POWERPOINT SCIENCE
... The measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles in an object. Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. These particles are always in motion even if the object they make up isn’t moving at all. Energy of motion is called kinetic energy, so all particle ...
... The measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles in an object. Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. These particles are always in motion even if the object they make up isn’t moving at all. Energy of motion is called kinetic energy, so all particle ...
~therm= heat,temperature
... • An organism that has adapted to living in very high temperatures or heat, such as bacteria or algae ...
... • An organism that has adapted to living in very high temperatures or heat, such as bacteria or algae ...
Cold Weather Heat Pump Operation Air to Air heat Pump Systems
... inside temperature will continue to drop. At 67 degrees the emergency heat strip with kick in and warm the space back up to 70 degrees. At this point the heat strip shut off. The fan continues to run and the compressor continues to run to heat the space to 72. This does not happen since it is too co ...
... inside temperature will continue to drop. At 67 degrees the emergency heat strip with kick in and warm the space back up to 70 degrees. At this point the heat strip shut off. The fan continues to run and the compressor continues to run to heat the space to 72. This does not happen since it is too co ...
Physical Property Notes
... 3) Measure the temperature change in the water bath **We must make the assumption that all heat/energy lost by the hot metal is transferred and gained by the water** qlost by metal = qgained by water mmetalCpmetal∆Tmetal = mH2OCpH2O∆TH2O 4) Solve for unknown Cp of the metal using known Cp of wate ...
... 3) Measure the temperature change in the water bath **We must make the assumption that all heat/energy lost by the hot metal is transferred and gained by the water** qlost by metal = qgained by water mmetalCpmetal∆Tmetal = mH2OCpH2O∆TH2O 4) Solve for unknown Cp of the metal using known Cp of wate ...
Golden Valley HS • AP Chemistry
... and feel warm or hot. Heat can be defined in calories, which is the amount of heat needed to raise 1 gram of H2O 1oC. The joule is the SI unit of energy. 1 calorie = 4.184 J This is also the specific heat of water (4.184 J/goC). Specific heat of other substances is defined as the energy needed to r ...
... and feel warm or hot. Heat can be defined in calories, which is the amount of heat needed to raise 1 gram of H2O 1oC. The joule is the SI unit of energy. 1 calorie = 4.184 J This is also the specific heat of water (4.184 J/goC). Specific heat of other substances is defined as the energy needed to r ...
Cooling, thermal resistance, modeling of heat transfer as an electric
... Internal circulation of air flow ...
... Internal circulation of air flow ...
Physics 41 Exam 3 Practice HW
... maintained at temperatures of 40°C and 280°C, respectively. The thermal conductivity of aluminum is 205 W/m∙K of copper is 385 W/m∙K. The rate at which heat is conducted in the rod is closest to A) B) C) D) E) ...
... maintained at temperatures of 40°C and 280°C, respectively. The thermal conductivity of aluminum is 205 W/m∙K of copper is 385 W/m∙K. The rate at which heat is conducted in the rod is closest to A) B) C) D) E) ...
Heat Transfer LAB
... the flow of heat or electricity easily. Convection is the transfer of heat by currents within a fluid; liquid or gas. The hotter the fluid the faster the particle movement and the less dense the material is thus making it rise. The cooler a fluid is the slower the particle movement and the more dens ...
... the flow of heat or electricity easily. Convection is the transfer of heat by currents within a fluid; liquid or gas. The hotter the fluid the faster the particle movement and the less dense the material is thus making it rise. The cooler a fluid is the slower the particle movement and the more dens ...
WORKSHOP 2: Dimensional Analysis and
... 8. If the density of a liquid is known to be 0.785 g/mL, calculate the mass of the liquid if its volume is 18.8 mL. 14.8 g 9. Given the table of specific heat values below, what is the identity of a 26.2 g metal sample that increases by 8.5 ºC when 100.0 J of energy is absorbed? Use the formula q = ...
... 8. If the density of a liquid is known to be 0.785 g/mL, calculate the mass of the liquid if its volume is 18.8 mL. 14.8 g 9. Given the table of specific heat values below, what is the identity of a 26.2 g metal sample that increases by 8.5 ºC when 100.0 J of energy is absorbed? Use the formula q = ...
