats have dilated cardiomyop ...
... similar to the canine form. It is uncommon in cats but can be associated with taurine (an essential feline amino acid) deficiency. Although most commercial cat foods today are well supplemented, special diets or owner-created diets may be deficient. A small percentage of cats have dilated cardiomyop ...
Tailored acute heart failure treatment
... modern treatment strategies1,2. Most CS-related deaths occur during the first 48 hours1–3. Thus, instant simple bedside diagnostic predictors could help optimize therapy for these patients. Data from the SHOCK trial3 revealed that the stroke volume (SVi) is the strongest early hemodynamic predictor ...
... modern treatment strategies1,2. Most CS-related deaths occur during the first 48 hours1–3. Thus, instant simple bedside diagnostic predictors could help optimize therapy for these patients. Data from the SHOCK trial3 revealed that the stroke volume (SVi) is the strongest early hemodynamic predictor ...
Weekly EMS Drill Sudden Cardiac Death
... In 90 percent of adult victims of sudden cardiac death, two or more major coronary arteries are narrowed by fatty buildups. Scarring from a prior heart attack is found in two-thirds of victims. When sudden death occurs in young adults, other heart abnormalities are more likely causes. Adrenaline re ...
... In 90 percent of adult victims of sudden cardiac death, two or more major coronary arteries are narrowed by fatty buildups. Scarring from a prior heart attack is found in two-thirds of victims. When sudden death occurs in young adults, other heart abnormalities are more likely causes. Adrenaline re ...
The_heart_and_the_circulatory_system - divaparekh
... -- It sends electrical signals through the walls of the heart at regular intervals, according to the need of the body -- If it stops working-an artificial pacemaker is placed to do the job ...
... -- It sends electrical signals through the walls of the heart at regular intervals, according to the need of the body -- If it stops working-an artificial pacemaker is placed to do the job ...
Lorna LVNC
... Patients with LVHT have poorly functioning dilated ventricles; therefore, some believe this to be a form of DCM (Murphy et al., 2005). Others have described it as a restrictive cardiomyopathy (Ichida et al., 1999). The pathophysiolgic mechanisms of heart failure, systolic dysfunction, and arrhythm ...
... Patients with LVHT have poorly functioning dilated ventricles; therefore, some believe this to be a form of DCM (Murphy et al., 2005). Others have described it as a restrictive cardiomyopathy (Ichida et al., 1999). The pathophysiolgic mechanisms of heart failure, systolic dysfunction, and arrhythm ...
Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM) - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital
... Genes are packages of genetic information that tell our bodies how to develop and function. DCM can be caused by a change or mutation in a gene that encodes proteins important for the contraction or squeeze of the heart muscle. Mutations in these genes result in familial DCM, which is inherited in a ...
... Genes are packages of genetic information that tell our bodies how to develop and function. DCM can be caused by a change or mutation in a gene that encodes proteins important for the contraction or squeeze of the heart muscle. Mutations in these genes result in familial DCM, which is inherited in a ...
Atrial fibrillation - patient information
... Atrial fibrillation occurs when abnormal electrical impulses suddenly start firing in the atria. These impulses override the heart’s natural pacemaker, which can no longer control the rhythm of the heart. This causes you to have a highly irregular pulse rate. The cause isn’t fully understood, but it ...
... Atrial fibrillation occurs when abnormal electrical impulses suddenly start firing in the atria. These impulses override the heart’s natural pacemaker, which can no longer control the rhythm of the heart. This causes you to have a highly irregular pulse rate. The cause isn’t fully understood, but it ...
Cardiovascular System
... to remove excess body fluids, elastic support hose, and oxygen therapy. In addition, rest and lifestyle changes are needed to relieve symptoms. ...
... to remove excess body fluids, elastic support hose, and oxygen therapy. In addition, rest and lifestyle changes are needed to relieve symptoms. ...
Popular Links
... failure suffer from sudden cardiac death secondary to ventricular arrhythmias. There are approximately 4-5 million Americans with heart failure with the AHA estimating about 550,000 new diagnosis each year. Since 1996 when the MADIT study arrived on the scene in the NEJM we have known that prophylac ...
