File
... Name:_____________________________________________ Class:________________ General Chapter 5 Review This is a general review for the material covered in this chapter. It is intended to be a supplementary study tool that should be used in conjunction with all notes, worksheets, and your text. Please s ...
... Name:_____________________________________________ Class:________________ General Chapter 5 Review This is a general review for the material covered in this chapter. It is intended to be a supplementary study tool that should be used in conjunction with all notes, worksheets, and your text. Please s ...
Climate influences File
... 1. Elevation or altitude - The higher the elevation, the colder the climate. Less dense air cannot hold heat, while more dense air can hold heat. 2. Distance from an ocean or large body of water - Moderates the temperature, less extreme heat and cold. Water is “thermal mass” and holds heat 3. Latitu ...
... 1. Elevation or altitude - The higher the elevation, the colder the climate. Less dense air cannot hold heat, while more dense air can hold heat. 2. Distance from an ocean or large body of water - Moderates the temperature, less extreme heat and cold. Water is “thermal mass” and holds heat 3. Latitu ...
1-14 The filament of a 150 W incandescent lamp is 5 cm long and
... 1-14 The filament of a 150 W incandescent lamp is 5 cm long and has a diameter of 0.5 mm. The heat flux on the surface of the filament, the heat flux on the surface of the glass bulb, and the annual electricity cost of the bulb are to be determined. Assumptions Heat transfer from the surface of the ...
... 1-14 The filament of a 150 W incandescent lamp is 5 cm long and has a diameter of 0.5 mm. The heat flux on the surface of the filament, the heat flux on the surface of the glass bulb, and the annual electricity cost of the bulb are to be determined. Assumptions Heat transfer from the surface of the ...
Types of Heat Related Illnesses
... Every system in your body depends on proper hydration to function properly. Water makes up a large portion of our body. It makes up approximately 50% of a woman and 60% of a man’s body mass. You should consume at least half your body weight in ounces of water per day. Water from foods such as fruits ...
... Every system in your body depends on proper hydration to function properly. Water makes up a large portion of our body. It makes up approximately 50% of a woman and 60% of a man’s body mass. You should consume at least half your body weight in ounces of water per day. Water from foods such as fruits ...
Electronics Cooling MEP 635
... Automotive Electronics Electronic content in cars and trucks has significantly increased in the last 30 years. Much of the functional content of these vehicles is now generated or controlled by electronic systems. ...
... Automotive Electronics Electronic content in cars and trucks has significantly increased in the last 30 years. Much of the functional content of these vehicles is now generated or controlled by electronic systems. ...
Worksheet 6a
... A 15.0 gram sample of nickel metal is heated to 100.0 °C and dropped into 55.0 grams of water, initially at 23.0 °C. Assuming that all the heat lost by the nickel is absorbed by the water, calculate the final temperature of the nickel and water. (The specific heat of nickel is 0.444 J/g •°C) 25.2 oC ...
... A 15.0 gram sample of nickel metal is heated to 100.0 °C and dropped into 55.0 grams of water, initially at 23.0 °C. Assuming that all the heat lost by the nickel is absorbed by the water, calculate the final temperature of the nickel and water. (The specific heat of nickel is 0.444 J/g •°C) 25.2 oC ...
The impressively simple Joulia-Inline technology proves
... to warm the incoming cold water pipe. In this way the cold water arrives at the mixing valve up to 15°C warmer than before. Therefore, substantially less hot water is needed. ...
... to warm the incoming cold water pipe. In this way the cold water arrives at the mixing valve up to 15°C warmer than before. Therefore, substantially less hot water is needed. ...
problem-set-7c-cal-2016
... b) The amount of heat absorbed by the water was the amount of heat lost by the iron. If the piece of iron was 35 g and the specific heat of iron is 0.451 J/g . Co what was the original temperature of the iron? (hint: the iron was dropped into the water, so you know the final temperature of the iron) ...
... b) The amount of heat absorbed by the water was the amount of heat lost by the iron. If the piece of iron was 35 g and the specific heat of iron is 0.451 J/g . Co what was the original temperature of the iron? (hint: the iron was dropped into the water, so you know the final temperature of the iron) ...
Thermochemistry
... Cp is the variable for specific heat ◦ Could be in units of J/(g•˚C) or cal/(g•˚C) q is the variable for heat (joules or calories) M is the variable for mass (grams) ΔT (Tf – Ti) is the variable for change in temperature (˚C) ...
... Cp is the variable for specific heat ◦ Could be in units of J/(g•˚C) or cal/(g•˚C) q is the variable for heat (joules or calories) M is the variable for mass (grams) ΔT (Tf – Ti) is the variable for change in temperature (˚C) ...
Snow-melting and Deicing System Using Underground Thermal
... (1) Use of stable, clean geothermal energy as a heat source The system utilizes natural geothermal energy. Therefore, this abundant natural resource offers a sufficient and stable quantities of heat even during the cold winter months. In addition, the system employs a high-performance ground source ...
... (1) Use of stable, clean geothermal energy as a heat source The system utilizes natural geothermal energy. Therefore, this abundant natural resource offers a sufficient and stable quantities of heat even during the cold winter months. In addition, the system employs a high-performance ground source ...
Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
... a pool is cooler at the deep end? • Examples: air movement in a home, pot of heating water. • Pick one of these examples and draw the circular pattern in your notes. ...