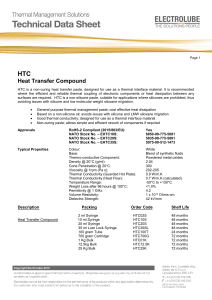
Product Code: HTC
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
phy 1044 determination of specific heat spring 03
... OBJECTIVE: The amount of heat energy that can be transferred to or from a material is dependent on the mass of material, the temperature gradient, and a material property known as its specific heat capacity. The principles of calorimetry will be employed to determine an experimental value for a mate ...
... OBJECTIVE: The amount of heat energy that can be transferred to or from a material is dependent on the mass of material, the temperature gradient, and a material property known as its specific heat capacity. The principles of calorimetry will be employed to determine an experimental value for a mate ...
Metals and non-metals III IMPORTANT POINTS Non-metals
... form ions by gaining electrons and are said to be electronegative nare oxidising agents as they react by gaining electrons N + n e == N react with air or oxygen to form acidic oxides, which can dissolve in water to form acids do not react with dilute acids, water or steam form covalent compounds wit ...
... form ions by gaining electrons and are said to be electronegative nare oxidising agents as they react by gaining electrons N + n e == N react with air or oxygen to form acidic oxides, which can dissolve in water to form acids do not react with dilute acids, water or steam form covalent compounds wit ...
File 2 - College of Science | Oregon State University
... state going through exactly the same intermediate states as when the gas was expanded – or going back along the same path In the p-V space. ...
... state going through exactly the same intermediate states as when the gas was expanded – or going back along the same path In the p-V space. ...
SC151 - CHAPTER 9 LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... converting between units of Joules, calories, and Calories Demonstrate an understanding of thermochemistry by: • explaining the relationships among the following: system, surroundings, and universe; exothermic process and endothermic process; internal energy (E) and enthalpy (H); ∆E, ∆H, qv, and qp ...
... converting between units of Joules, calories, and Calories Demonstrate an understanding of thermochemistry by: • explaining the relationships among the following: system, surroundings, and universe; exothermic process and endothermic process; internal energy (E) and enthalpy (H); ∆E, ∆H, qv, and qp ...
HTC Heat Transfer Compound
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
... There are many methods of measuring thermal conductivity, resulting in large variances in results. Electrolube utilise a heat flow method which takes into account the surface resistance of the test substrate, thus offering highly accurate results of true thermal conductivity. Some alternative method ...
Microclimatology 2 FALL 2008
... Conduction is the process through which heat is diffused to cooler materials as radiation is absorbed. Land surfaces heat quickly, while water bodies can mix and have higher heat capacity. Solids (land) are better conductors than gases (atmosphere). Convection is physical mixing with a strong vertic ...
... Conduction is the process through which heat is diffused to cooler materials as radiation is absorbed. Land surfaces heat quickly, while water bodies can mix and have higher heat capacity. Solids (land) are better conductors than gases (atmosphere). Convection is physical mixing with a strong vertic ...
Lab: Specific Heat of Copper
... 2. Water keeps temperatures in coastal areas more moderate by ______________________________ heat during summer and __________________________ heat during winter 3. Metals tend to have (high/low) specific heats. 4. Copper is a good choice for coating pots and pans because a small mount of heat will ...
... 2. Water keeps temperatures in coastal areas more moderate by ______________________________ heat during summer and __________________________ heat during winter 3. Metals tend to have (high/low) specific heats. 4. Copper is a good choice for coating pots and pans because a small mount of heat will ...
heat energy - Parkway C-2
... this then causes the next particles to move faster and so on. In this way heat in an object travels from: ...
... this then causes the next particles to move faster and so on. In this way heat in an object travels from: ...
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF WATER
... Haifaa altoumah& Rabab Alfaraj SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF WATER ...
... Haifaa altoumah& Rabab Alfaraj SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF WATER ...
Why Thermal Management?
... impurities in semiconductors, pinholes in insulating oxide, etc. Due to electrical overstress: overstress during operation or else exposure to electrostatic discharge Due to chemical reactions: corrosion or formation of intermetallic compounds; exacerbated by high temperatures ...
... impurities in semiconductors, pinholes in insulating oxide, etc. Due to electrical overstress: overstress during operation or else exposure to electrostatic discharge Due to chemical reactions: corrosion or formation of intermetallic compounds; exacerbated by high temperatures ...