... failure suffer from sudden cardiac death secondary to ventricular arrhythmias. There are approximately 4-5 million Americans with heart failure with the AHA estimating about 550,000 new diagnosis each year. Since 1996 when the MADIT study arrived on the scene in the NEJM we have known that prophylac ...
Nefrologie číslo X, 200X
... congestive heart failure. According to the 2001 ACC/ACA guidelines and BNP level greater than 100 pg/ml supports the diagnosis of abnormal ventricular function or symptomatic HF. Its use in differentiating dyspnoe due to HF from pulmonary disease and in managing patients with HF is under investigati ...
... congestive heart failure. According to the 2001 ACC/ACA guidelines and BNP level greater than 100 pg/ml supports the diagnosis of abnormal ventricular function or symptomatic HF. Its use in differentiating dyspnoe due to HF from pulmonary disease and in managing patients with HF is under investigati ...
eXercISe - Birchaven Village
... contract faster than normal and cause the heart to beat 300 to 400 times per minute. “Some people with AF don’t have symptoms. Others may feel frequent palpitations, shortness of breath during exertion, chest pain, and episodes of dizziness or fainting. The irregular heartbeat may come and go, or it ...
... contract faster than normal and cause the heart to beat 300 to 400 times per minute. “Some people with AF don’t have symptoms. Others may feel frequent palpitations, shortness of breath during exertion, chest pain, and episodes of dizziness or fainting. The irregular heartbeat may come and go, or it ...
Heart Attack in a Nut Shell: A Simple Guide to Understanding
... How a Heart Attack (MI) is Diagnosed 1. ECG-electrocardiogram for those of you who do not know what that is, a non-invasive picture of the electrical activity in your heart with sticky electrodes taped to your chest. It can tell how much damage to your heart muscle there was if any, and where in the ...
... How a Heart Attack (MI) is Diagnosed 1. ECG-electrocardiogram for those of you who do not know what that is, a non-invasive picture of the electrical activity in your heart with sticky electrodes taped to your chest. It can tell how much damage to your heart muscle there was if any, and where in the ...
Cardiovascular powerpoint
... 2. The heart is supplied with nutrients and gases by the cardiac vessels (the presence of the blood in the heart does not accomplish this). These are called coronary arteries and coronary veins. a. The blood from the veins empties into the coronary sinus in the right atrium. b. When these vessels b ...
... 2. The heart is supplied with nutrients and gases by the cardiac vessels (the presence of the blood in the heart does not accomplish this). These are called coronary arteries and coronary veins. a. The blood from the veins empties into the coronary sinus in the right atrium. b. When these vessels b ...
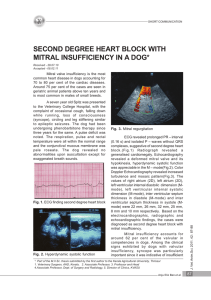
second degree heart block with mitral insufficiency in a dog
... turbulence and mosaic pattern(Fig.3). The values of right atrium (2D), left atrium (2D), left ventricular internal diastolic dimension (Mmode), left ventricular internal systolic dimension (M-mode), inter ventricular septum thickness in diastole (M-mode) and inter ventricular septum thickness in sys ...
... turbulence and mosaic pattern(Fig.3). The values of right atrium (2D), left atrium (2D), left ventricular internal diastolic dimension (Mmode), left ventricular internal systolic dimension (M-mode), inter ventricular septum thickness in diastole (M-mode) and inter ventricular septum thickness in sys ...
PHYSIOLOGY OF HEART
... Extrasystole & compensatory pause Local areas of ischemia Small calcified plaques at different points of heart- irritating Mechanical stimulation during cardiac catheterisation Toxic irritation nicotine, caffeine, drugs Pulse deficite & bigeminal pulse ...
... Extrasystole & compensatory pause Local areas of ischemia Small calcified plaques at different points of heart- irritating Mechanical stimulation during cardiac catheterisation Toxic irritation nicotine, caffeine, drugs Pulse deficite & bigeminal pulse ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.