... a pool is cooler at the deep end? • Examples: air movement in a home, pot of heating water. • Pick one of these examples and draw the circular pattern in your notes. ...
The fundamental principles of radiant heat barrier
... radiant heat barrier / reflective foil Reflective insulation materials work on a different concept than conventional bulk insulation like rigid foam boards or fibrous blankets. Unlike conventional bulk insulation, reflective insulation has very low emittance values “e-values” (typically 0.03, compar ...
... radiant heat barrier / reflective foil Reflective insulation materials work on a different concept than conventional bulk insulation like rigid foam boards or fibrous blankets. Unlike conventional bulk insulation, reflective insulation has very low emittance values “e-values” (typically 0.03, compar ...
Page 1 of 2 Gerbing`s Heated Clothing // How it Works 02/11/2009
... Being as tiny as they are, and made from stainless steel, our strands (and therefore our wire) is incredibly flexible and exceptionally rugged. Also, at about .025” (vs. about .075 for the copper resistance wire that’s been in use all these years), Microwire is exceptionally thin. So much so you can ...
... Being as tiny as they are, and made from stainless steel, our strands (and therefore our wire) is incredibly flexible and exceptionally rugged. Also, at about .025” (vs. about .075 for the copper resistance wire that’s been in use all these years), Microwire is exceptionally thin. So much so you can ...
World Biomes - Tartu Veeriku Kool
... • Another growthform adapted to desert conditions is the ephemeral. This is an especially short-lived annual plant that completes its life cycle in two-three weeks. The seeds are encased in a waterproof coating that prevents desiccation for years if necessary. • Perennial plants with underground bul ...
... • Another growthform adapted to desert conditions is the ephemeral. This is an especially short-lived annual plant that completes its life cycle in two-three weeks. The seeds are encased in a waterproof coating that prevents desiccation for years if necessary. • Perennial plants with underground bul ...
Measuring Energy Changes In A Chemical Reaction Sept. 2016
... If we assume that: heat lost/gained by the system = heat gained/lost by the surroundings then we can experimentally determine the energy changes in chemical reactions ...
... If we assume that: heat lost/gained by the system = heat gained/lost by the surroundings then we can experimentally determine the energy changes in chemical reactions ...
Chapters 19&20
... • Quantity Q + W = ΔEint (change of internal energy) is path-independent • 1st law of thermodynamics: the internal energy of a system increases if heat is added to the system or work is done on the system ...
... • Quantity Q + W = ΔEint (change of internal energy) is path-independent • 1st law of thermodynamics: the internal energy of a system increases if heat is added to the system or work is done on the system ...
Note: Moving air
... Answer: The shiny surface of foil reflects infrared radiation, which would reduce heating from outside radiation. The surface also does not emit IR very well, so it would lose less energy by radiation than a non-shiny surface. ...
... Answer: The shiny surface of foil reflects infrared radiation, which would reduce heating from outside radiation. The surface also does not emit IR very well, so it would lose less energy by radiation than a non-shiny surface. ...
2 - D STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION
... These equations may be solved by spreadsheet iteration 'updating' each temperature 'cell' in sequence . Alternatively an array of simultaneous equations may be set up and solved by Gaussian elimination, either by hand (!) or by computer. BOUNDARY CONDITIONS The above equations apply to interior poin ...
... These equations may be solved by spreadsheet iteration 'updating' each temperature 'cell' in sequence . Alternatively an array of simultaneous equations may be set up and solved by Gaussian elimination, either by hand (!) or by computer. BOUNDARY CONDITIONS The above equations apply to interior poin ...
Heat illness
... What to Do to Keep Yourself Cool During normal work activities, especially, during summer months, workers may be required to work in hot environments. When the body is unable to cool itself by sweating, several heat-induced illnesses can occur, and can result in death. ...
... What to Do to Keep Yourself Cool During normal work activities, especially, during summer months, workers may be required to work in hot environments. When the body is unable to cool itself by sweating, several heat-induced illnesses can occur, and can result in death. ...
Specific Heat Capacity - Tasker Milward
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
HormonesCascade
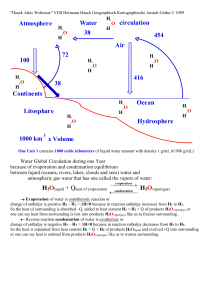
... One Unit 1 contains 1000 cubic kilometers of liquid water amount with density 1 g/mL (0.996 g/mL) ...
... One Unit 1 contains 1000 cubic kilometers of liquid water amount with density 1 g/mL (0.996 g/mL) ...
4.5 THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT . PRACTICE
... Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy and potential energy of all the particles of a substance. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance. 2. (a) The average kinetic energy of the milk molecules is less than the average kinetic energy of the water molecules. The ...
... Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy and potential energy of all the particles of a substance. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance. 2. (a) The average kinetic energy of the milk molecules is less than the average kinetic energy of the water molecules. The ...
physics of foil - P1 International
... PHYSICAL CONTACT of one part of the same body with another part, or of one body with another. For instance, if one end of an iron rod is heat, the heat travels by conduction through the metal to the other end; it also travels to the surface and is conducted to the surrounding air which is another, b ...
... PHYSICAL CONTACT of one part of the same body with another part, or of one body with another. For instance, if one end of an iron rod is heat, the heat travels by conduction through the metal to the other end; it also travels to the surface and is conducted to the surrounding air which is another, b ...